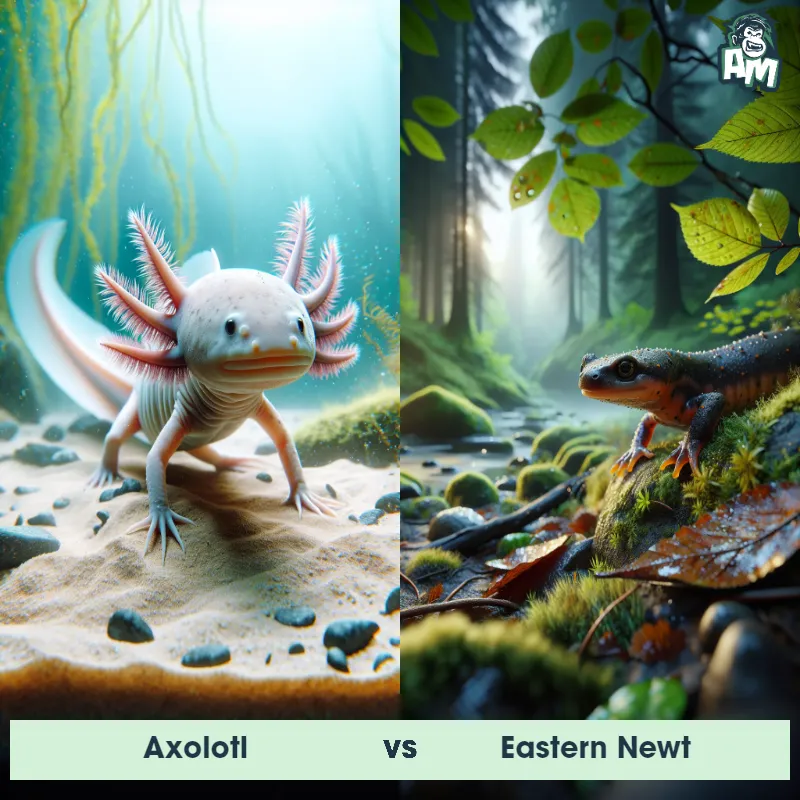
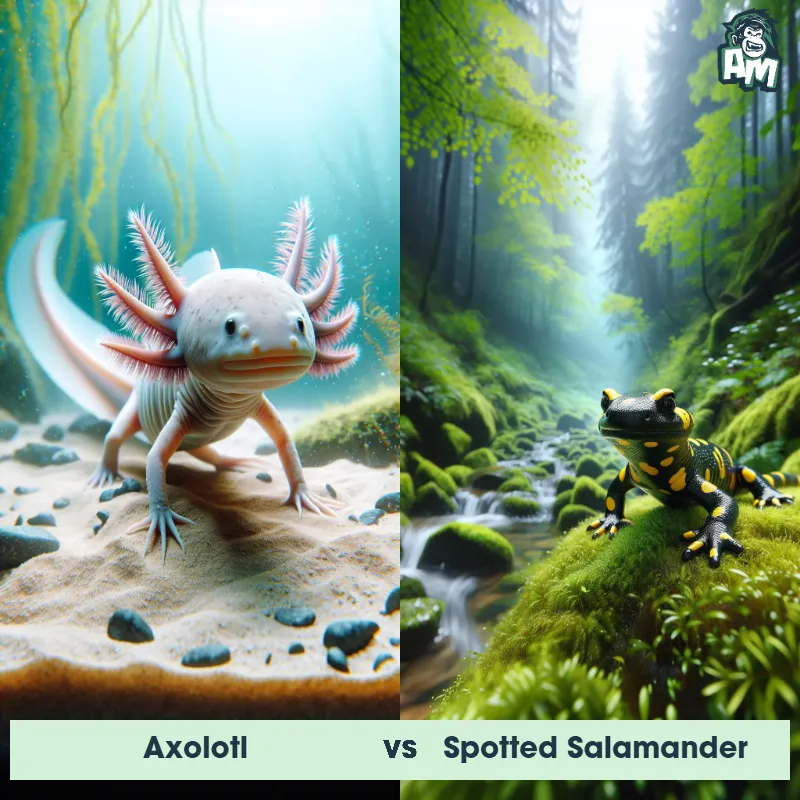
The Axolotl
The Axolotl, also known as the Mexican walking fish, is a type of salamander native to Mexico. They have a unique appearance with external gills that give them a feathery look, along with a long, slender body and limbs. Axolotls are known for being neotenic, meaning they retain their juvenile features into adulthood, including their permanent larval characteristics.
