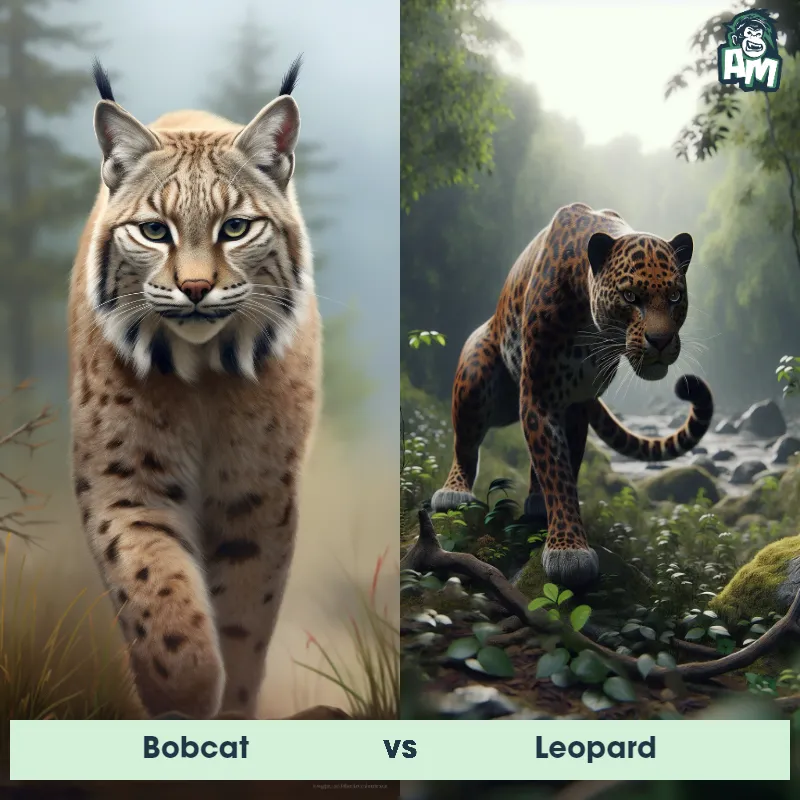
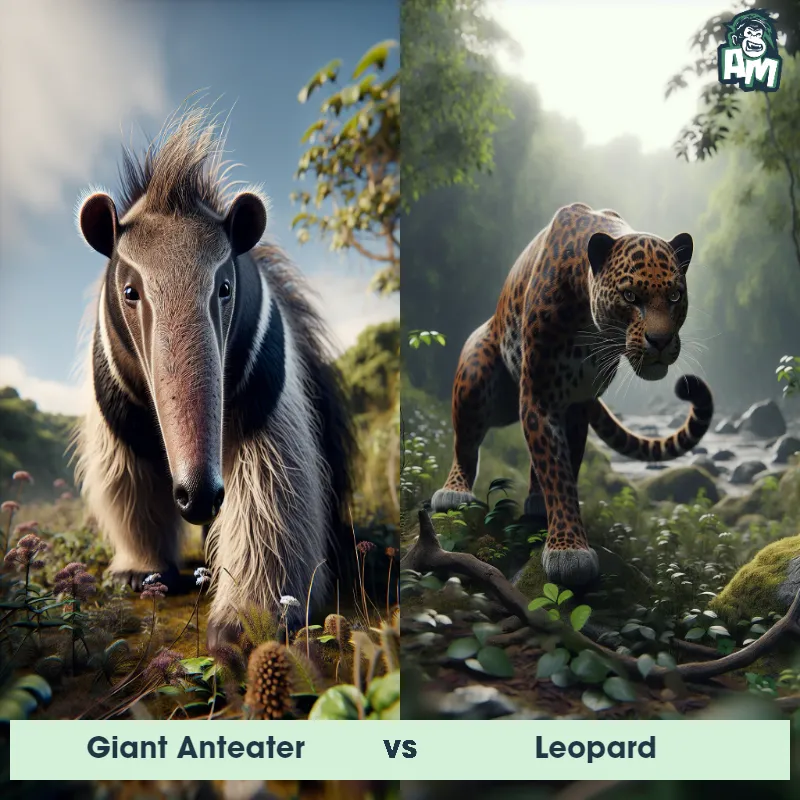
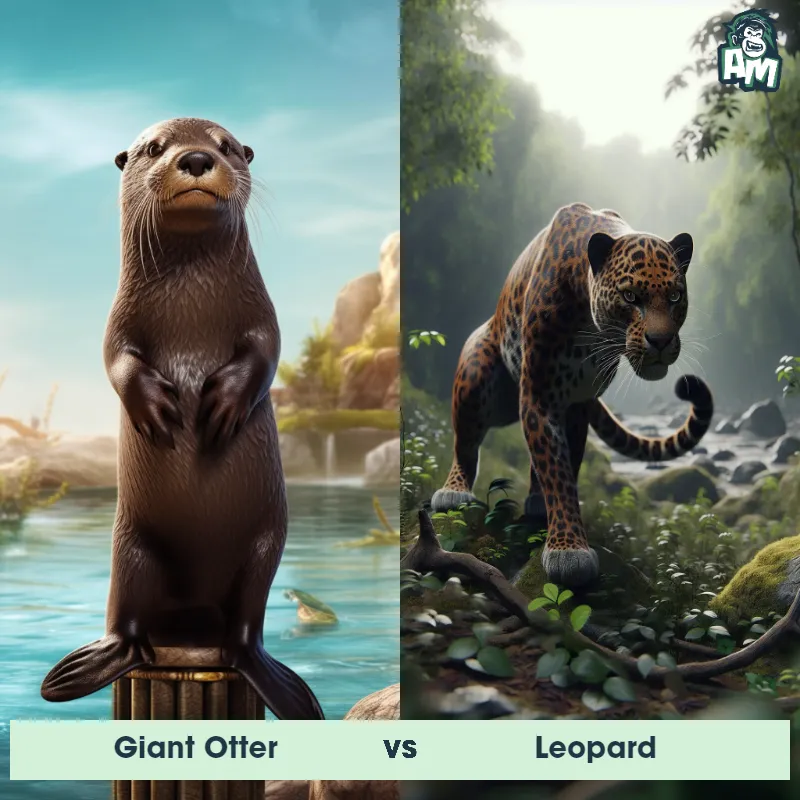
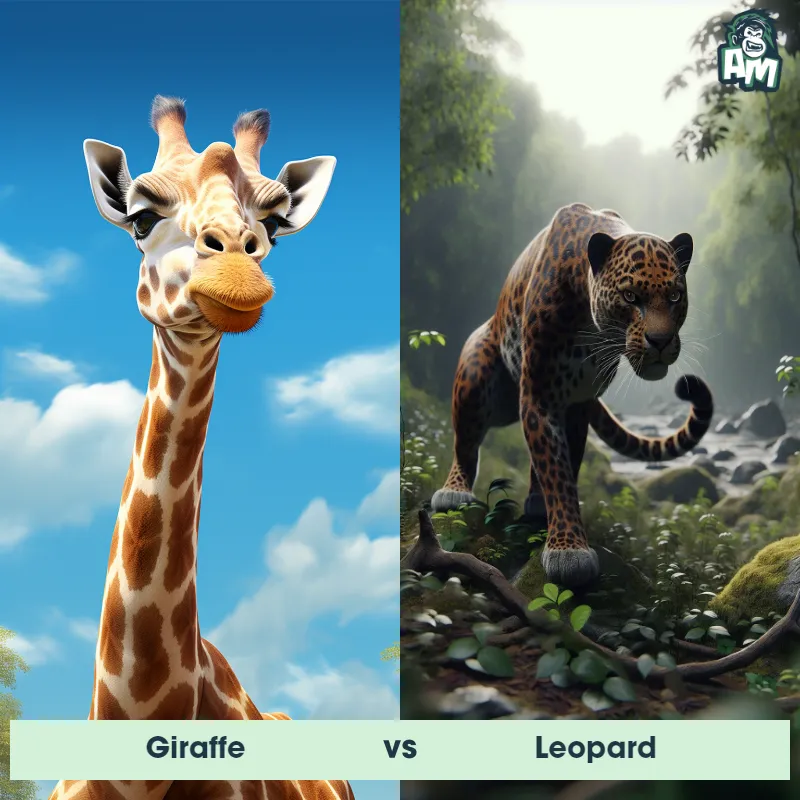
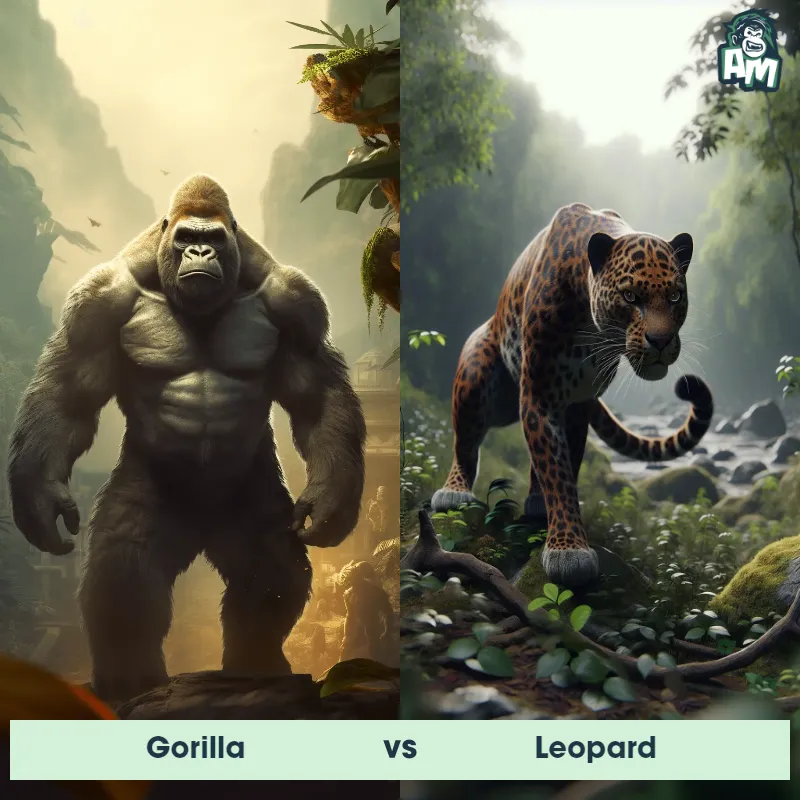
