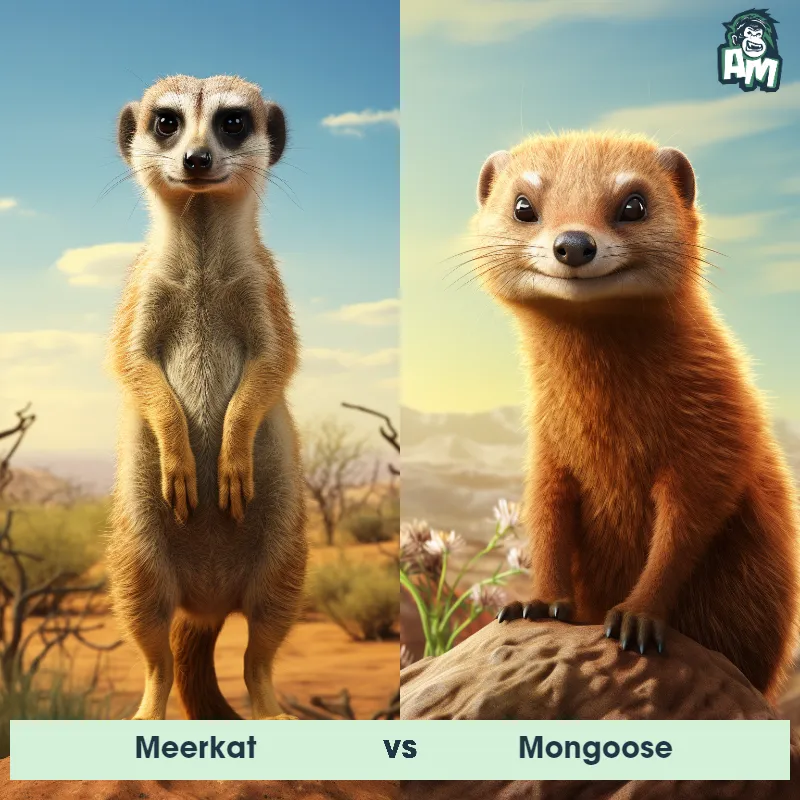
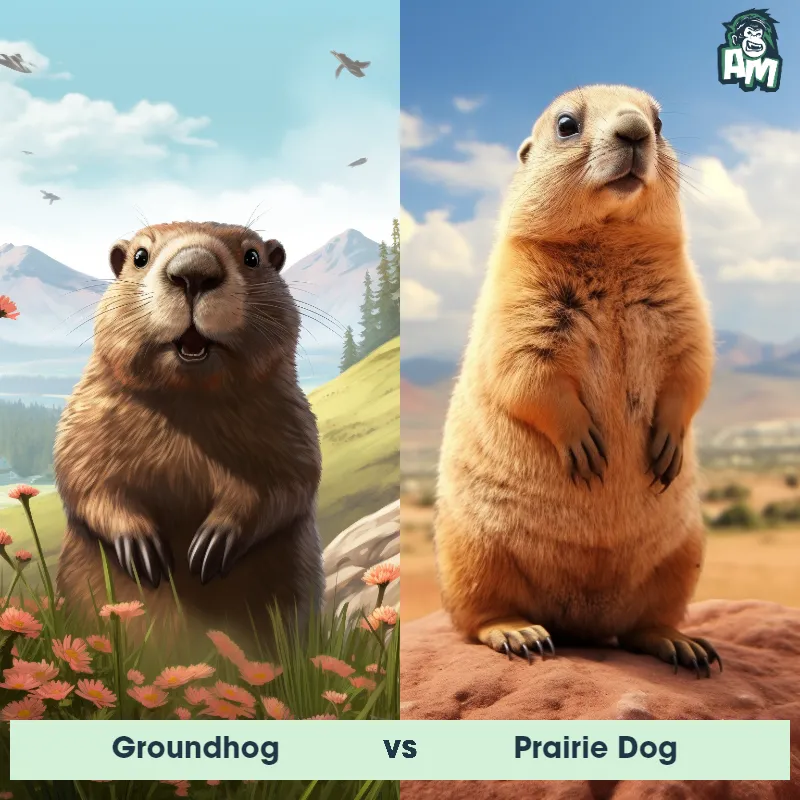
Meerkat vs Prairie DogSee Who Wins

Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to this thrilling matchup between two fascinating creatures of the animal kingdom. We've got a battle of the burrowers here tonight, as the agile meerkat takes on the sturdy prairie dog. Both animals are known for their outstanding digging abilities and are ready to showcase their skills in this three-round fight. So, let's dive right into the action!
