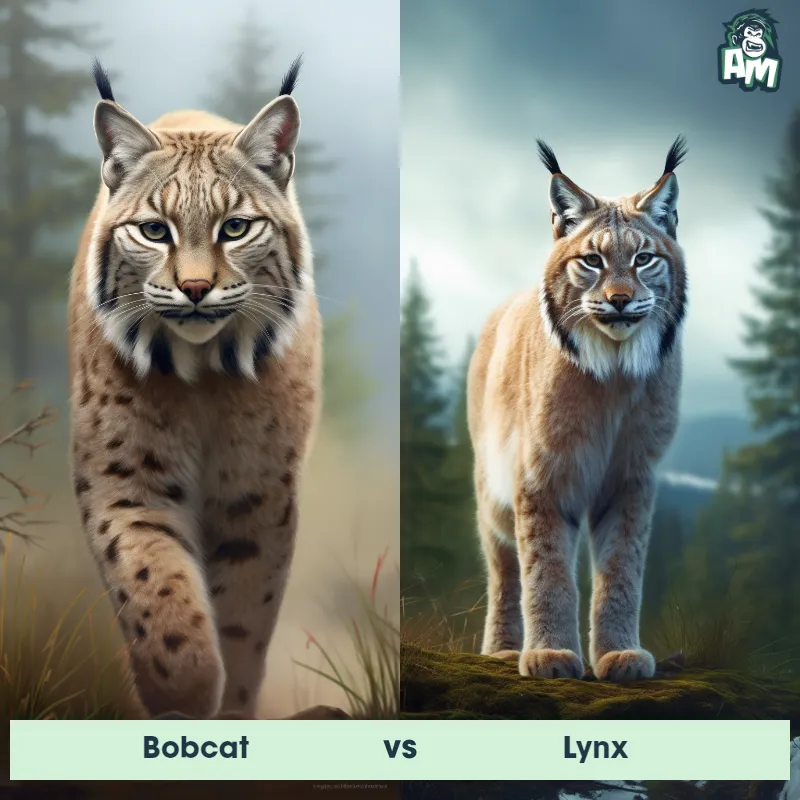
Puma vs LynxSee Who Wins

Prepare for an exhilarating showdown between two of the most agile and stealthy wildcats - the elusive Puma and the cunning Lynx! I'll be providing you with the play by play for this electrifying three-round encounter. Get ready for a fast-paced, feline face-off!
Contender 1: Puma
The Puma, also known as the mountain lion or cougar, is a large, solitary cat found in North and South America. They have a muscular build, short fur that ranges in color from tan to gray, and distinctive black markings on their face, ears, and tail. Pumas are known for their agility and can jump up to 18 feet in a single bound. They are also excellent hunters, with sharp claws and teeth that allow them to take down prey much larger than themselves.
Fun Fact: Pumas are one of the few big cats that can purr, which they do when they are content or communicating with other pumas.
Contender 2: Lynx
The Lynx is a medium-sized wild cat with distinctive tufted ears, short tail, and spotted fur. They have powerful legs and sharp claws, which make them excellent hunters. Lynx are solitary animals and are found in forests and mountainous regions across Europe, Asia, and North America.
Fun Fact: Lynx have excellent hearing and can detect prey up to 75 feet away, even under a thick layer of snow.
Matchup Stats
| Puma | Lynx | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 2-3 feet (0.6-0.9 meters) at the shoulder | 18-24 inches (45-60 cm) at the shoulder |
| Weight | 100-200 pounds (45-90 kilograms) | 18-24 pounds (8-11 kg) |
| Speed | Speed: 50 mph (80.47 km/hr) | Speed: 50 mph (80.47 km/hr) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaws and sharp claws | Powerful legs and sharp claws |
| Biggest Weakness | Vulnerable to attacks from behind | Short tail |
Current Votes
Puma vs Lynx
See Who Wins
Matchup Videos
All of our videos contain verified footage of natural encounters between the Puma and the Lynx. These are true sightings and observations filmed by tourists, scientists, and wildlife documentarians.View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Puma | Lynx | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Puma concolor | Lynx |
| Family | Felidae | Felidae |
| Habitat | Mountains, forests, deserts | Forests and mountainous regions |
| Geography | North and South America | Europe, Asia, and North America |
| Diet | Carnivorous, primarily deer and smaller mammals | Small mammals, birds, and fish |
| Lifespan | 8 years - 13 years | 10 years - 15 years |
Key Differences between Puma and Lynx
- Prey: Pumas are capable of taking down large prey such as deer and elk, while Lynx primarily hunt smaller prey such as rodents and birds.
- Tail: Pumas have a long, thick tail that is about one-third of their body length, while Lynx have a short, stubby tail.
- Color: Pumas are typically tan or brown with black spots, while Lynx have a grayish-brown coat with black tufts on their ears.
- Hunting style: Pumas are ambush predators that rely on stealth and speed to catch their prey, while Lynx are stalk-and-ambush predators that use their excellent hearing and vision to locate prey before pouncing.
- Habitat: Pumas are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, deserts, and grasslands, while Lynx are primarily found in boreal forests and mountainous regions.
- Ears: Lynx have distinctive tufts of black hair on the tips of their ears, while Pumas have rounded ears without tufts.
- Size: Pumas are larger than Lynx, with an average weight of 100-150 pounds compared to the Lynx's average weight of 18-24 pounds.