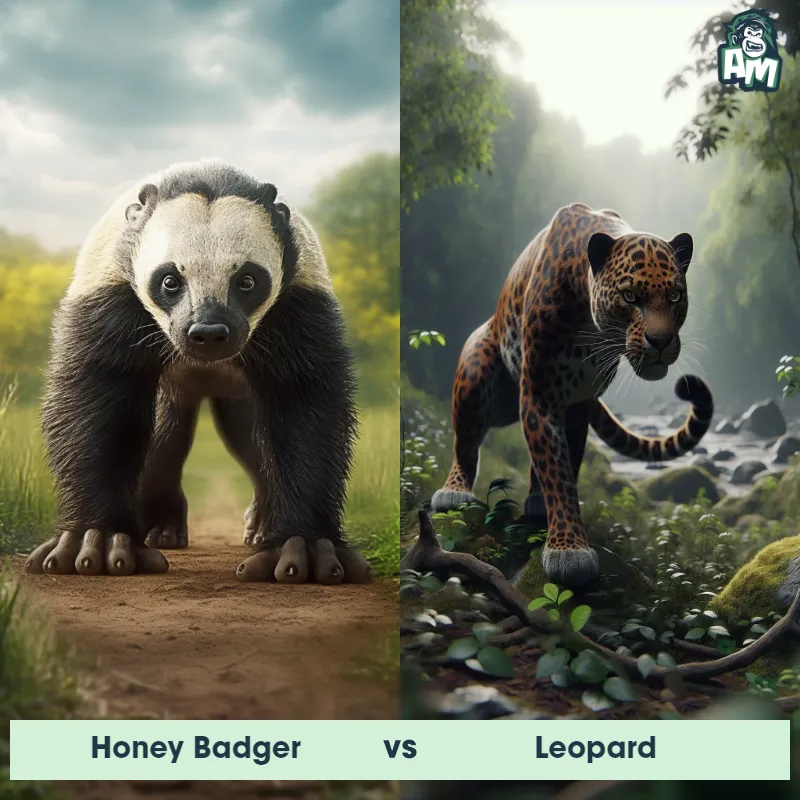
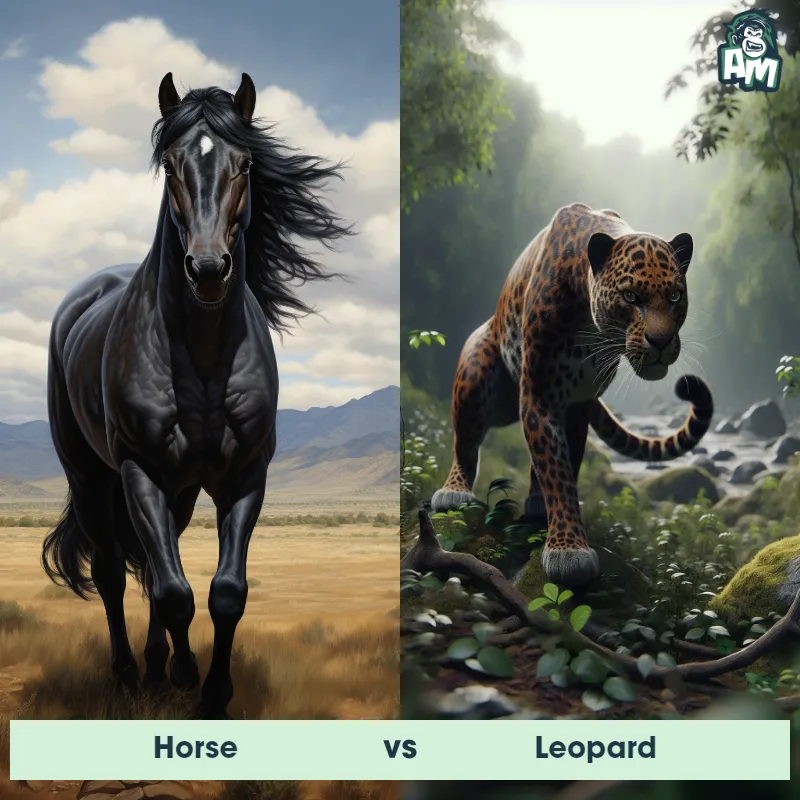
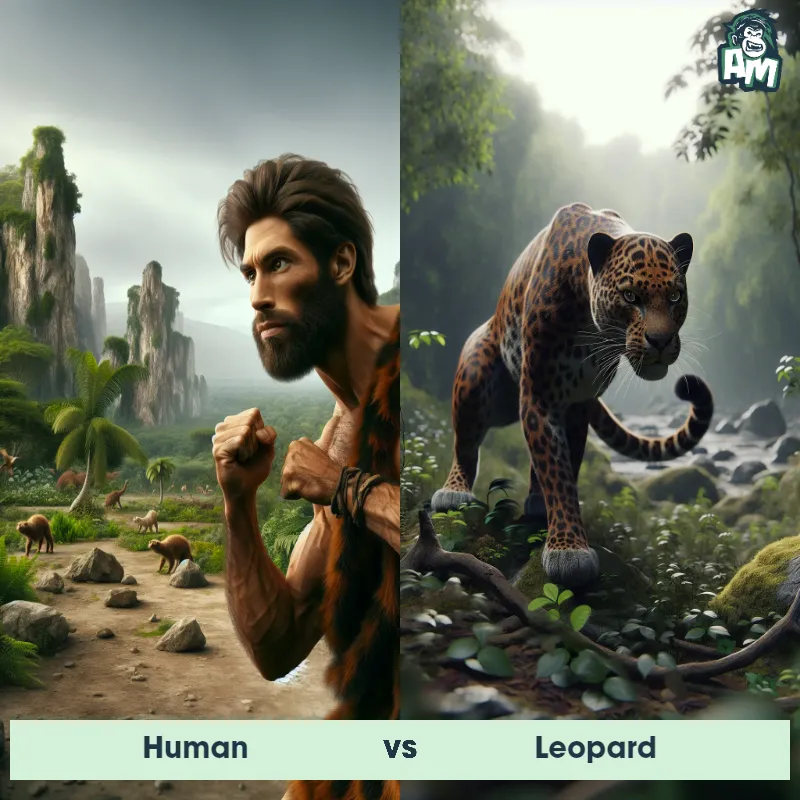
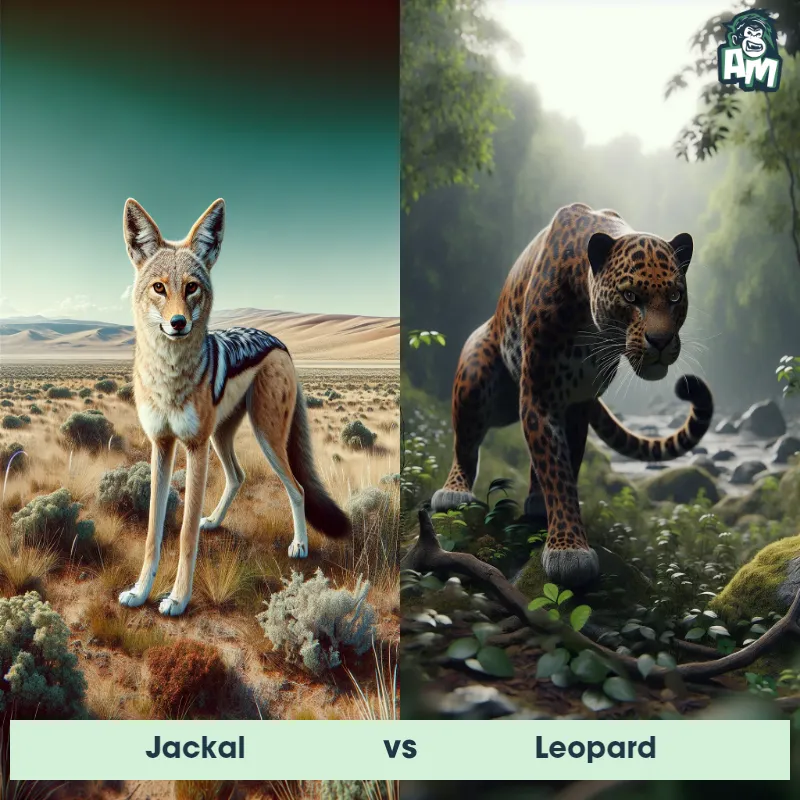
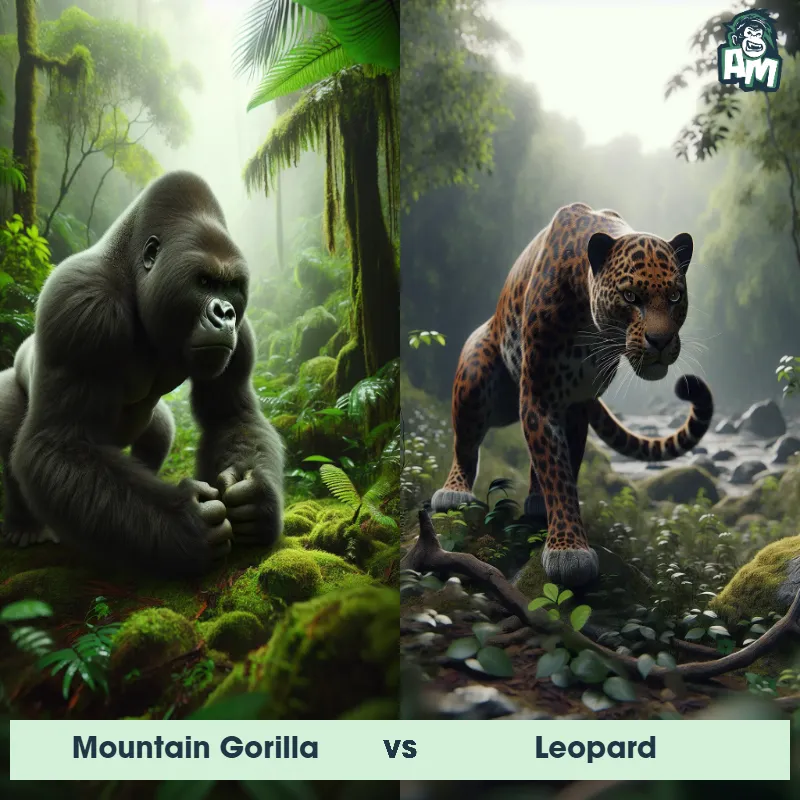
