Marmot vs LemmingSee Who Wins

# Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to this thrilling matchup between two fierce competitors in the animal kingdom. Today, we have a showdown between a Marmot and a Lemming, both known for their agility and cunning. It's going to be a battle of wits and strength as these two animals prepare to face off in the ring. Let's dive right into the action!
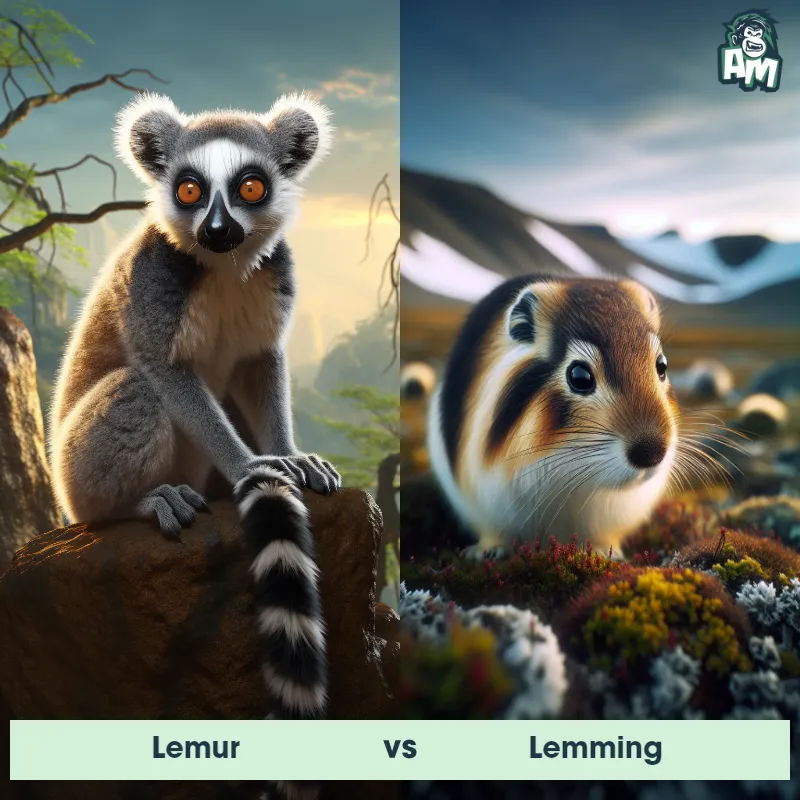
Contender 1: Marmot
The Marmot, also known as a groundhog or woodchuck, is a medium-sized rodent belonging to the squirrel family. It is characterized by its stout body, short legs, and bushy tail. Marmots have a short, coarse fur that can vary in color from brown to gray, depending on the species. They are well adapted to an underground lifestyle, with strong claws for digging burrows that can be up to 30 feet long. Marmots are social animals, living in colonies that consist of complex tunnel systems with separate chambers for nesting and hibernating. They are herbivores, feeding primarily on grasses, leaves, and flowers.
Fun Fact: Marmots are excellent diggers and can move up to a ton of soil when constructing their burrows.
Contender 2: Lemming
The Lemming is a small rodent typically found in the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. Known for their plump bodies and short limbs, Lemmings have dense fur that helps protect them from the cold climate. They have a rounded head with small ears and a pointed snout. Lemmings are social animals and often live in large colonies, constructing intricate tunnel systems in the ground. They are herbivorous and mainly feed on grasses, mosses, and shrubs.
Fun Fact: Lemmings have a unique behavior known as "lemming migration," where large numbers of Lemmings move in a mass migration across vast distances in search of new habitats or food sources.
Matchup Stats
| Marmot | Lemming | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Up to 2 feet long (60 centimeters) | 3-6 inches (7.6-15.2 cm) in length |
| Weight | Up to 13 pounds (6 kilograms) | 1-4 ounces (28-113 grams) |
| Speed | 20mph (32km/h) | 5mph (8km/h) |
| Key Strength | Agility and ability to retreat into burrow | N/A |
| Biggest Weakness | Relatively small size and lack of offensive weapons | N/A |
Current Votes
Marmot vs Lemming
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Marmot | Lemming | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Marmota | Lemmus lemmus |
| Family | Sciuridae | Cricetidae |
| Habitat | Mountains and meadows | Tundra and alpine meadows |
| Geography | North America, Europe, Asia | Northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia |
| Diet | Herbivorous, primarily grasses, leaves, and flowers | Grasses, mosses, and shrubs |
| Lifespan | 6 years - 10 years | 1 years - 2 years |
Key Differences between Marmot and Lemming
- Size: Marmots are significantly larger than Lemmings, with an adult Marmot reaching lengths of 20 to 30 inches, including their tail, while Lemmings typically measure only 3 to 6 inches in length.
- Coloration: Marmots have a more diverse color range, ranging from shades of brown, gray, and black, often with lighter patches on their stomachs. On the other hand, Lemmings generally have a consistent fur color, often brown or gray, without notable variations or patterns.
- Habitat: Marmots are primarily found in alpine and mountainous regions, where they create burrows for shelter. Meanwhile, Lemmings inhabit predominantly tundra and boreal forest areas, digging tunnels and constructing nests within the vegetation.
- Facial Features: Marmots have a distinctive and prominent snout and large incisors, allowing for efficient herbivorous feeding. In contrast, Lemmings have a more compact snout, similar to a typical rodent, without as pronounced incisors.
- Behavior: Marmots are highly social animals, living in colonies and displaying complex behaviors such as alarm calling and communal hibernation. Lemmings, however, are generally solitary creatures, with limited social interactions and a more independent lifestyle.
- Tail: Marmots possess a relatively long and bushy tail, which they use for balance, communication, and warmth during colder months. Lemmings, on the other hand, have shorter tails that are less bushy and less utilized for similar purposes.