Lemur vs LemmingSee Who Wins

Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to this thrilling matchup between two fascinating creatures. Get ready for an intense face-off that will surely keep you on the edge of your seats. We have a Lemur versus a Lemming, both known for their unique skills and agility. It's sure to be a battle of wits, strategy, and sheer determination. Let the fight begin!
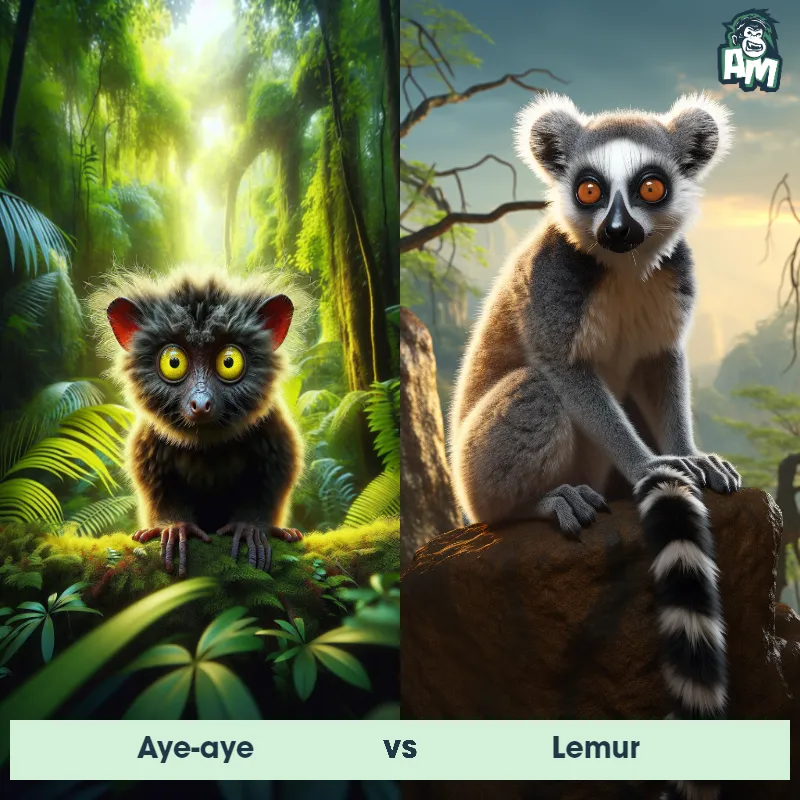
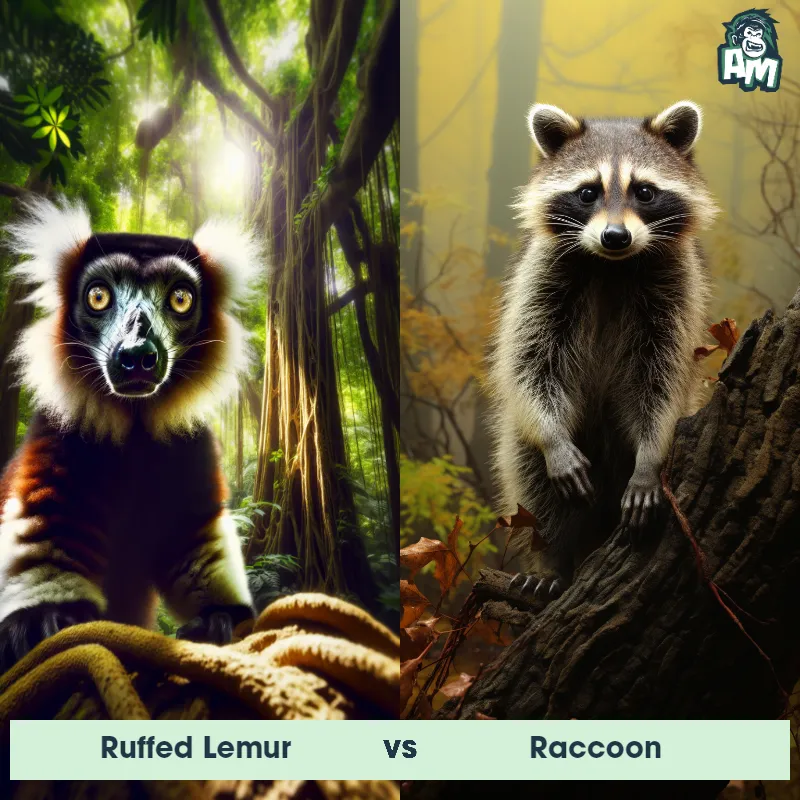
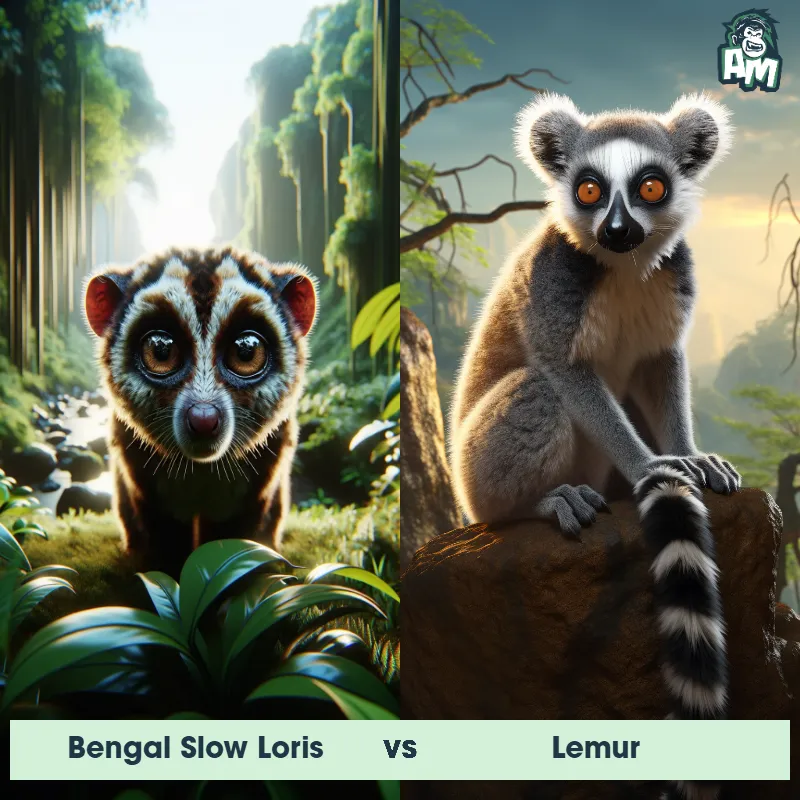
Contender 1: Lemur
The Lemur is a type of primate known as a prosimian, native to the island of Madagascar. Lemurs come in various sizes and colors, but they are typically characterized by a pointed snout, large eyes, and a long tail that can be longer than their body. Many lemur species have a thick and woolly fur that ranges in color from reddish-brown to gray and black. Lemurs are arboreal animals, spending most of their time in trees, and their diet consists of fruits, leaves, flowers, and insects.
Fun Fact: Lemurs communicate with each other using a variety of vocalizations, body postures, and scent markings, exhibiting a complex and intriguing social structure.