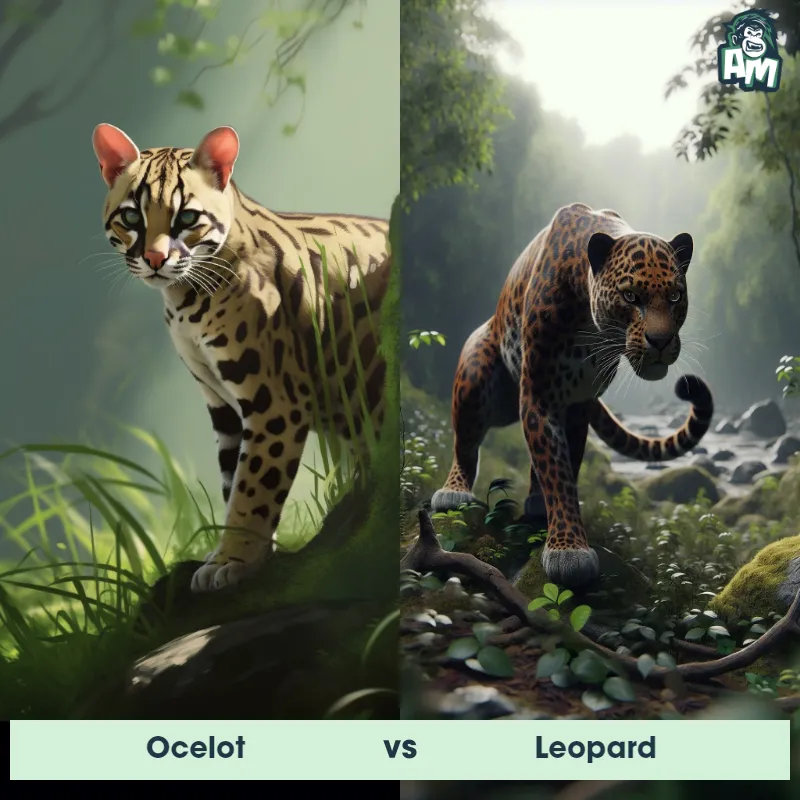
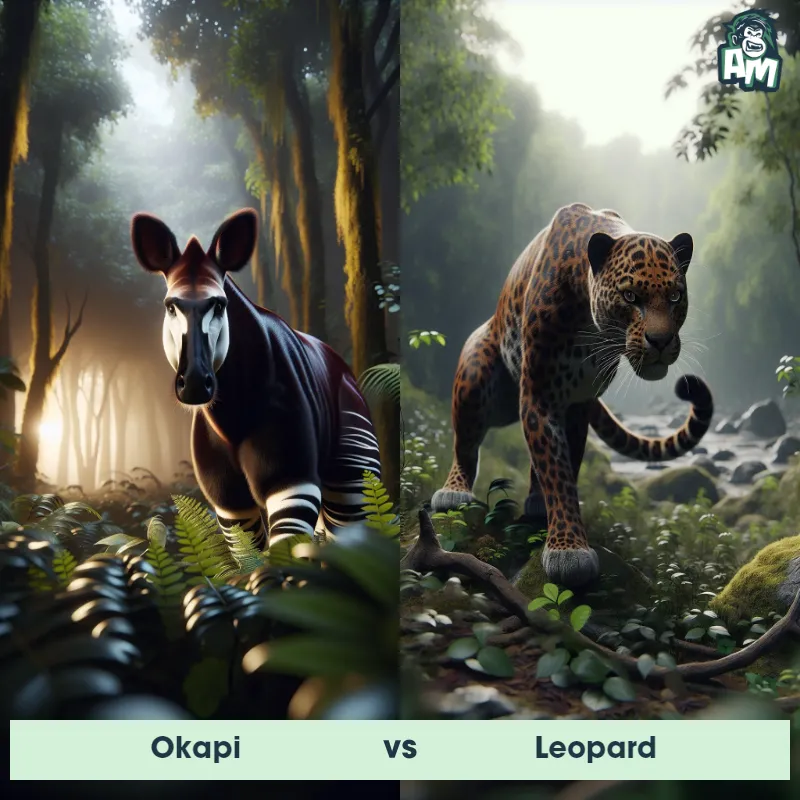
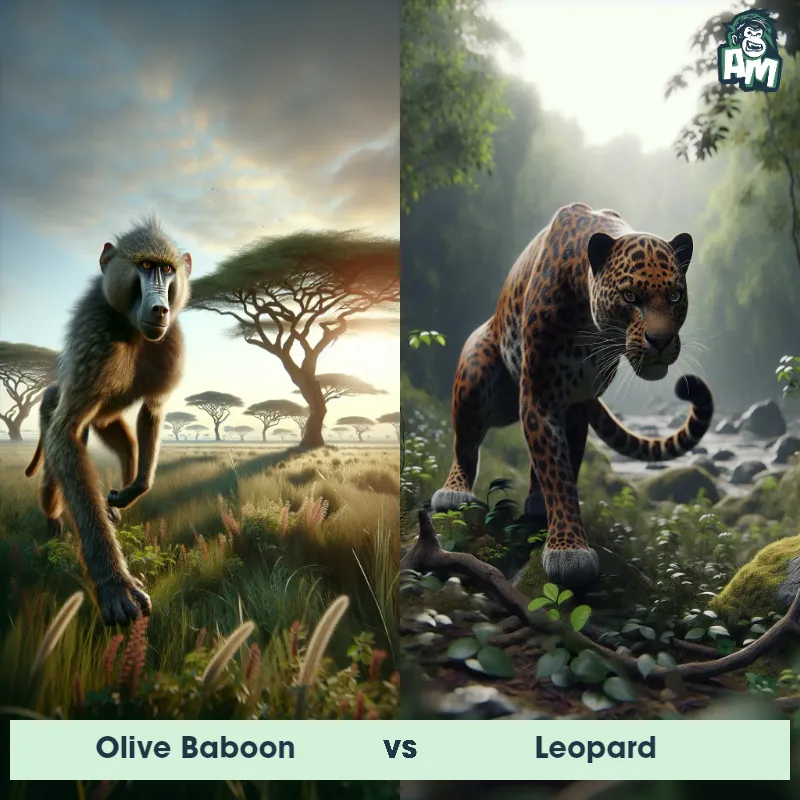
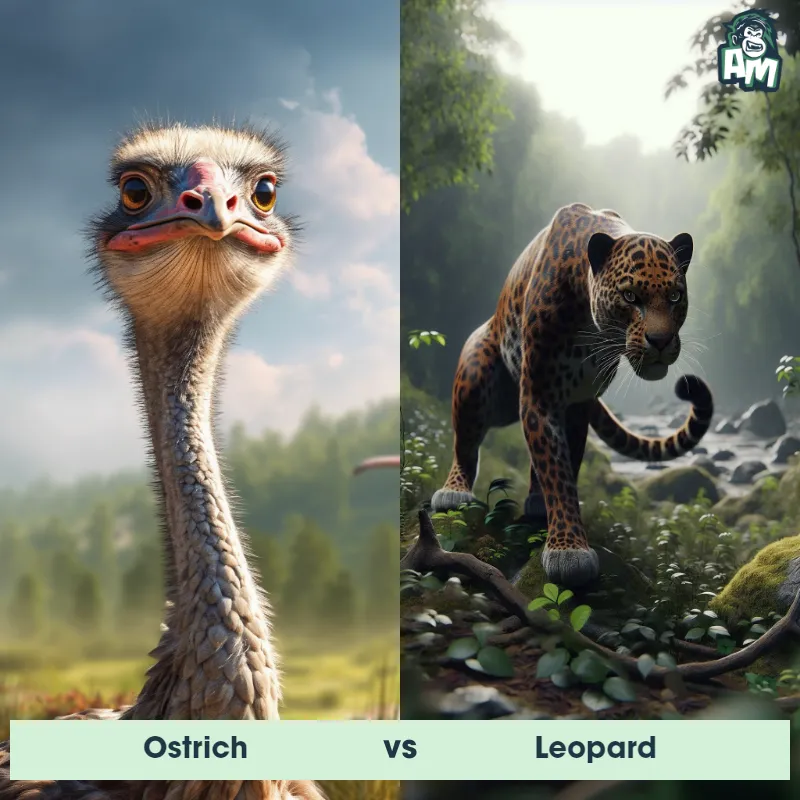
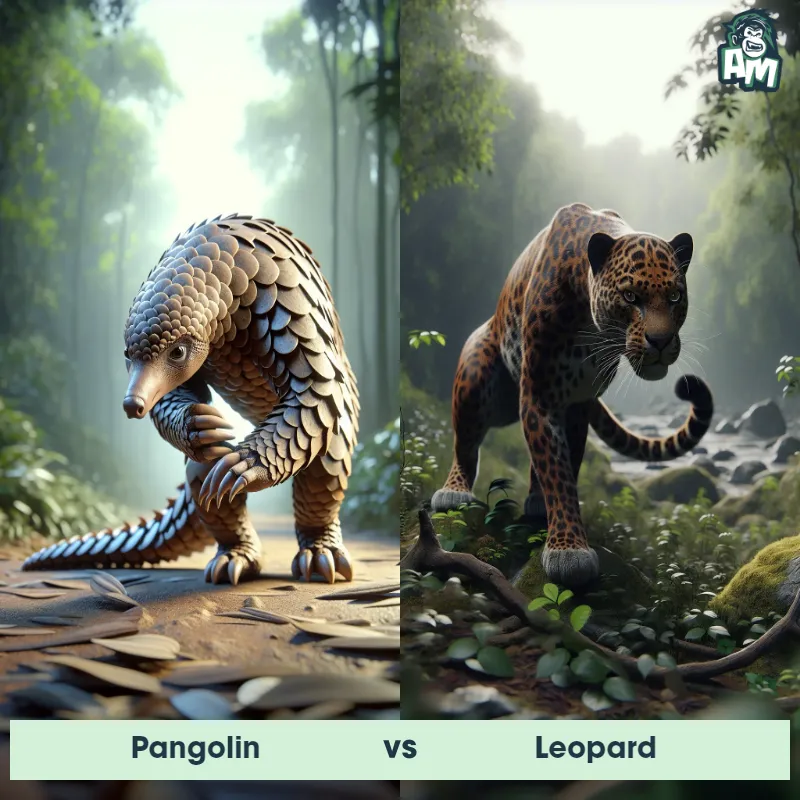
