Axolotl vs Eastern NewtSee Who Wins

Welcome to today's matchup between the Axolotl and Eastern Newt! Both of these amphibians are known for their unique characteristics and abilities. It's going to be an exciting duel between these two aquatic creatures.
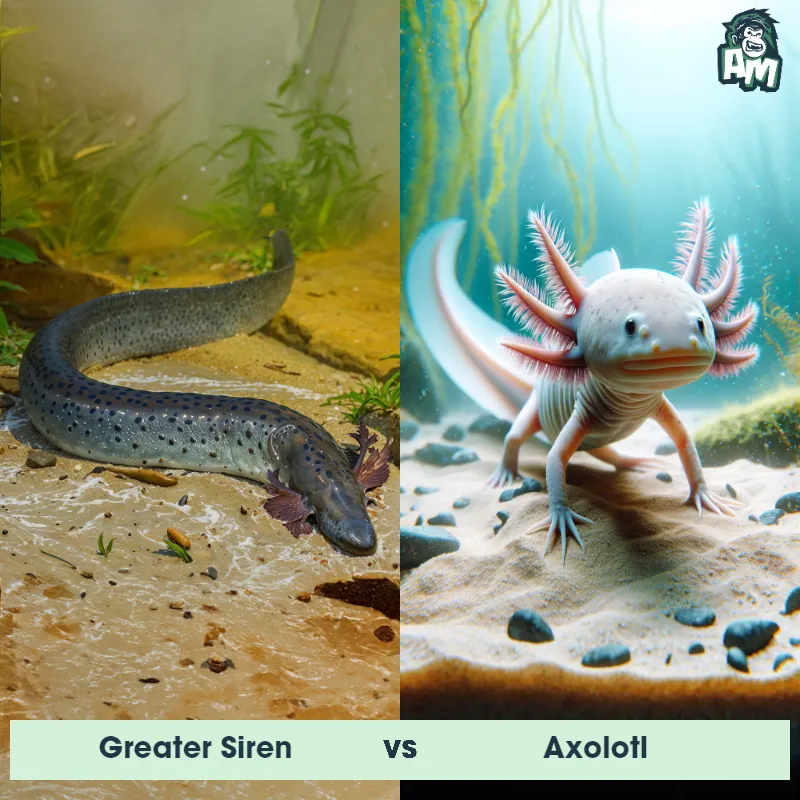
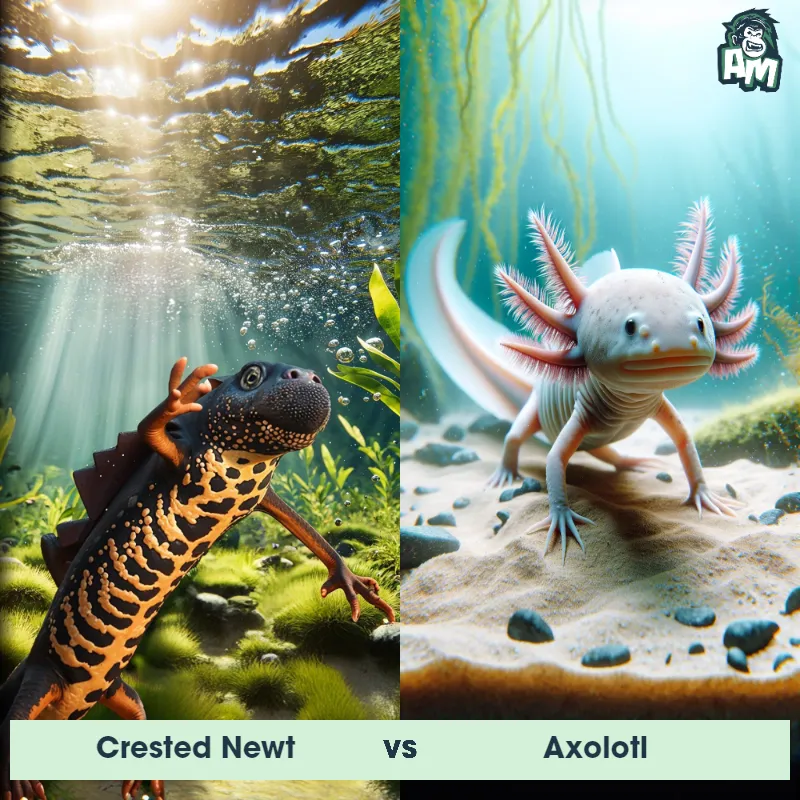
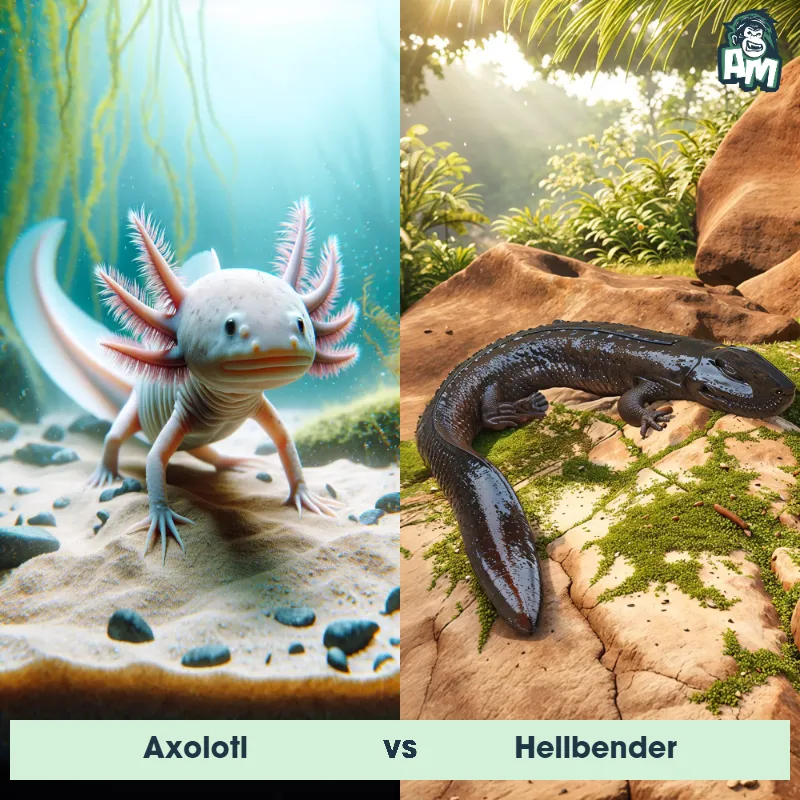