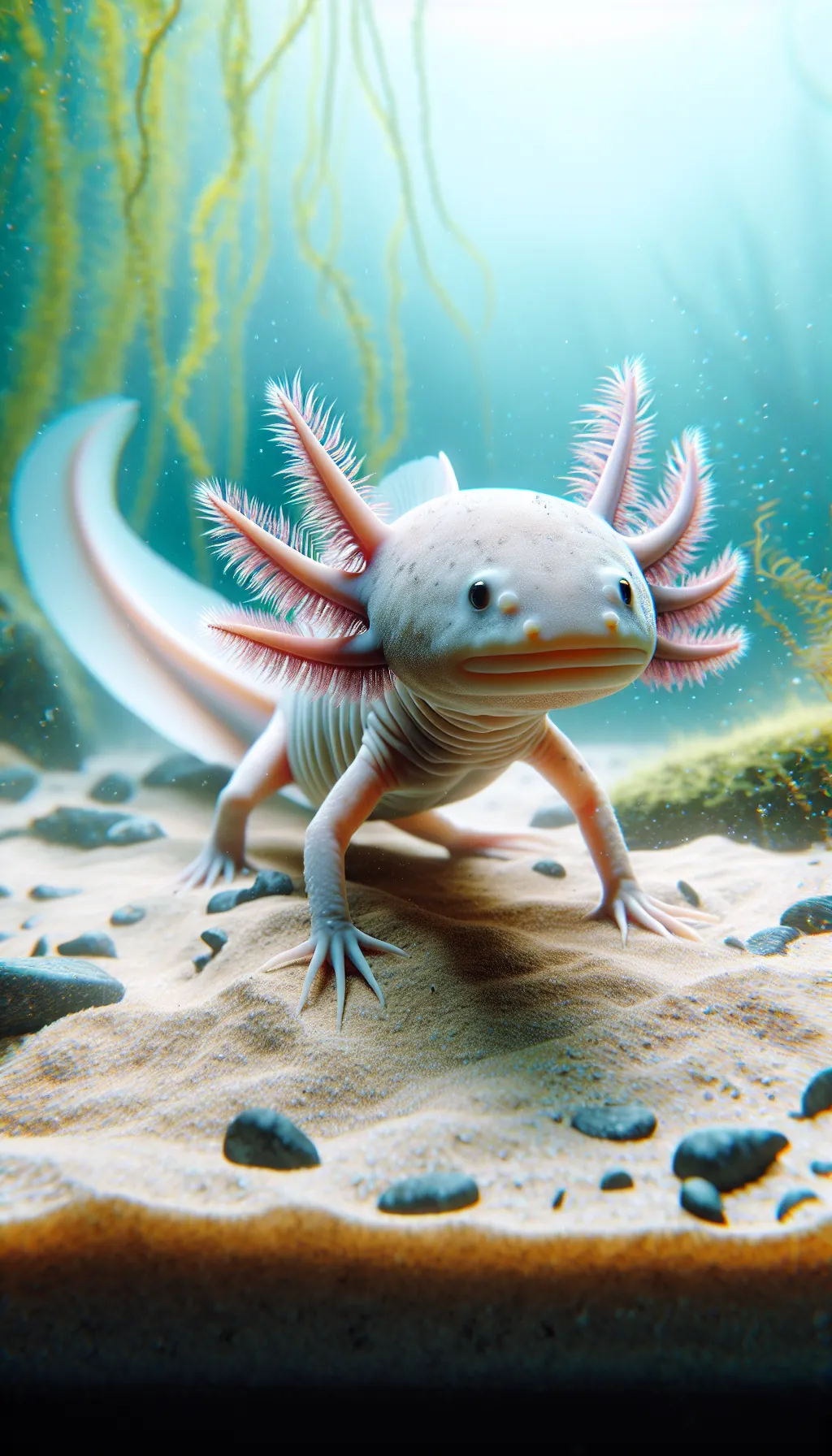

| Axolotl | |
|---|---|
| Size | Up to 9-12 inches (23-30 cm) |
| Weight | 8-16 ounces (225-450 grams) |
| Speed | 5 mph (8 km/h) |
| Key Strength | Regenerative abilities |
| Biggest Weakness | Presence of external gills can be vulnerable |
| Scientific Name | Ambystoma mexicanum |
| Family | Ambystomatidae |
| Habitat | Freshwater |
| Geography | Originally found in the waters of Lake Xochimilco in Mexico |
| Diet | Carnivorous, feeds on small fish, worms, insects, and some plant matter |
| Lifespan | 10 years - 15 years |

The Axolotl
The Axolotl, also known as the Mexican walking fish, is a type of salamander native to Mexico. They have a unique appearance with external gills that give them a feathery look, along with a long, slender body and limbs. Axolotls are known for being neotenic, meaning they retain their juvenile features into adulthood, including their permanent larval characteristics.