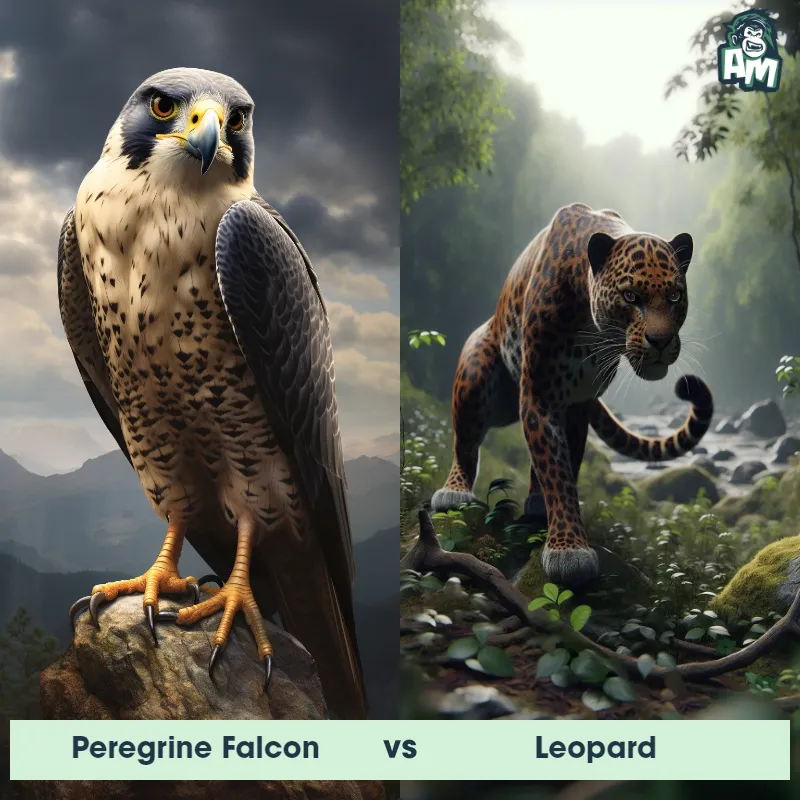
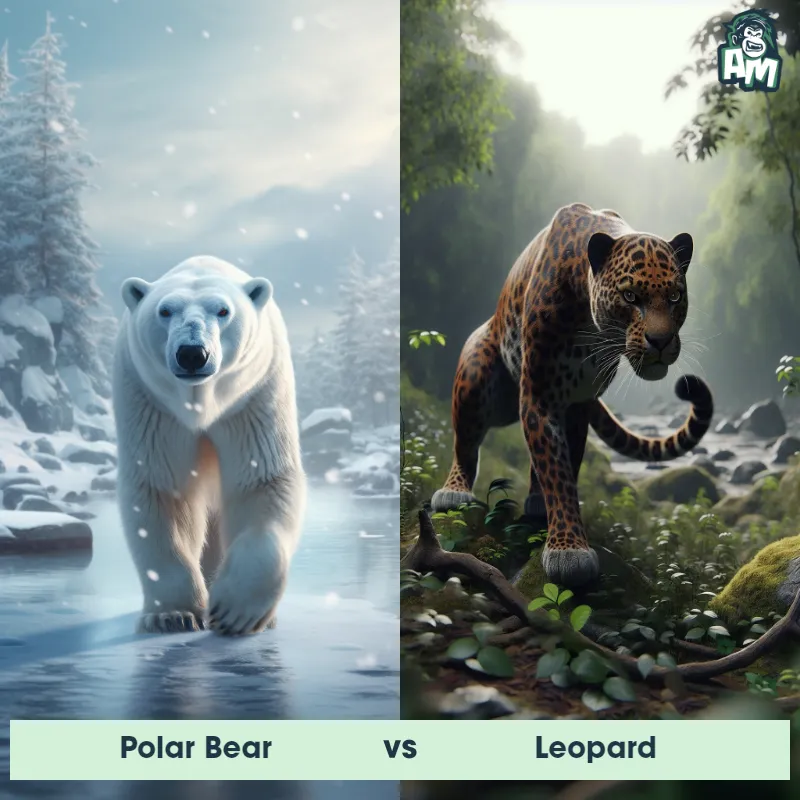
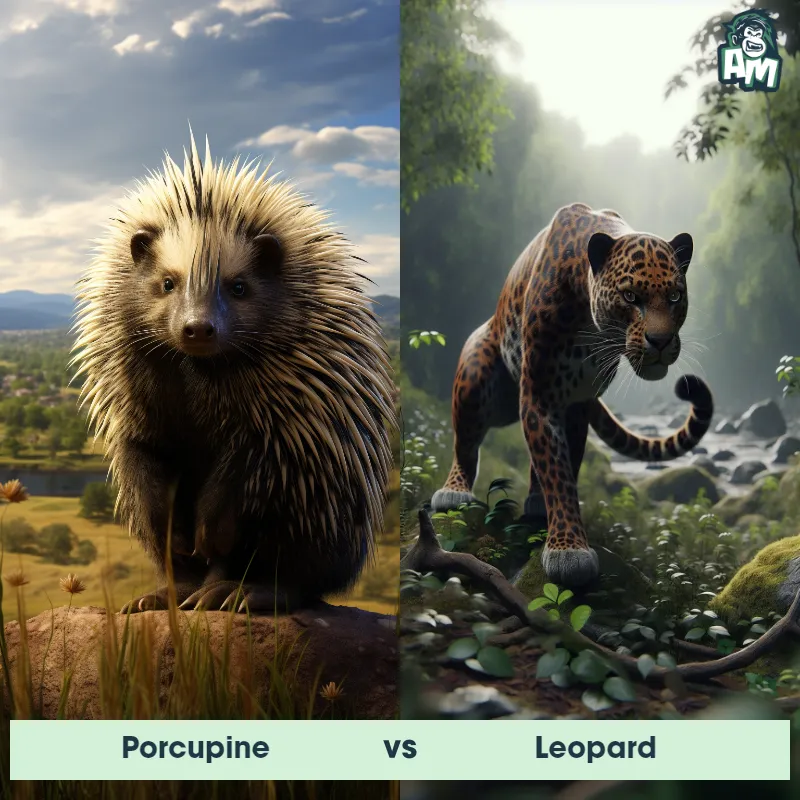
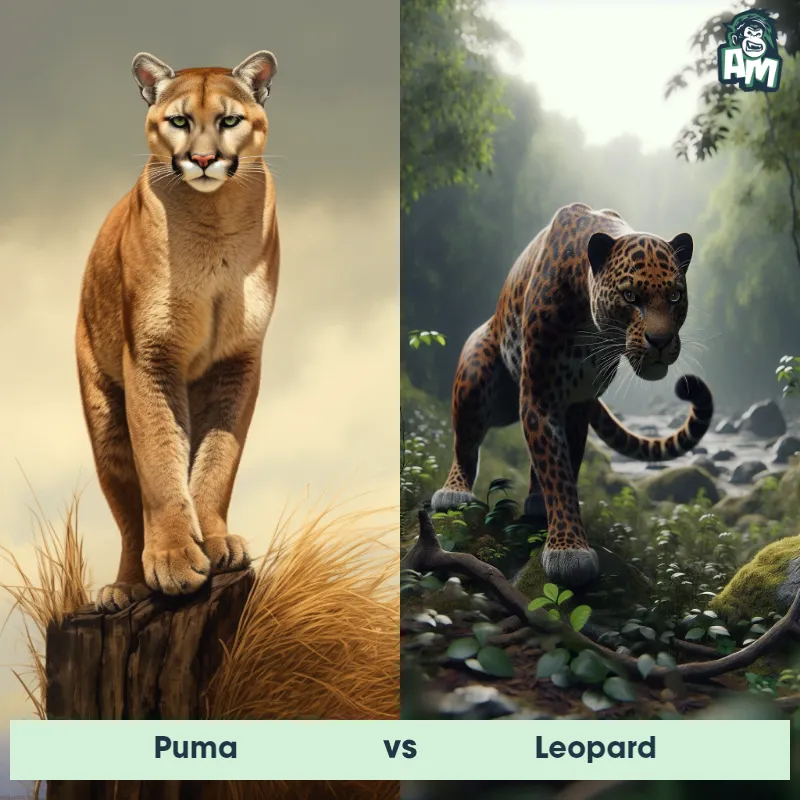
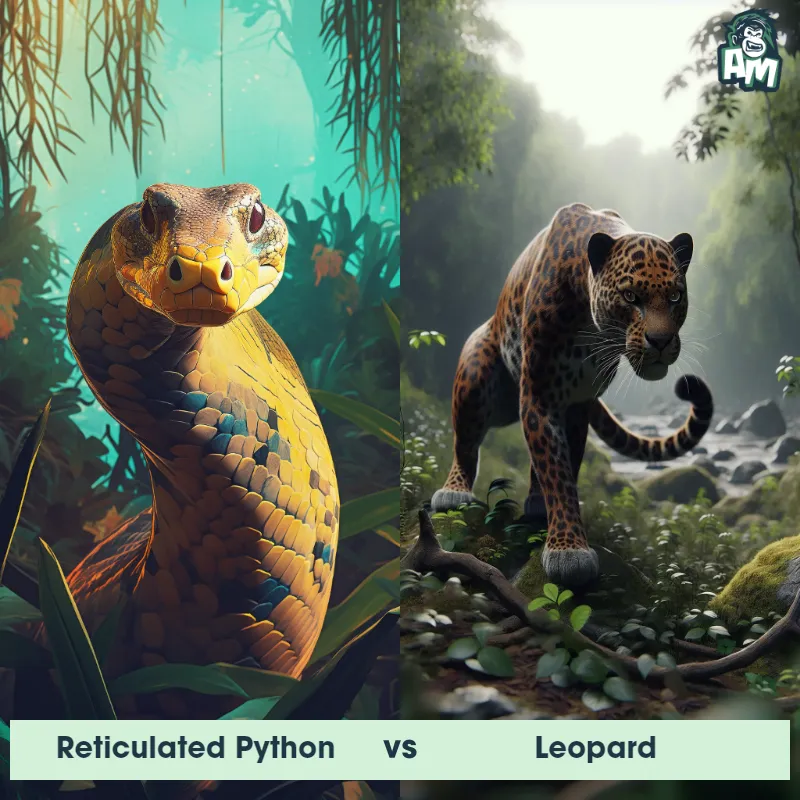
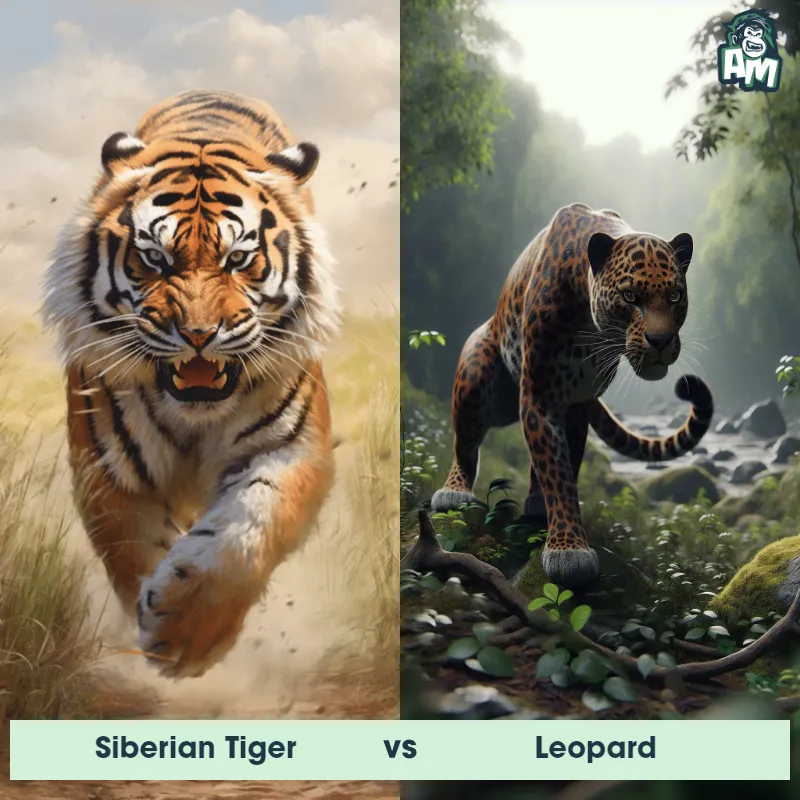
