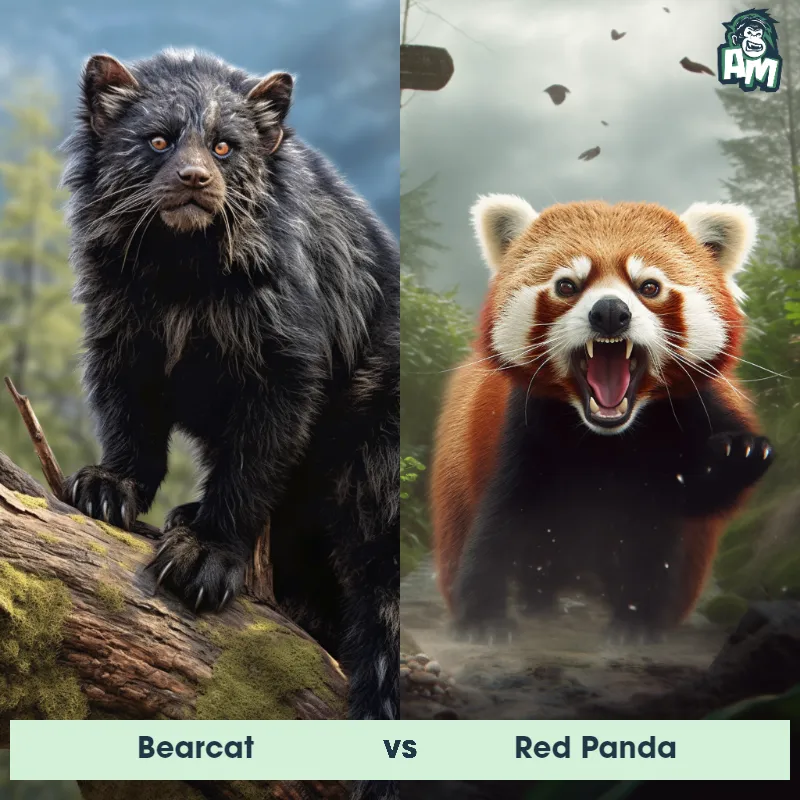
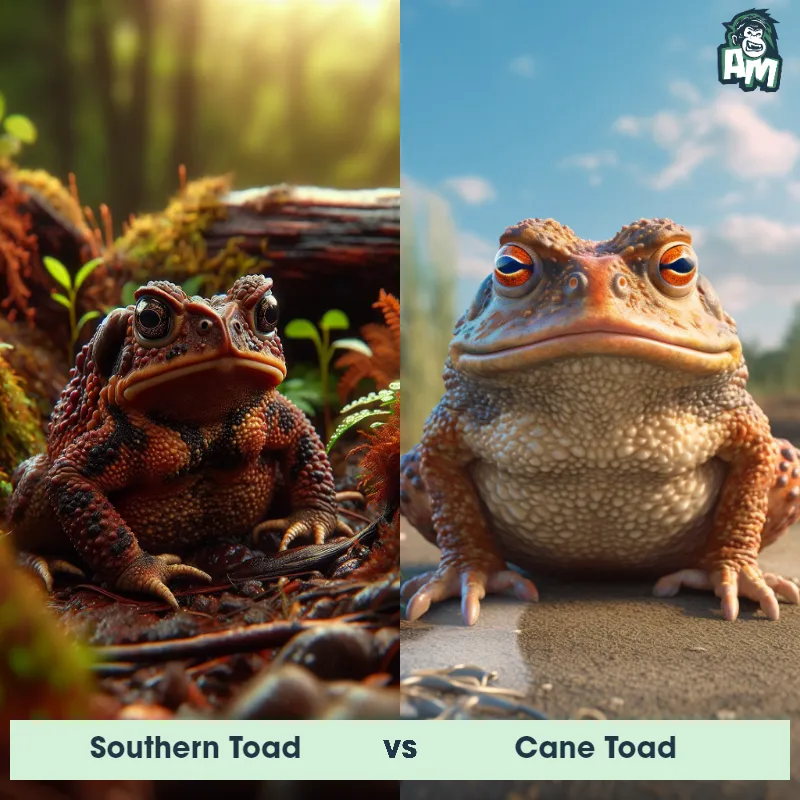
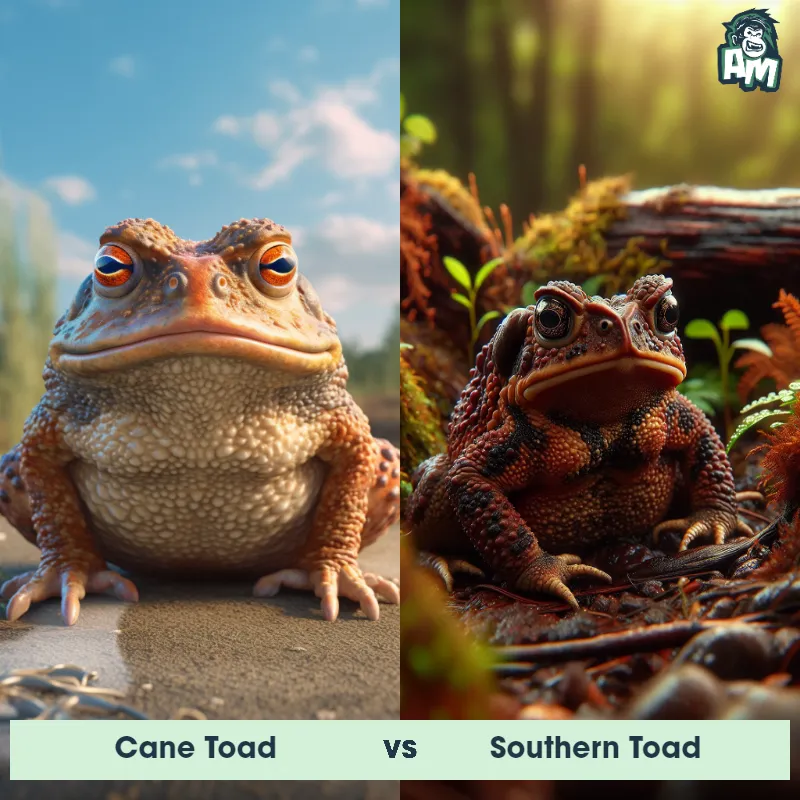
Suriname Toad vs Southern ToadSee Who Wins

Welcome, ladies and gentlemen, to this exciting matchup between two formidable toads. Both competitors are ready to show off their skills and prove who is the superior amphibian. Let's see how this fight unfolds.
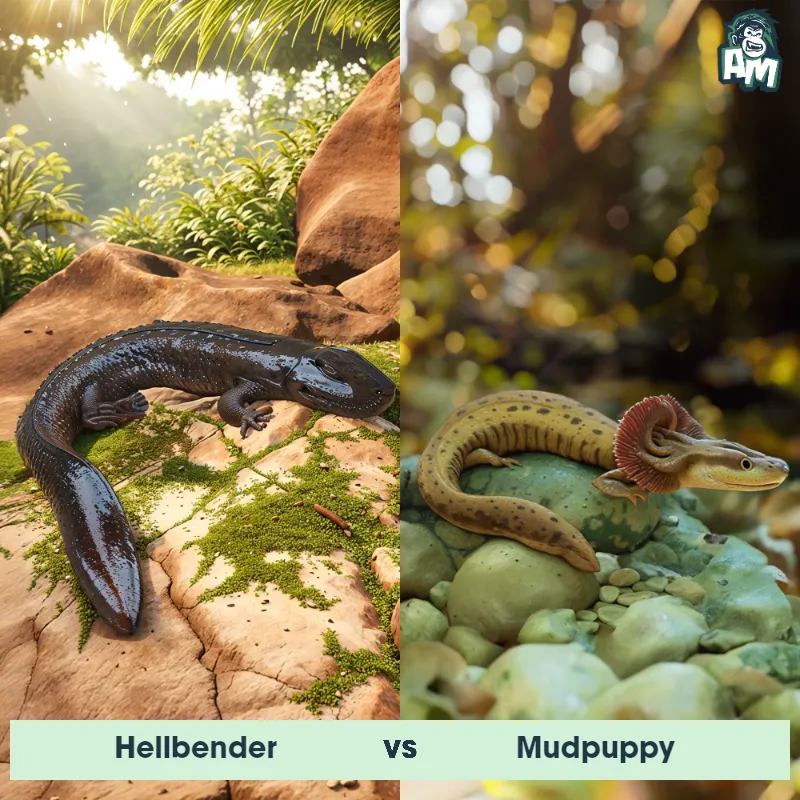
Contender 1: Suriname Toad
The Suriname Toad, also known as the Star-Fingered Toad, is a unique amphibian found in South America. It has a flattened body and webbed hands and feet, resembling a leaf as it lies still on the bottom of the water. This toad is known for its unusual reproductive behavior, where the female carries eggs on her back until they hatch into fully formed tadpoles.