Fun Fact: The Axolotl has impressive regenerative abilities, capable of regrowing entire limbs, tail, and even parts of vital organs like the heart and brain.
| Axolotl | |
|---|---|
| Size | Up to 9-12 inches (23-30 cm) |
| Weight | 8-16 ounces (225-450 grams) |
| Speed | 5 mph (8 km/h) |
| Key Strength | Regenerative abilities |
| Biggest Weakness | Presence of external gills can be vulnerable |
| Scientific Name | Ambystoma mexicanum |
| Family | Ambystomatidae |
| Habitat | Freshwater |
| Geography | Originally found in the waters of Lake Xochimilco in Mexico |
| Diet | Carnivorous, feeds on small fish, worms, insects, and some plant matter |
| Lifespan | 10 years - 15 years |
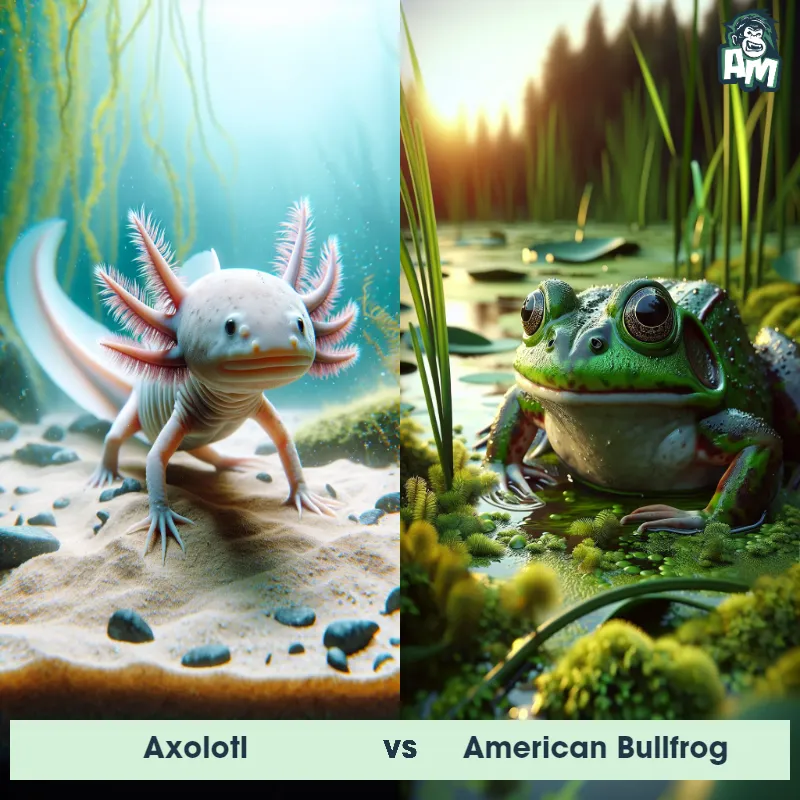