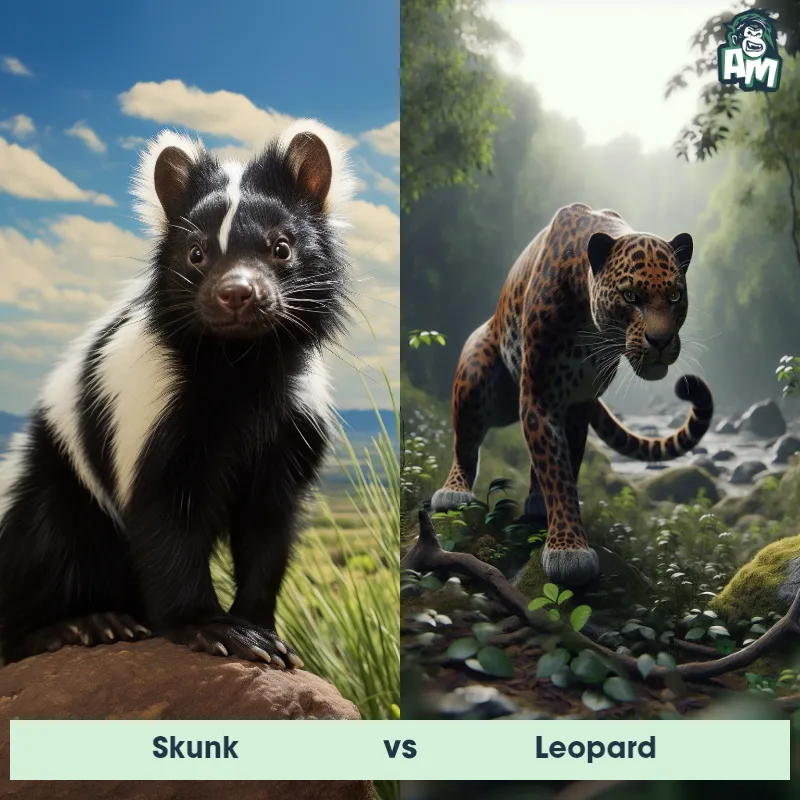
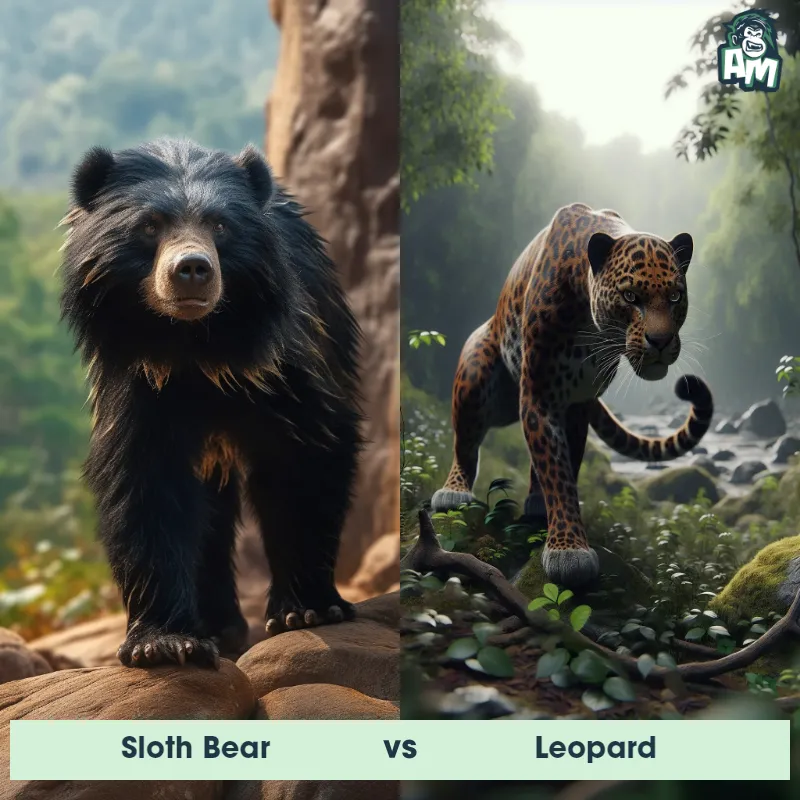
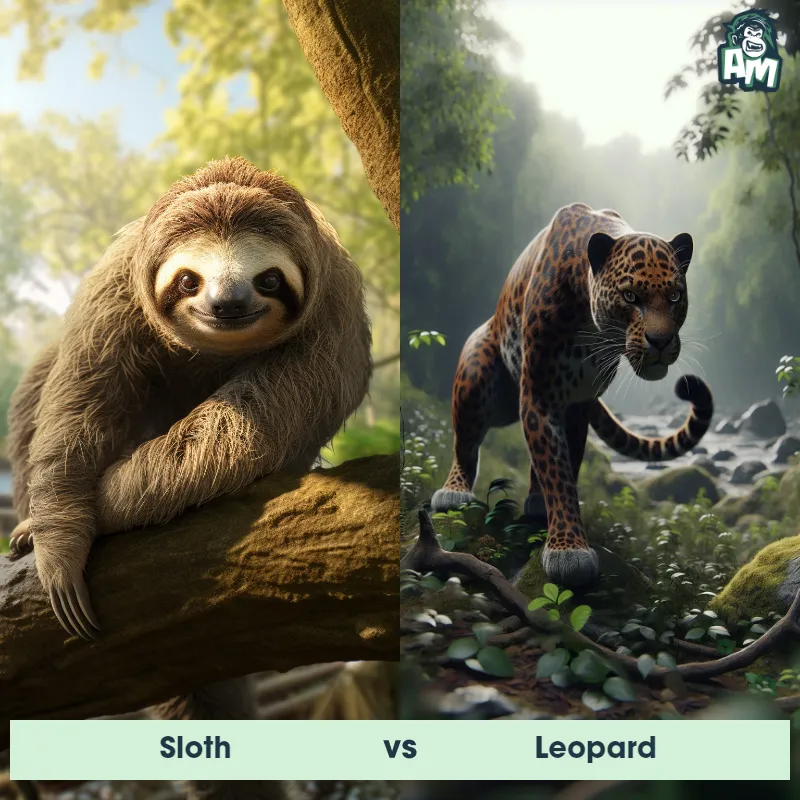
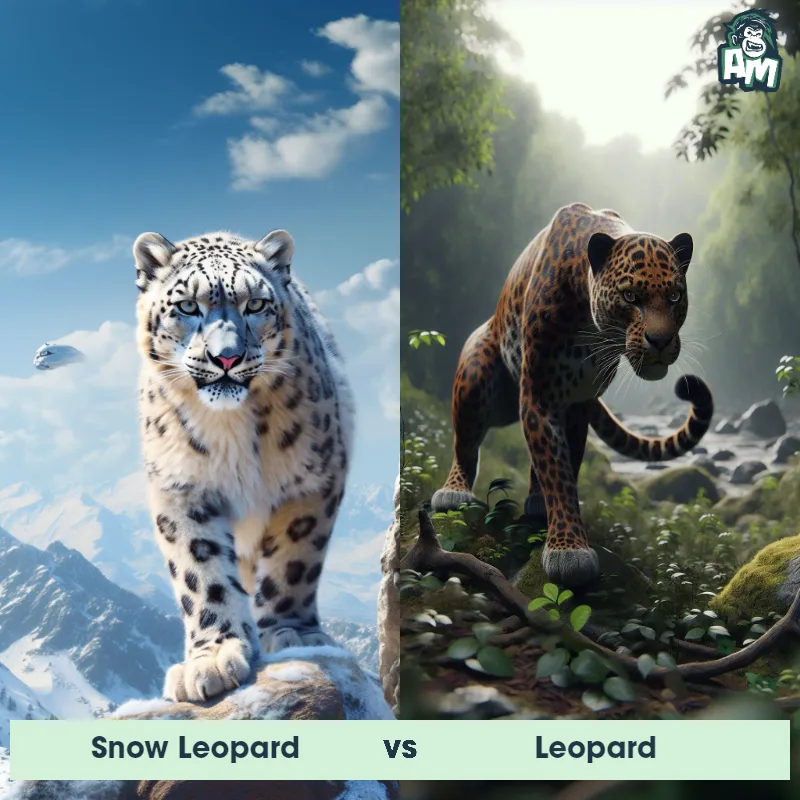
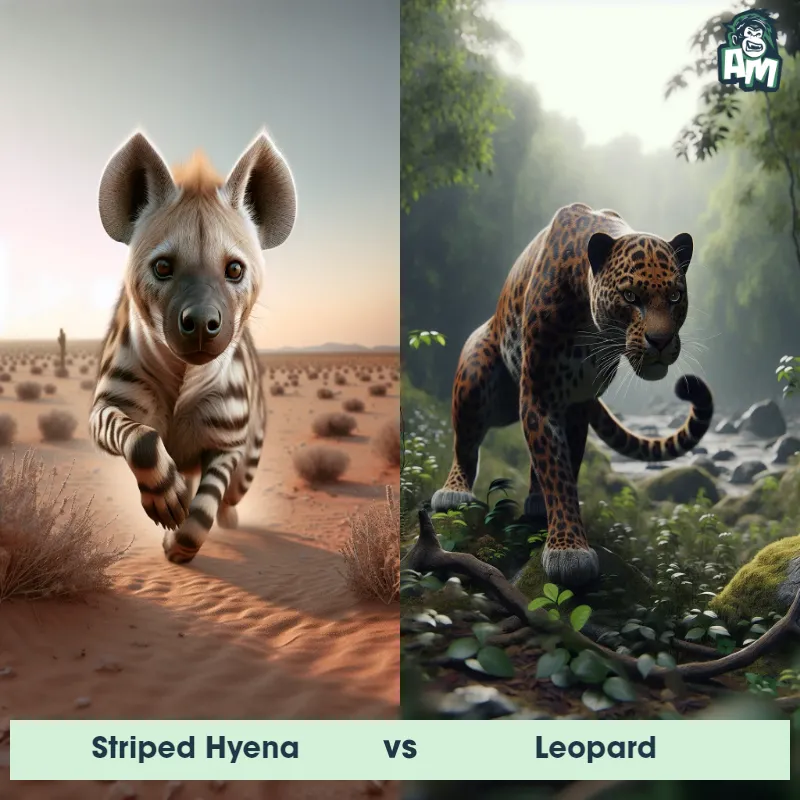