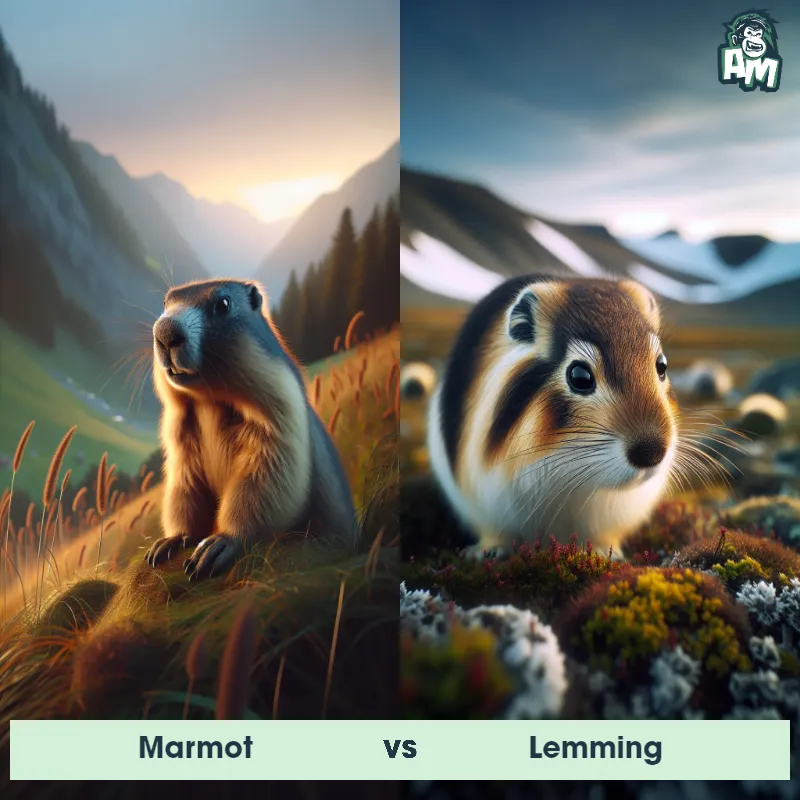
Contender 2: Lemming
The Lemming is a small rodent typically found in the northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia. Known for their plump bodies and short limbs, Lemmings have dense fur that helps protect them from the cold climate. They have a rounded head with small ears and a pointed snout. Lemmings are social animals and often live in large colonies, constructing intricate tunnel systems in the ground. They are herbivorous and mainly feed on grasses, mosses, and shrubs.
Fun Fact: Lemmings have a unique behavior known as "lemming migration," where large numbers of Lemmings move in a mass migration across vast distances in search of new habitats or food sources.
Matchup Stats
| Lemur | Lemming | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Varies by species, 3.5 inches to 2.5 feet (9 cm to 76 cm) | 3-6 inches (7.6-15.2 cm) in length |
| Weight | Varies by species, 1 ounce to 20 pounds (30 grams to 9 kg) | 1-4 ounces (28-113 grams) |
| Speed | 20mph (32km/h) | 5mph (8km/h) |
| Key Strength | Agility and speed | N/A |
| Biggest Weakness | Small size and lack of aggressive behavior | N/A |
Current Votes
Lemur vs Lemming
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Lemur | Lemming | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Lemuriformes | Lemmus lemmus |
| Family | Lemuridae | Cricetidae |
| Habitat | Forests and jungles | Tundra and alpine meadows |
| Geography | Madagascar | Northern regions of North America, Europe, and Asia |
| Diet | Fruits, leaves, flowers, and insects | Grasses, mosses, and shrubs |
| Lifespan | 16 years - 25 years | 1 years - 2 years |
Key Differences between Lemur and Lemming
- Behavior: Lemurs are highly social animals, living in groups called troops, whereas Lemmings are solitary creatures that live in burrows and tunnels, typically displaying less social behavior.
- Coloration: Lemurs display a wide range of colors, with some species having distinct patterns including black and white rings, while Lemmings are generally brown or gray in color.
- Habitat: Lemurs are native to the island of Madagascar and can be found in the tropical rainforests, while Lemmings are found in Arctic regions such as tundra and alpine habitats.
- Facial features: Lemurs often have a pronounced snout, large round eyes, and mobile ears, giving them a distinctive face, whereas Lemmings have relatively smaller eyes and a more uniform head shape.
- Tail length: Lemurs have longer tails compared to Lemmings, often exceeding their own body length, while Lemmings have relatively shorter tails.
- Size: The Lemur is significantly larger than the Lemming, with some species of Lemur reaching up to 2 feet in length, while the Lemming is typically only about 3-6 inches long.