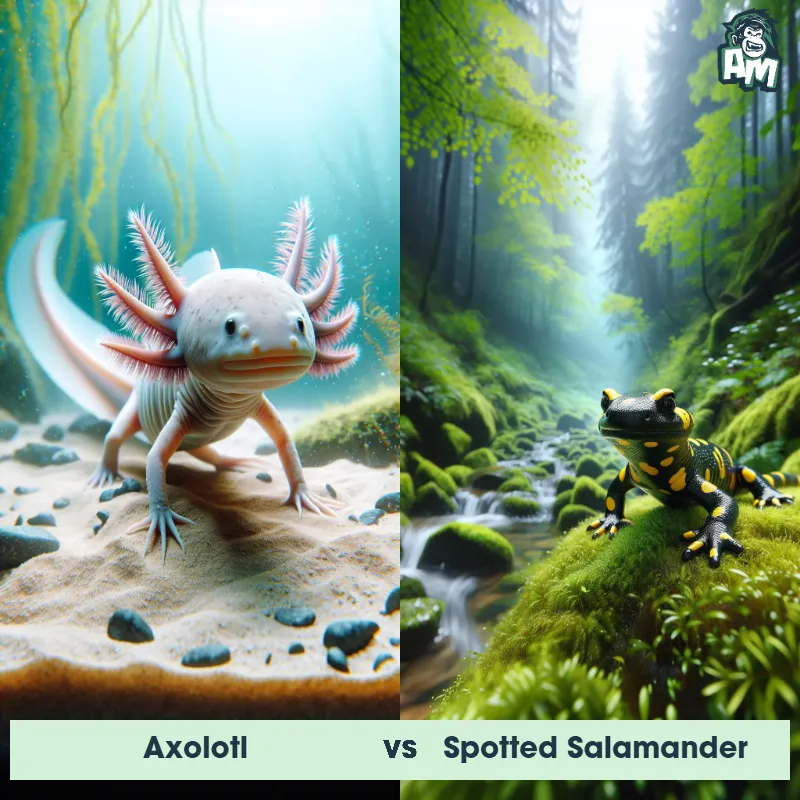
Contender 1: Axolotl
The Axolotl, also known as the Mexican Salamander or Mexican Walking Fish, is a unique amphibian known for its neotenic qualities, retaining its larval features throughout its adult life. It has external gills, a dorsal fin, and a long, slender body. Axolotls can come in various colors, including black, brown, gray, gold, and white.