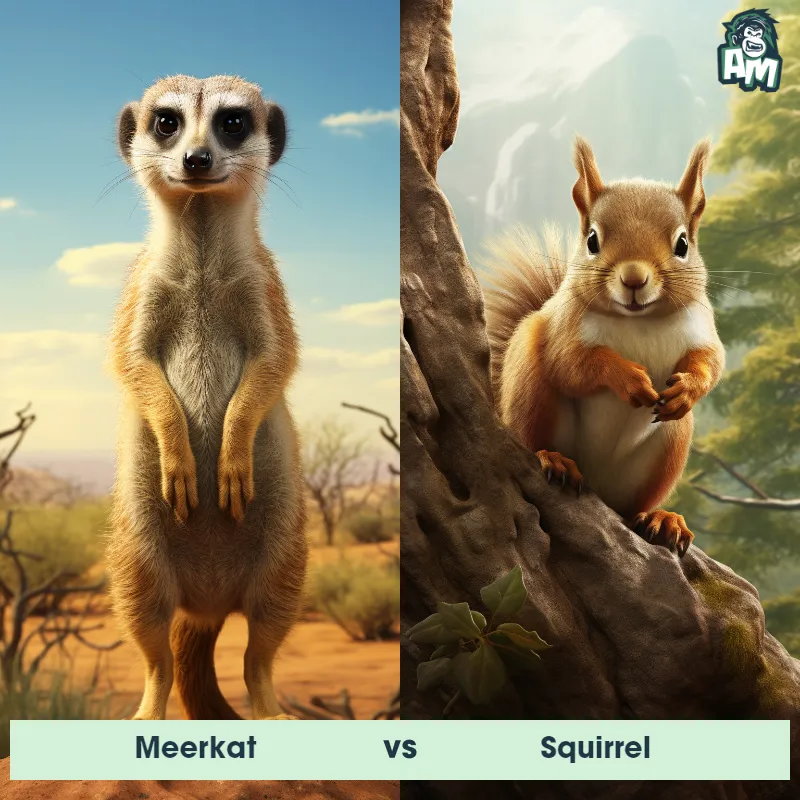
Contender 1: Meerkat
The Meerkat, a member of the mongoose family, is a small mammal known for its upright posture and social behavior. Meerkats are characterized by a slender, elongated body that can measure up to 14 inches, excluding the tail, which is around 10 inches long. They have a light gray to brown coat with darkly lined eyes that help protect against the sun's glare. Living in groups called clans or mobs, Meerkats reside in complex underground burrows in the arid regions of southern Africa, and their diet primarily consists of insects, spiders, and small mammals.
Fun Fact: Meerkats have a unique system of rotating tasks within their group, with some serving as lookouts for predators while others forage for food, showcasing a high level of social organization.