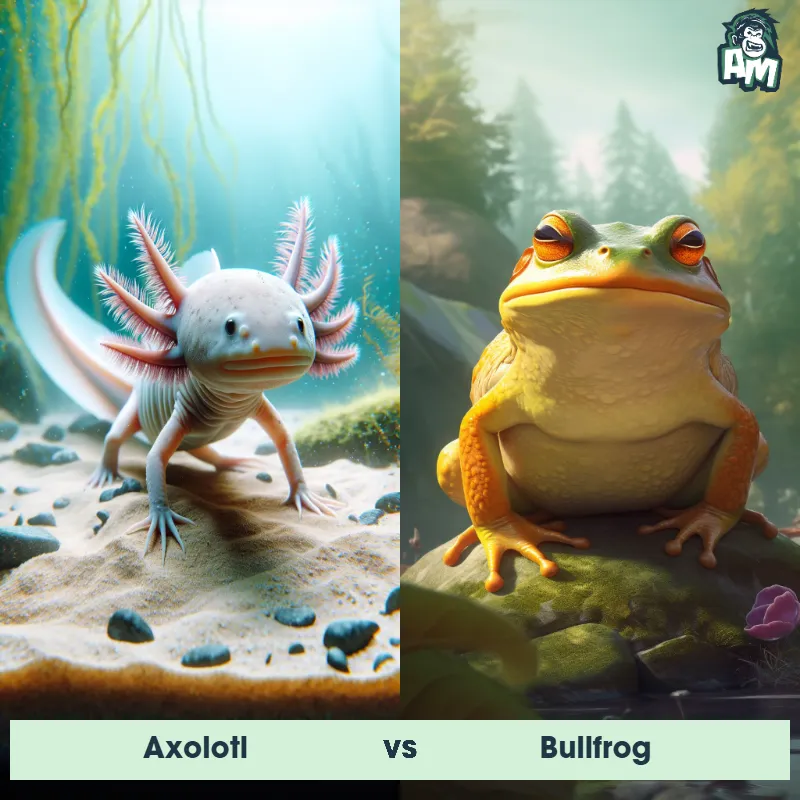
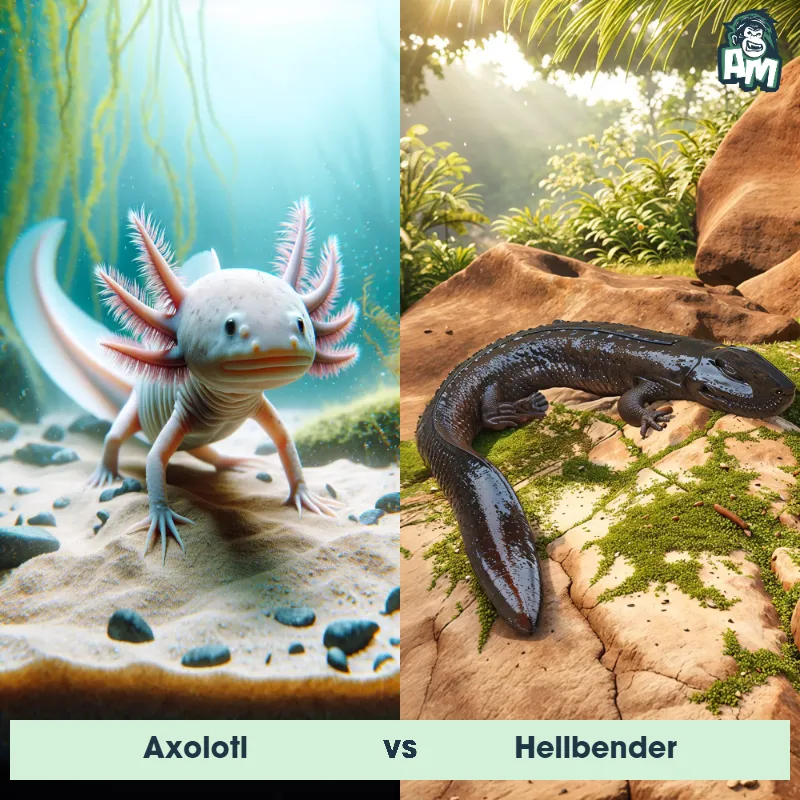
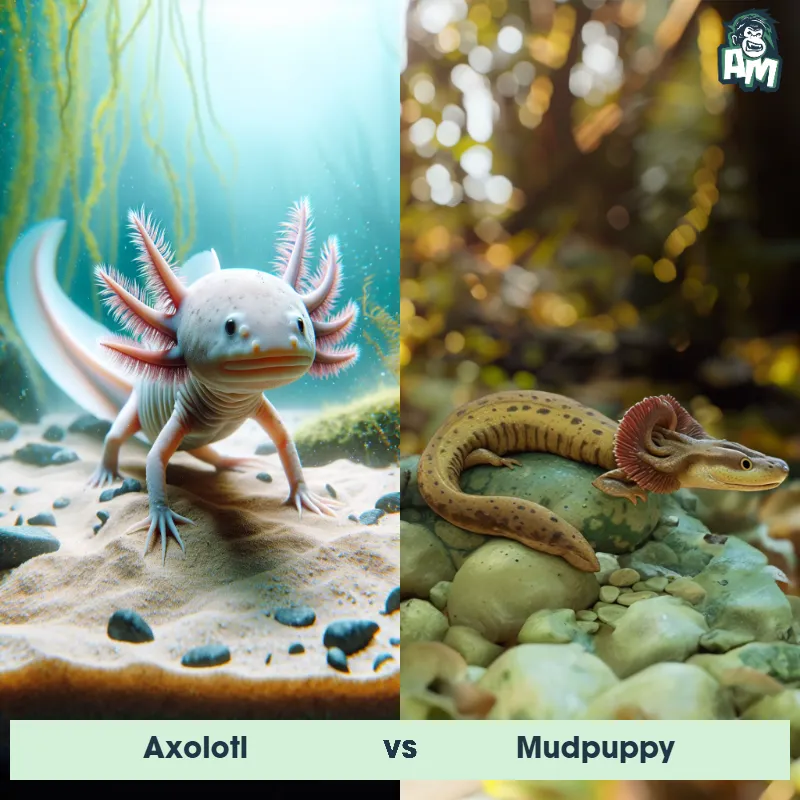
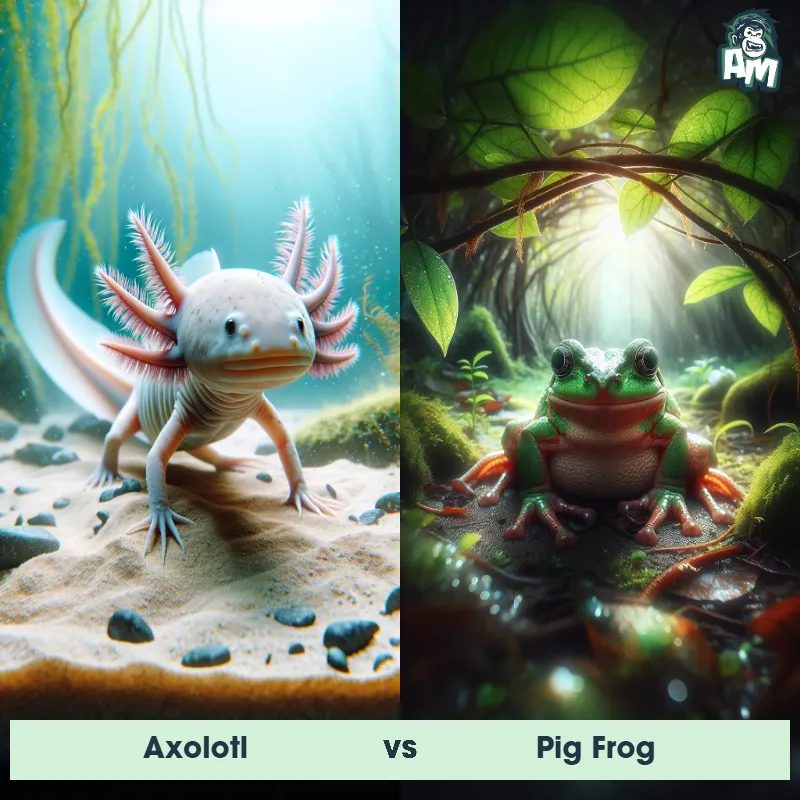
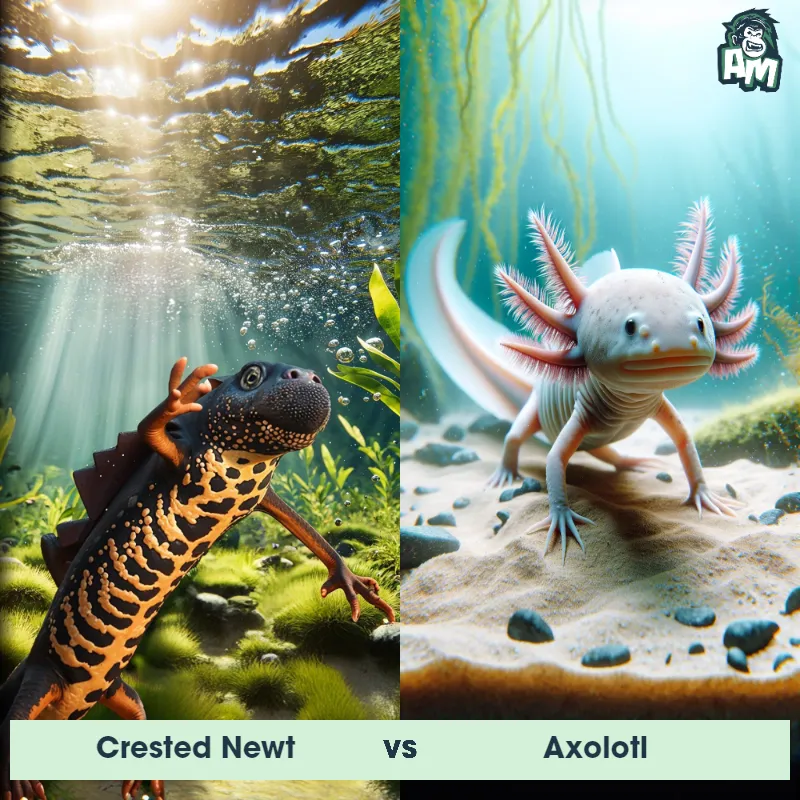
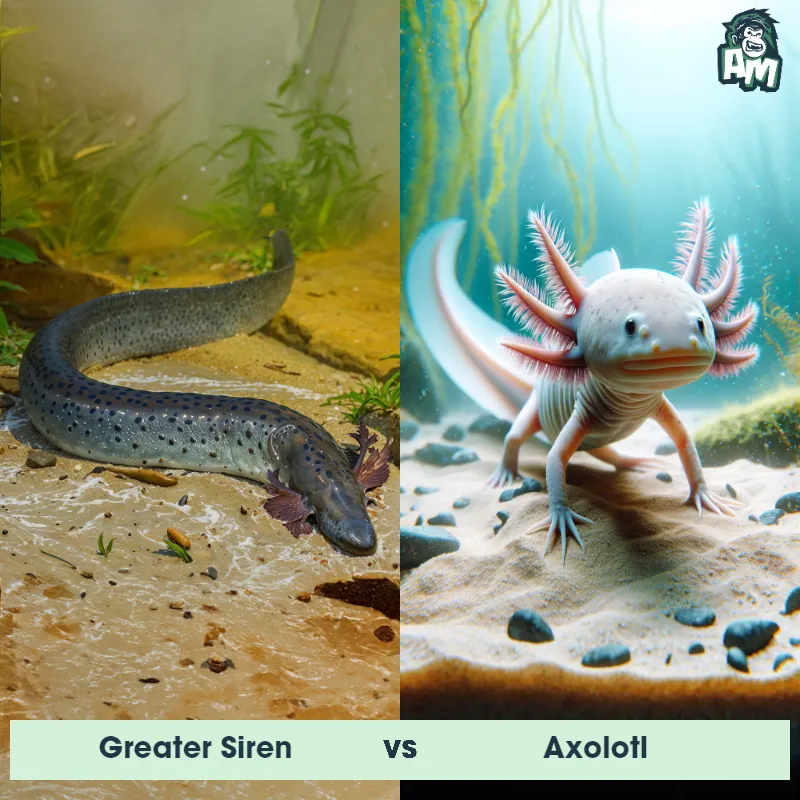
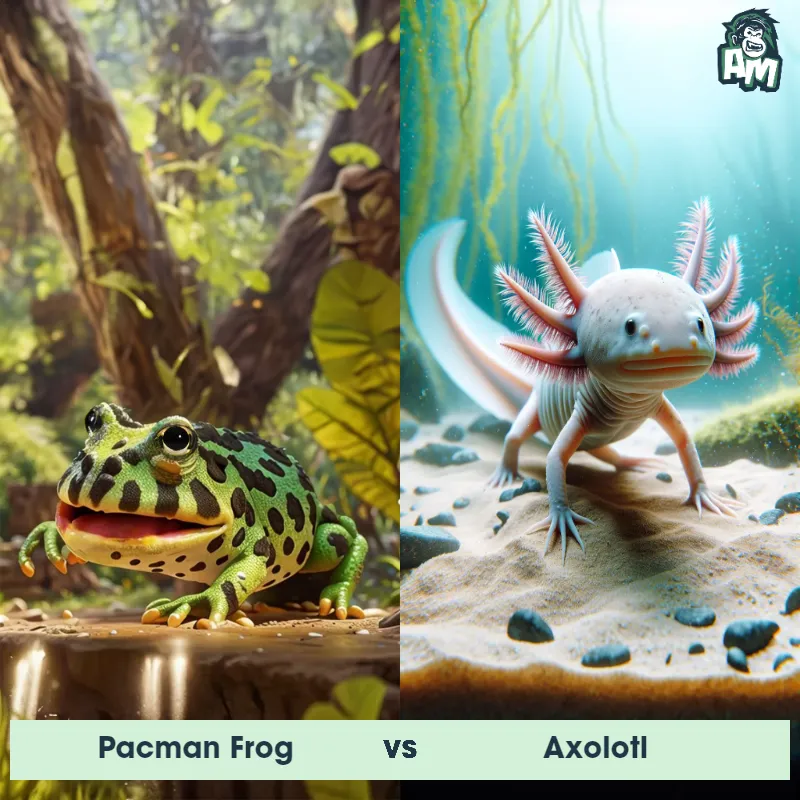
Axolotl Matchups
We use AI to simulate matchups between the Axolotl and other animals. Our simulation considers size, strength, and natural predatory behaviors to determine the most likely outcome.
Axolotl: Diet, Predators, Aggression, and Defensive Behaviors
What do Axolotls eat?
Axolotls are carnivorous and primarily feed on small prey such as worms, insects, small fish, and crustaceans. They are also known to consume aquatic plants and algae. In captivity, they can be