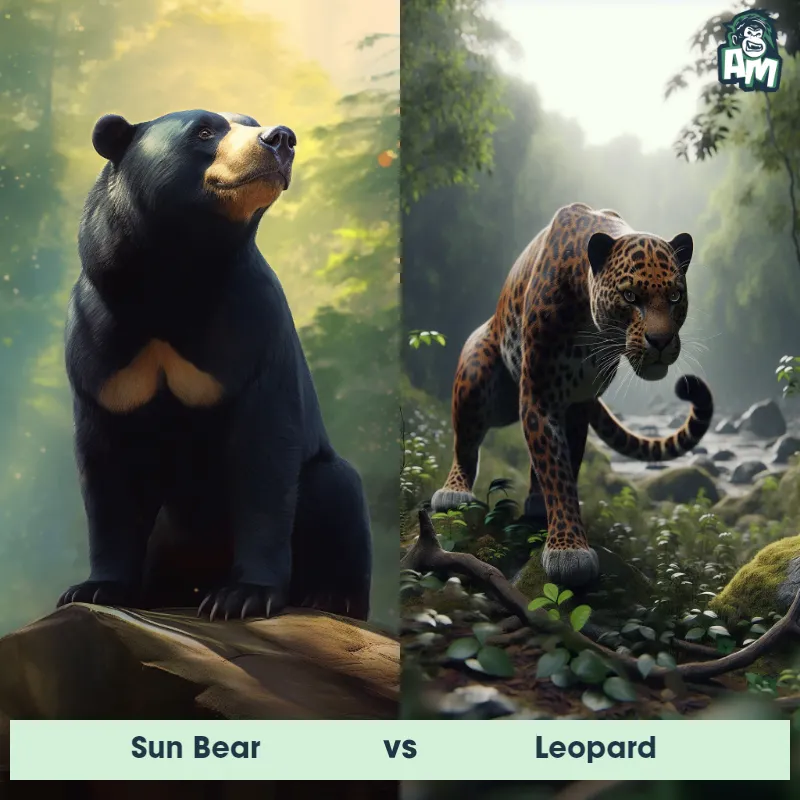
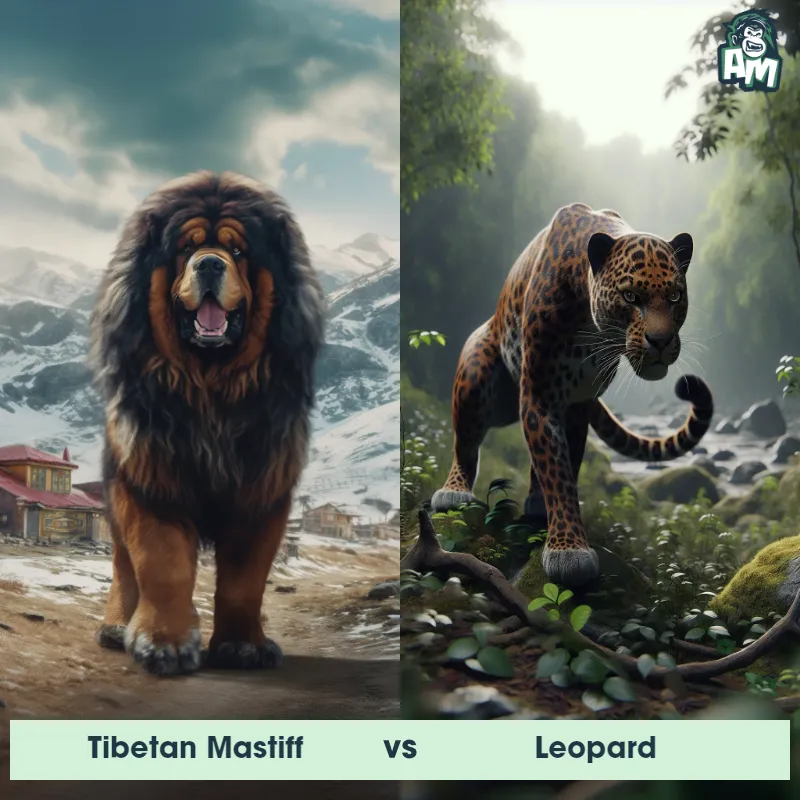
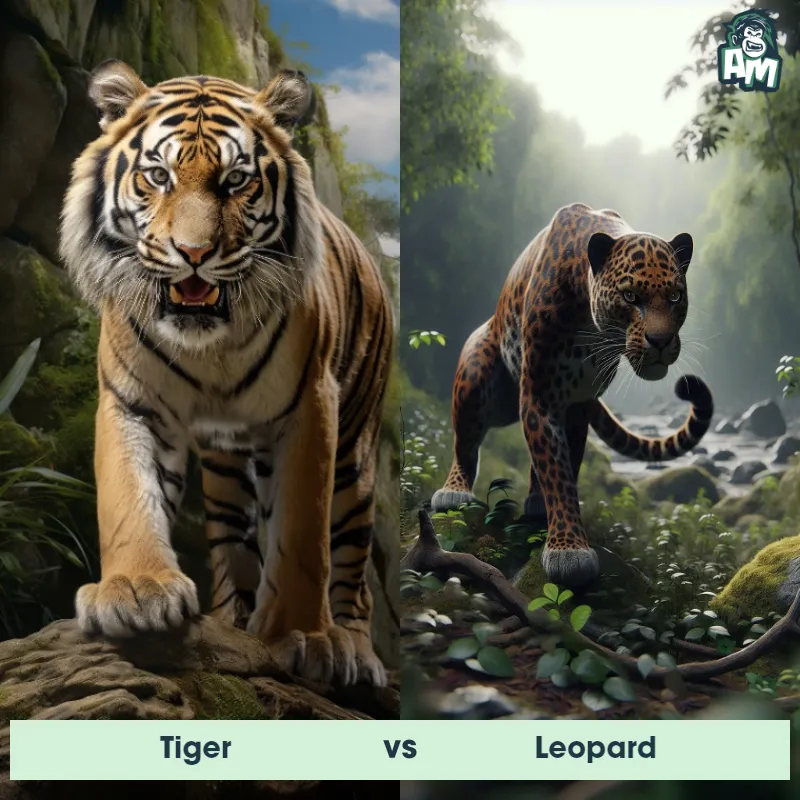
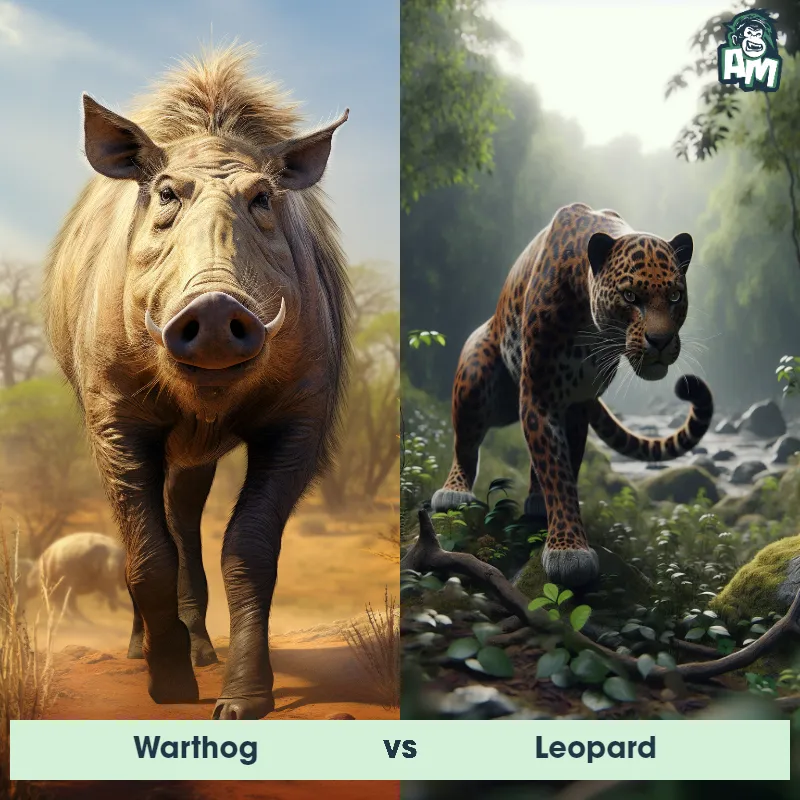
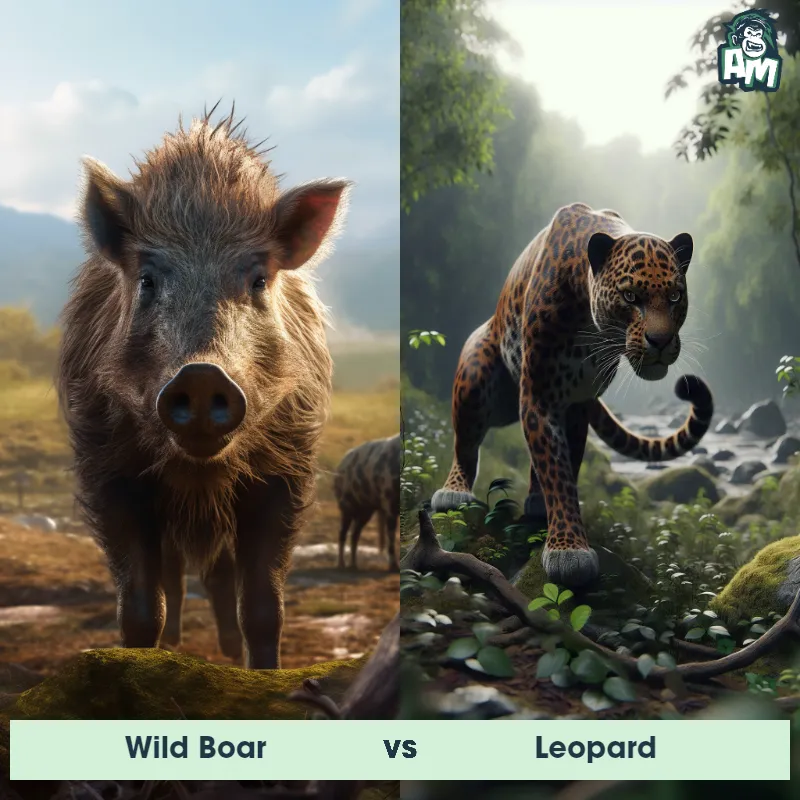