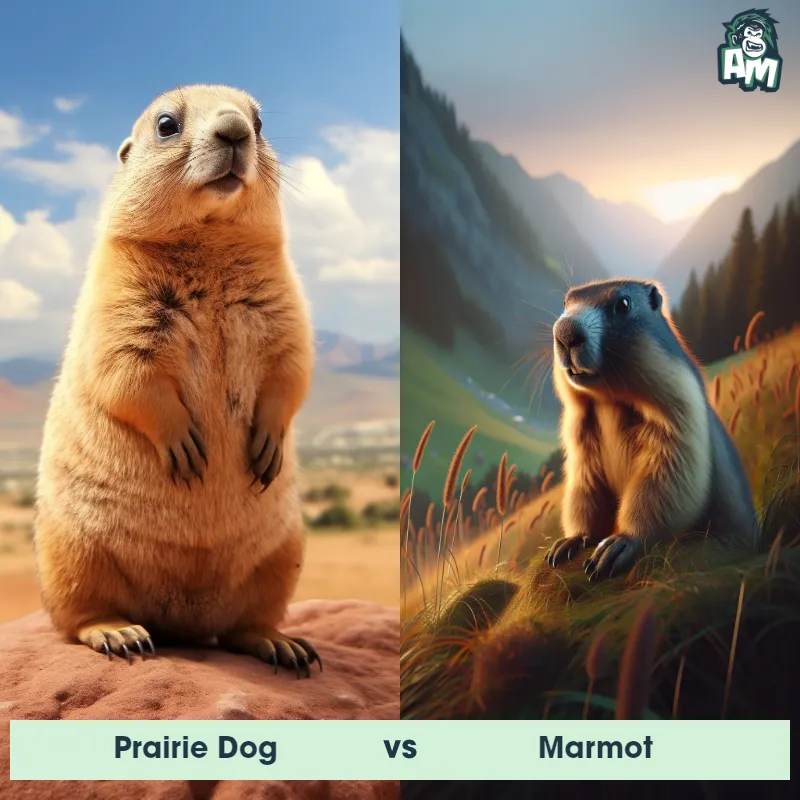
Contender 2: Prairie Dog
The prairie dog is a type of burrowing rodent native to the grasslands of North America. These small creatures have a stout body, a small head, and short legs, which are perfect for their lifestyle underground. They typically have a coat that ranges from brown to reddish in color. Prairie dogs are highly social animals, known to live in large colonies or 'towns' which can consist of hundreds or even thousands of individuals, and their intricate burrow systems can cover large areas.
Fun Fact: Prairie dogs have a complex communication system, using different sounds and calls to warn their colony about the approach of different types of predators.
Matchup Stats
| Meerkat | Prairie Dog | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 14 inches (35.56 cm) | 12-16 inches (30-40 cm) |
| Weight | 1.5 lbs (0.68 kg) | 1-3 lbs (0.45-1.36 kg) |
| Speed | 20mph (32km/h) | 35mph (56km/h) |
| Key Strength | Immunity to certain types of venom | Ability to burrow quickly to escape danger |
| Biggest Weakness | Small size and lack of physical strength | Small size and lack of strong defensive capabilities |
Current Votes
Meerkat vs Prairie Dog
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Meerkat | Prairie Dog | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Suricata suricatta | Cynomys |
| Family | Herpestidae | Sciuridae |
| Habitat | Arid regions, savannas, and grasslands | Grasslands |
| Geography | Southern Africa | North America |
| Diet | Insects, spiders, and small mammals | Herbivore (Grasses, seeds, and occasionally insects) |
| Lifespan | 12 years - 14 years | 3 years - 5 years |
Key Differences between Meerkat and Prairie Dog
- Tail length: Meerkats have a long, slender tail measuring approximately 7-10 inches, often with a black tip, while Prairie Dogs possess a shorter, bushy tail of about 3-5 inches in length.
- Social behavior: Meerkats live in highly organized groups called mobs or gangs, with a dominant breeding pair, while Prairie Dogs live in complex colonies, often comprising several interconnected family groups.
- Habitat differences: Meerkats are native to the arid regions of southern Africa, where they inhabit open grasslands and desert areas, while Prairie Dogs reside in the grasslands and prairies of North America.
- Ears: Meerkats have large, rounded ears positioned high on their heads, aiding in detecting potential predators, whereas Prairie Dogs have smaller, rounded ears located on the sides of their heads.
- Fur coloration: Meerkats display a sandy or light brown coat with distinct dark patches around their eyes, whereas Prairie Dogs exhibit a more varied coloration, ranging from tan and gray to reddish-brown, often featuring lighter patches on the belly.
- Size: Meerkats are significantly smaller, typically measuring around 10-14 inches in length and weighing about 1-2 pounds, while Prairie Dogs can range from 12-16 inches in length and weigh between 2-4 pounds.