Nile Crocodile vs Tiger SharkSee Who Wins

Ladies and gentlemen, welcome to this epic showdown between two of nature's most fearsome creatures. In one corner, we have the Nile Crocodile, a formidable reptile known for its immense power and jaw strength. And in the other corner, we have the Tiger Shark, a sleek and relentless predator of the deep seas. The tension is palpable as these two apex predators prepare to engage in an extraordinary battle. Let the contest begin!
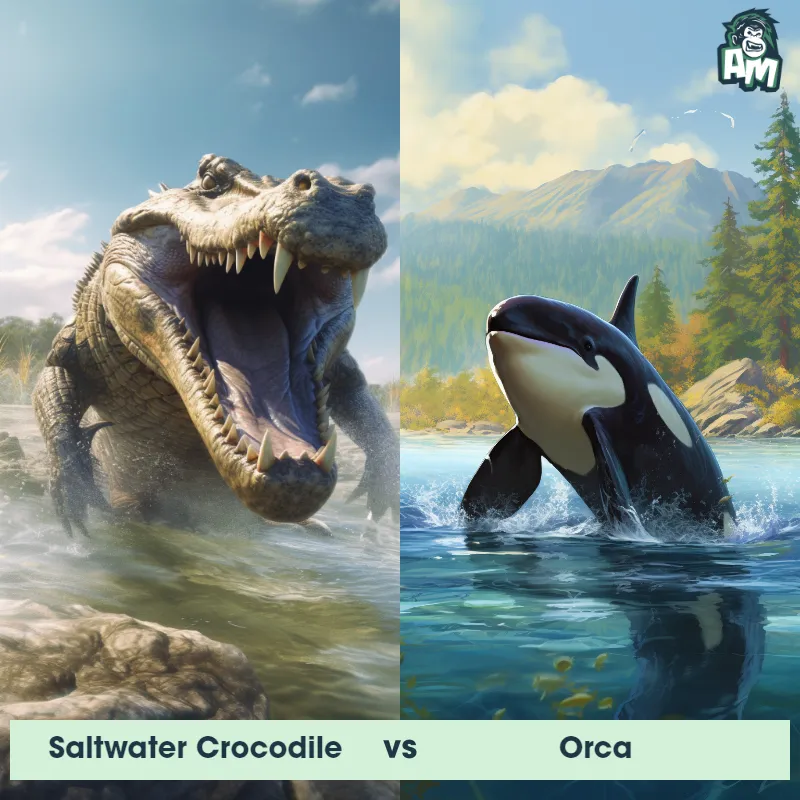
Contender 1: Nile Crocodile
The Nile Crocodile, also known as the common crocodile, is a large reptile that can grow up to 20 feet long and weigh over 1,000 pounds. They have a powerful jaw with sharp teeth and a tough, scaly skin that ranges in color from gray to brown. Nile Crocodiles are found throughout sub-Saharan Africa and are known for their aggressive behavior and ability to take down large prey, including humans.
Fun Fact: Nile Crocodiles are known for their incredible strength and are capable of dragging prey weighing up to 1,000 pounds out of the water and onto land.
Contender 2: Tiger Shark
The Tiger Shark, also known as Galeocerdo cuvier, is a large predatory shark that can grow up to 18 feet in length and weigh over 1,400 pounds. It is named for its distinctive striped pattern on its back, which fades as the shark ages. Tiger Sharks have a broad, flat head and powerful jaws filled with serrated teeth that can easily crush through the shells of sea turtles and clams. They are found in warm waters around the world and are known for their voracious appetite and ability to eat almost anything, including garbage and even other sharks.
Fun Fact: Tiger Sharks have a unique hunting strategy where they will bump into their prey before attacking, a behavior known as "bump and bite."
Matchup Stats
| Nile Crocodile | Tiger Shark | |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Up to 20 feet (6.1 meters) | Up to 18 feet (5.5 meters) |
| Weight | Over 1,000 pounds (453.6 kilograms) | Over 1,400 pounds (635 kilograms) |
| Speed | Land Speed: 11 mph (18 km/hr) | Speed: 20-30 mph (32-48 km/hr) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaw and strong bite force | Powerful jaws and teeth |
| Biggest Weakness | Slow on land and vulnerable to attacks on the underside of its body | Vulnerable to attacks on the gills |
Current Votes
Nile Crocodile vs Tiger Shark
See Who Wins
View More Matches
Looking For More?
Similar Matches
Scientific Stats
| Nile Crocodile | Tiger Shark | |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Crocodylus niloticus | Galeocerdo cuvier |
| Family | Crocodylidae | Carcharhinidae |
| Habitat | Freshwater rivers, lakes, and marshes | Warm waters |
| Geography | Sub-Saharan Africa | Found worldwide |
| Diet | Carnivorous, eats fish, birds, mammals, and occasionally humans | Varied, including sea turtles, clams, garbage, and other sharks |
| Lifespan | 70 years - 100 years | 27 years - 50 years |
Key Differences between Nile Crocodile and Tiger Shark
- Skin Texture: The Nile Crocodile has thick, scaly skin with a rough texture, while the Tiger Shark has a smoother skin covered in dermal denticles, small tooth-like structures that resemble scales.
- Size: The Nile Crocodile is typically larger than the Tiger Shark, with adult males ranging from 9 to 16 feet in length, while Tiger Sharks average around 10 to 12 feet in length.
- Coloration and Patterns: Nile Crocodiles possess a lighter brown or olive-colored skin tone, often with dark patches or spots, while Tiger Sharks have a dark bluish-gray or grayish-brown dorsal side and a pale yellowish-white or off-white ventral side.
- Tail Shape: The Nile Crocodile has a powerful tail that is flattened at the base and becomes more slender towards the tip, aiding in swimming and propulsion. Tiger Sharks possess a distinct, asymmetrical caudal fin known as a "heterocercal" tail, with the upper lobe being longer and more pronounced than the lower lobe.
- Head Shape: The Nile Crocodile's head is large, broad, and somewhat flat, with eyes and nostrils placed on top, allowing it to scan the surroundings even when its body is mostly submerged. In contrast, the Tiger Shark has a more pointed snout with eyes located on the sides of the head.
- Shape: The Nile Crocodile has a robust and compact body with strong legs and a broad snout, whereas the Tiger Shark has a more streamlined body shape with a distinctive, long, and tapering snout.