fed a diet of live or frozen bloodworms, brine shrimp, earthworms, and pellets specifically formulated for axolotls.
Do Axolotls have any predators?
In the wild, Axolotls face threats from predators such as larger fish, birds, and mammals. Their natural habitat in Lake Xochimilco, Mexico, is also being impacted by human activities, leading to a decline in their population. In captivity, Axolotls may be at risk from larger fish, turtles, and other predatory pets.
Are Axolotls aggressive?
Axolotls are not typically aggressive towards other animals or their own kind. They are known for their docile and shy nature, making them suitable pets for beginner aquarists. However, they may display territorial behavior or aggression during feeding if housed together with other Axolotls.
Do Axolotls fight?
While Axolotls may exhibit territorial behavior, they do not engage in physical fights or aggressive behaviors like some other types of animals. They may nip or push each other away during feeding time if they feel threatened or stressed. It is important to provide them with sufficient space and hiding spots to prevent conflicts.
How do Axolotls defend themselves?
Axolotls primarily rely on their ability to regenerate lost limbs as a defense mechanism. If attacked or injured, they can regenerate their limbs, tail, and gills, allowing them to recover from injuries and escape predators. They may also use their sharp teeth to defend themselves if threatened.
What is Axolotls' biggest weakness in a fight?
One of the biggest weaknesses of Axolotls in a fight is their slow movement and inability to swim quickly over long distances. Their unique body structure and lack of strong muscles make them vulnerable to faster predators or aggressive tankmates. Additionally, their reliance on regeneration for defense means that they need time to recover from injuries sustained during a fight.
Fun Fact: Axolotls have the ability to absorb oxygen through their skin, which is a crucial adaptation in their aquatic environment.
Fun Fact: In addition to their regenerative powers, Axolotls also have an amazing ability to camouflage themselves by changing their color to match their surroundings, helping them avoid predators in the wild.