Fun Fact: One fun fact about the Suriname Toad is that during mating, the male grasps the female's back and inseminates her as she arches her back to release the eggs, a process known as amplexus.
Contender 2: Southern Toad
The Southern Toad, also known as Bufo terrestris, is a stout-bodied amphibian with dry, warty skin and prominent ridges extending down its back. They typically have a brown or grayish coloration with dark spots and a cream-colored underside. Southern Toads have distinctive cranial crests above their eyes and elongated parotoid glands located behind their eyes. These toads are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, marshes, and urban areas.
Fun Fact: Southern Toads have a unique defense mechanism where they release a toxic substance from their parotoid glands when threatened by predators, causing irritation to mucous membranes and potentially discouraging the predator from attacking.
Matchup Stats
| Suriname Toad | Southern Toad | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Approximately 4-6 inches (10-15 cm) | 2-4 inches (5-10 cm) |
| Weight | Around 4-6 ounces (113-170 grams) | 1-3 ounces (28-85 grams) |
| Speed | 8mph (13km/h) | 4mph (6km/h) |
| Key Strength | Adaptation for camouflage and defense through its unique appearance | Camouflage and toxin secretion |
| Biggest Weakness | Slow-moving and vulnerable when out in the open | Slow movement |
Current Votes
Suriname Toad vs Southern Toad
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Suriname Toad | Southern Toad | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Pipa pipa | Bufo terrestris |
| Family | Pipidae | Bufonidae |
| Habitat | Freshwater habitats such as ponds, slow-moving streams, and flooded forests | Forests, marshes, urban areas |
| Geography | South America, particularly in countries like Suriname, Venezuela, and Brazil | Southeastern United States |
| Diet | Carnivorous, feeding on insects, small fish, crustaceans, and aquatic invertebrates | Insects, worms, small invertebrates |
| Lifespan | 10 years - 15 years | 4 years - 10 years |
Key Differences between Suriname Toad and Southern Toad
- Coloration: Suriname Toads have a mottled brown and green color pattern, whereas Southern Toads are generally more uniformly brown or gray.
- Skin texture: The Suriname Toad has a rough, warty skin texture, while the Southern Toad's skin is smoother with distinct ridges.
- Eye placement: The eyes of Suriname Toads are closer together and positioned more towards the top of the head, giving them a more forward-facing gaze compared to the Southern Toad's side-set eyes.
- Habitat: Suriname Toads are predominantly found in freshwater environments such as swamps and ponds, while Southern Toads are more commonly encountered in drier, terrestrial habitats like forests and gardens.
- Size: The Suriname Toad is larger, reaching up to 9 inches in length, while the Southern Toad typically only grows to around 5 inches.
- Toe shape: Suriname Toads have webbed toes, suited for their aquatic lifestyle, whereas Southern Toads have more distinct, separate toes adapted to terrestrial habitats.