Fun Fact: Axolotls have amazing regenerative abilities, being able to regrow lost body parts such as limbs, tail, and even parts of their brain.
Contender 2: Eastern Newt
The Eastern Newt, also known as the red-spotted newt, is a small amphibian found in Eastern North America. It has three distinct life stages - aquatic larva, terrestrial juvenile eft, and aquatic adult. The eft stage is characterized by bright orange skin with red spots, which serves as a warning coloration to predators. As adults, they develop smooth, olive-green skin with a yellow belly.
Fun Fact: One fun fact about the Eastern Newt is that they are the only newt species in North America to have a bright orange juvenile stage known as the eft.
Matchup Stats
| Axolotl | Eastern Newt | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Up to 9-12 inches (23-30 cm) | 3-5 inches (7.6-12.7 cm) |
| Weight | 8-16 ounces (225-450 grams) | 1-5 grams (0.04-0.18 oz) |
| Speed | 5 mph (8 km/h) | 3.7 mph (6 km/h) |
| Key Strength | Regenerative abilities | Agility and speed |
| Biggest Weakness | Presence of external gills can be vulnerable | Size and physical strength |
Current Votes
Axolotl vs Eastern Newt
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Axolotl | Eastern Newt | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ambystoma mexicanum | Notophthalmus viridescens |
| Family | Ambystomatidae | Salamandridae |
| Habitat | Freshwater | Freshwater ponds, marshes, streams, and wetlands |
| Geography | Originally found in the waters of Lake Xochimilco in Mexico | Eastern North America |
| Diet | Carnivorous, feeds on small fish, worms, insects, and some plant matter | Insect larvae, worms, small crustaceans |
| Lifespan | 10 years - 15 years | 12 years - 15 years |
Key Differences between Axolotl and Eastern Newt
- Conservation status: Axolotls are listed as critically endangered in the wild due to habitat loss and pollution, while Eastern Newts are not currently considered threatened or endangered.
- Color: Axolotls are typically spotted with shades of white, gray, brown, and gold, while Eastern Newts are usually solid shades of orange or red with black markings.
- Size: The Axolotl is much larger than the Eastern Newt, with adults reaching up to 12 inches in length, while Eastern Newts typically only grow to around 3-5 inches.
- Body shape: Axolotls have a more elongated body with feathery gills on either side of their head, while Eastern Newts have a more streamlined body and distinct webbed feet.
- Habitat: Axolotls are fully aquatic and live their entire lives in water, while Eastern Newts start out aquatic as larvae but then transform into terrestrial adults, living both in the water and on land.
- Reproduction: Axolotls are neotenic, meaning they retain their larval characteristics into adulthood and are able to reproduce without undergoing metamorphosis, while Eastern Newts undergo metamorphosis from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults for reproduction.