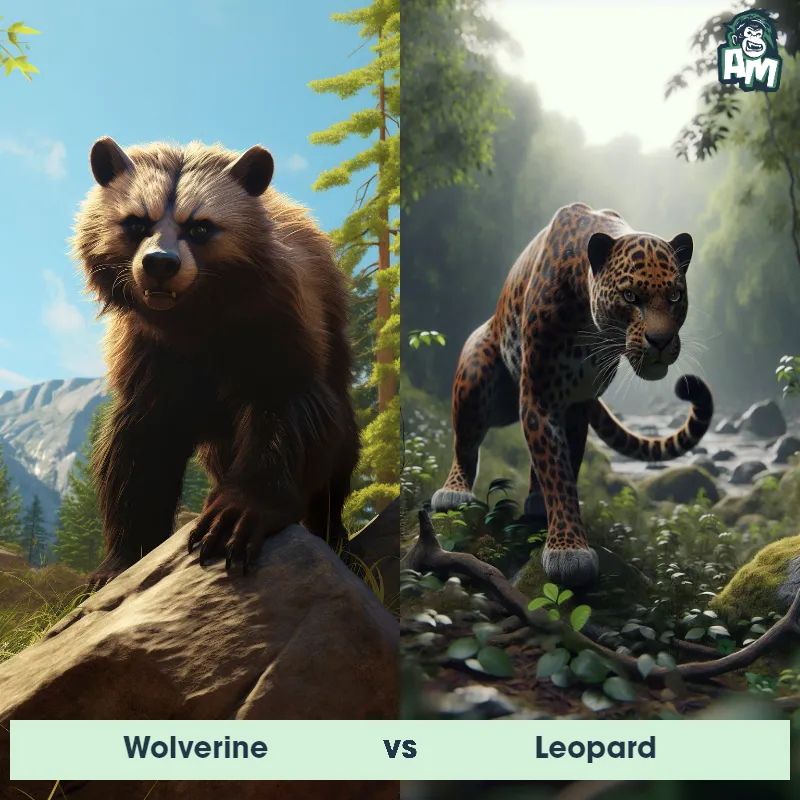
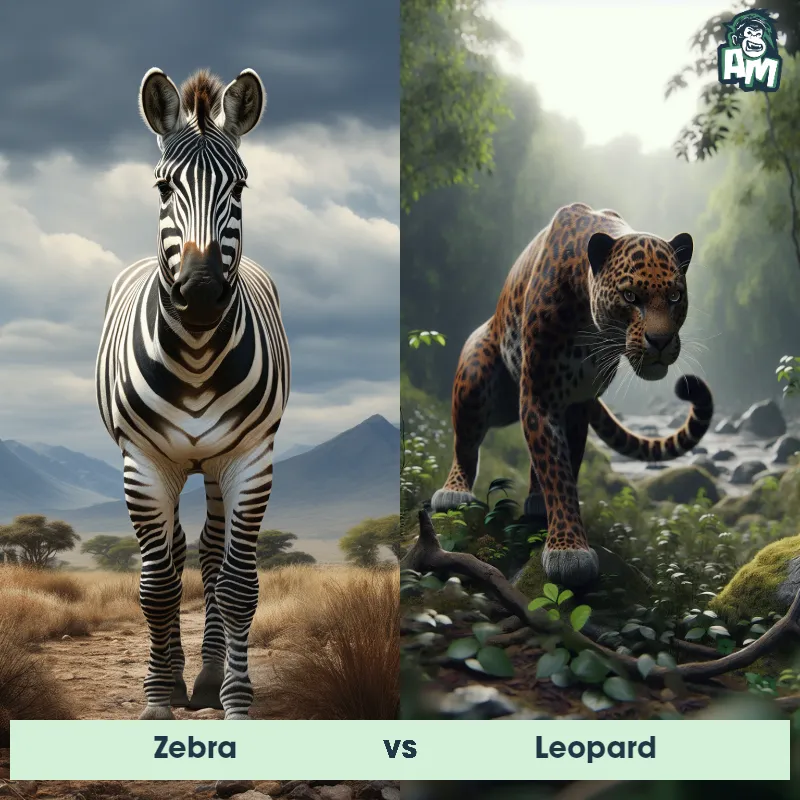
The Leopard
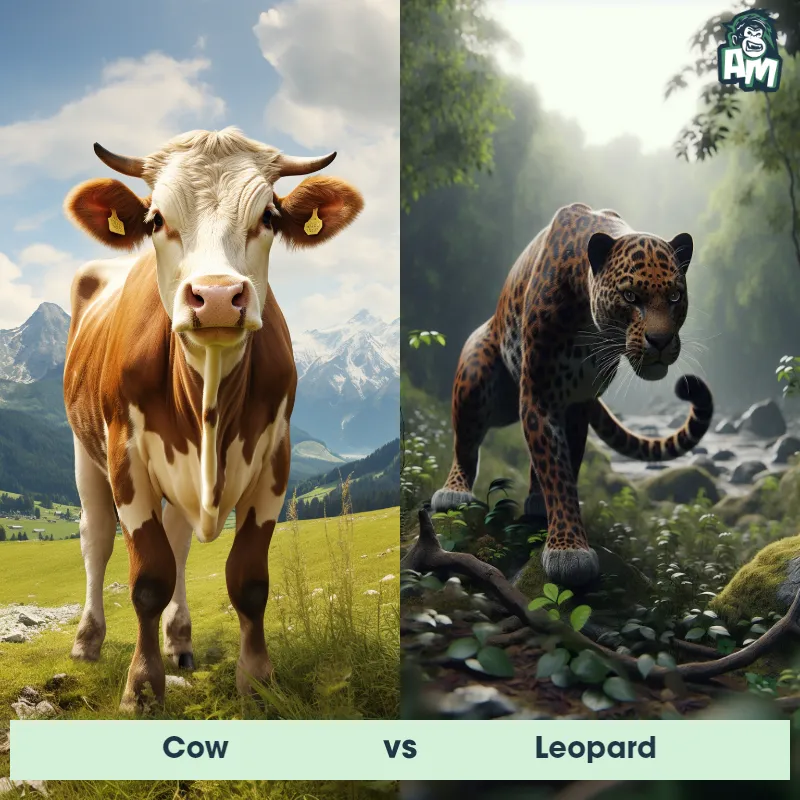
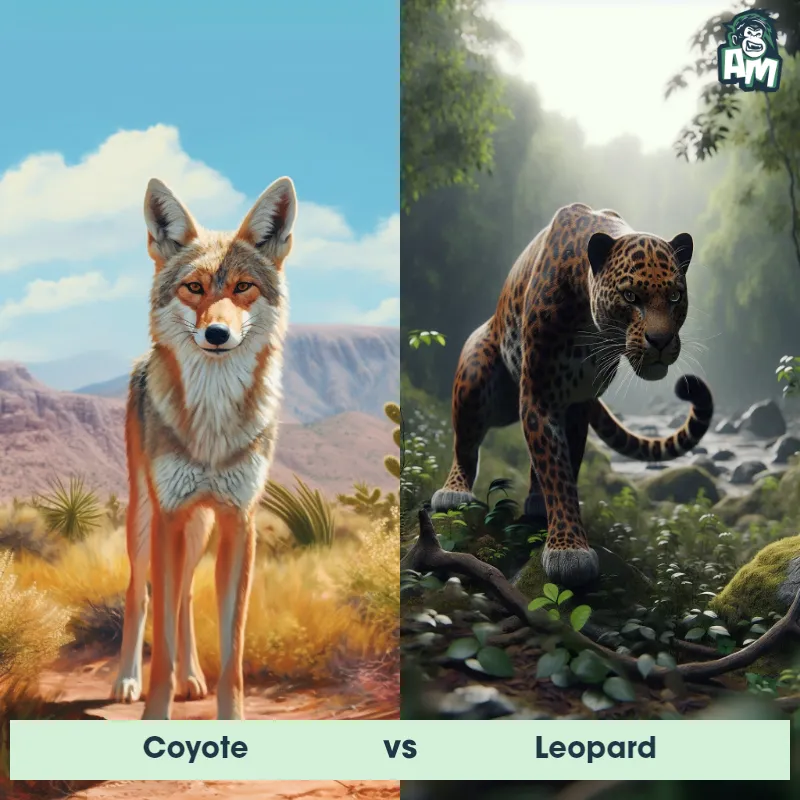
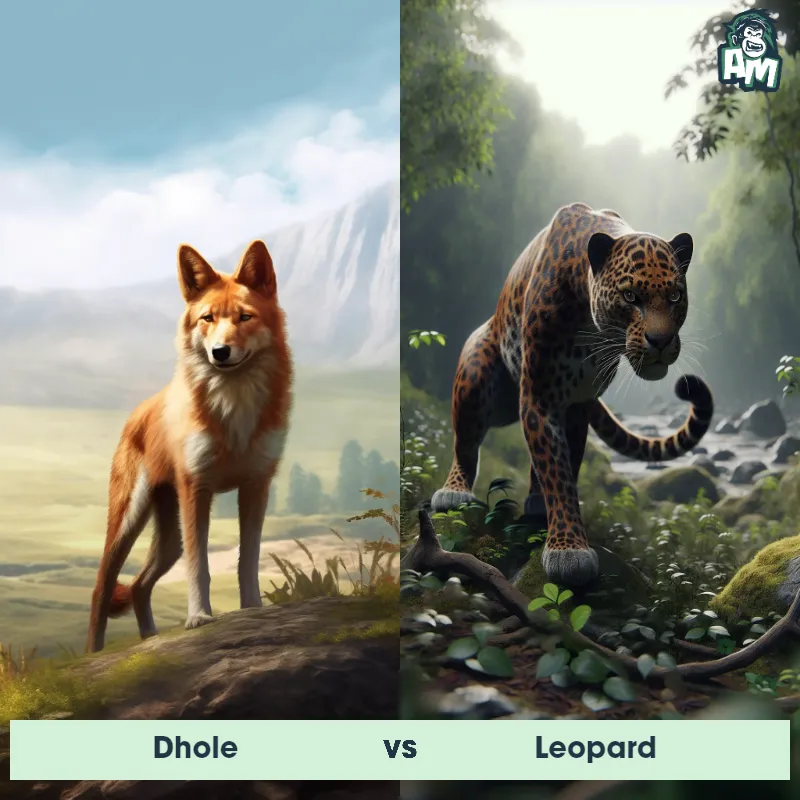
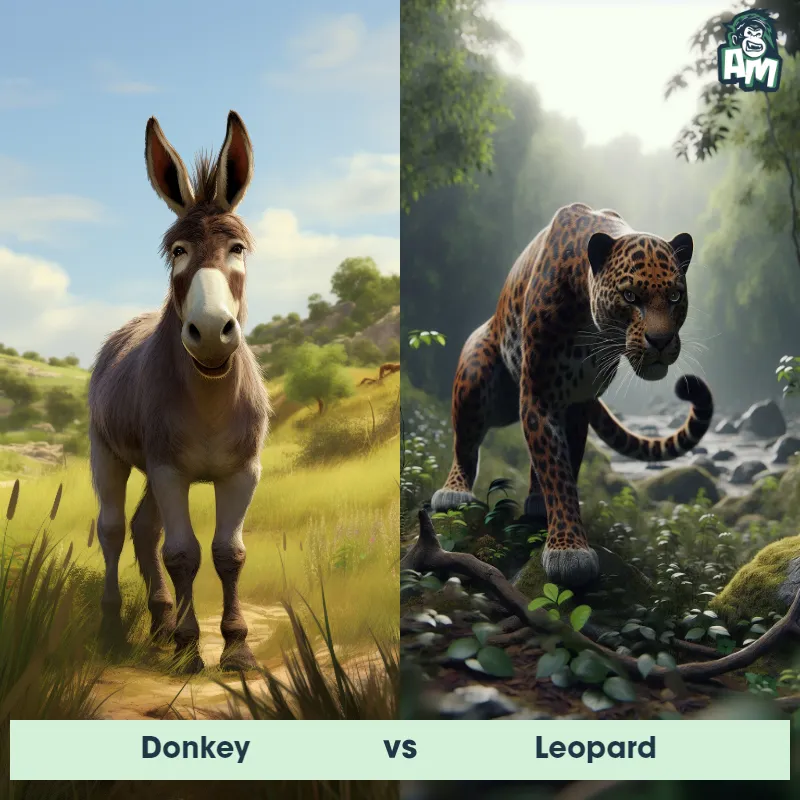
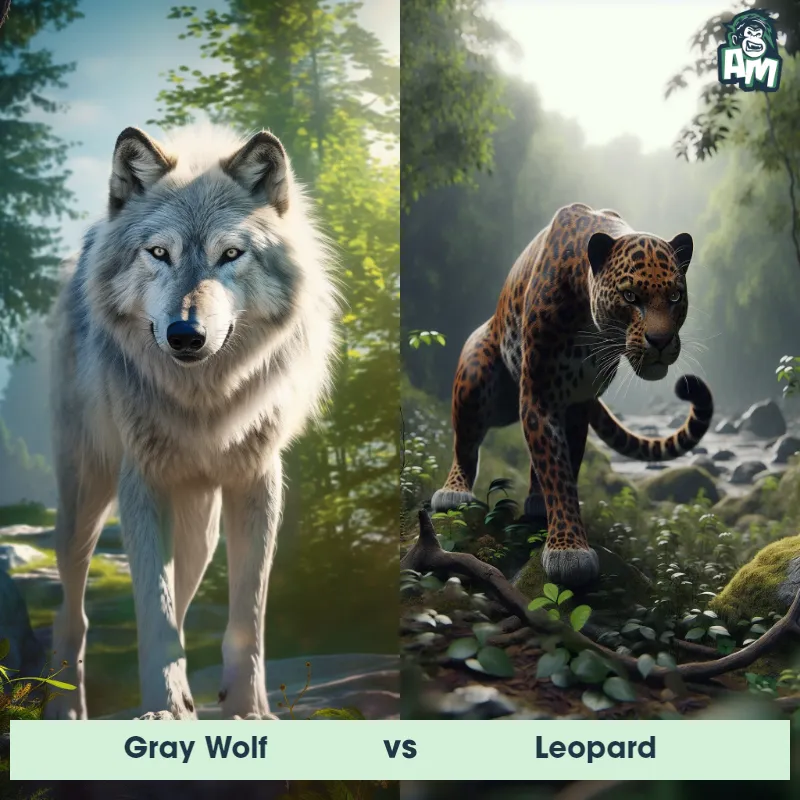
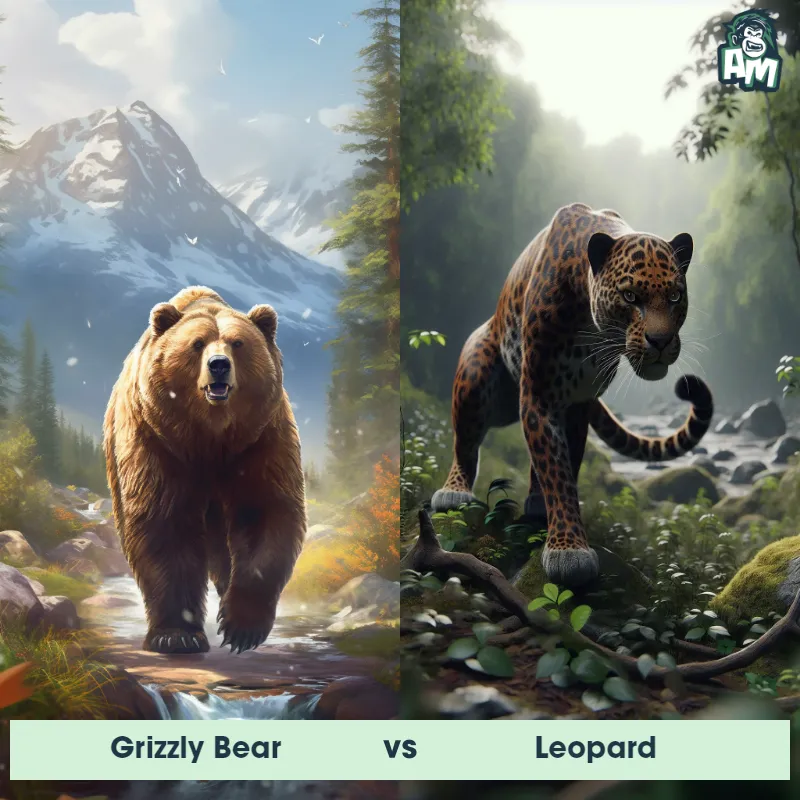
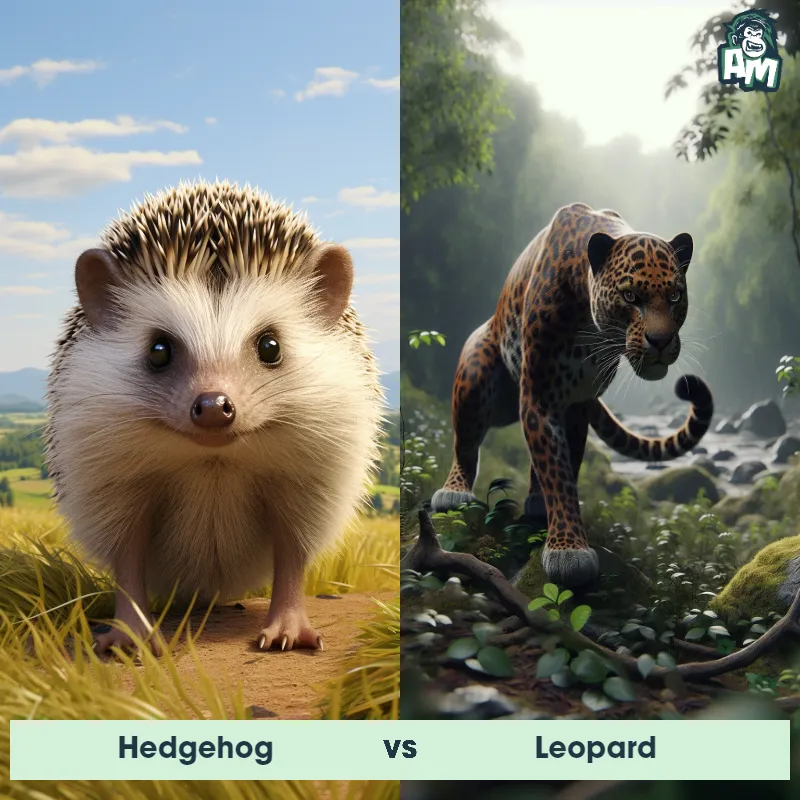
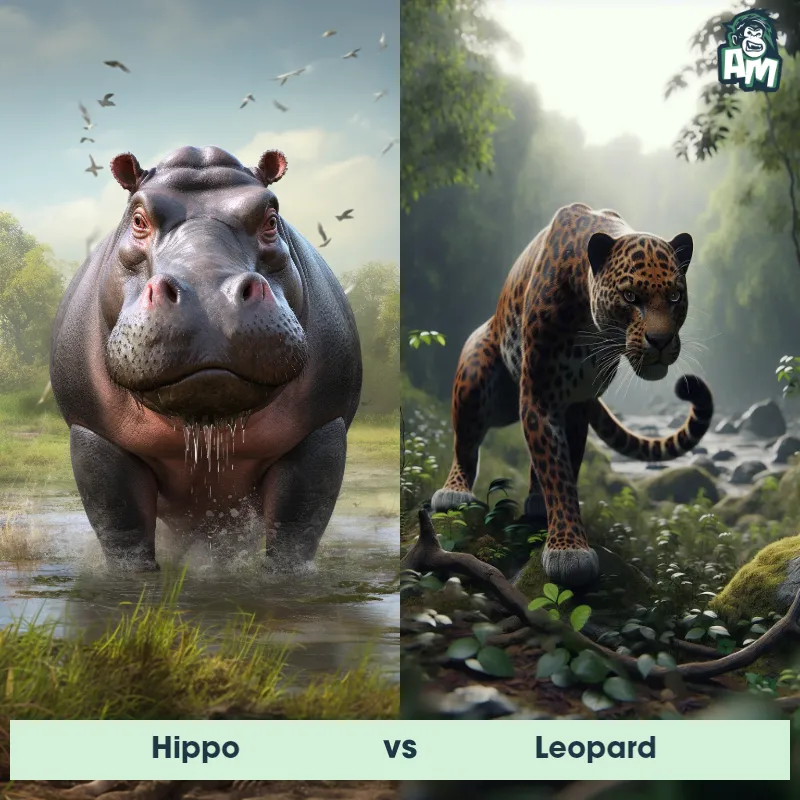
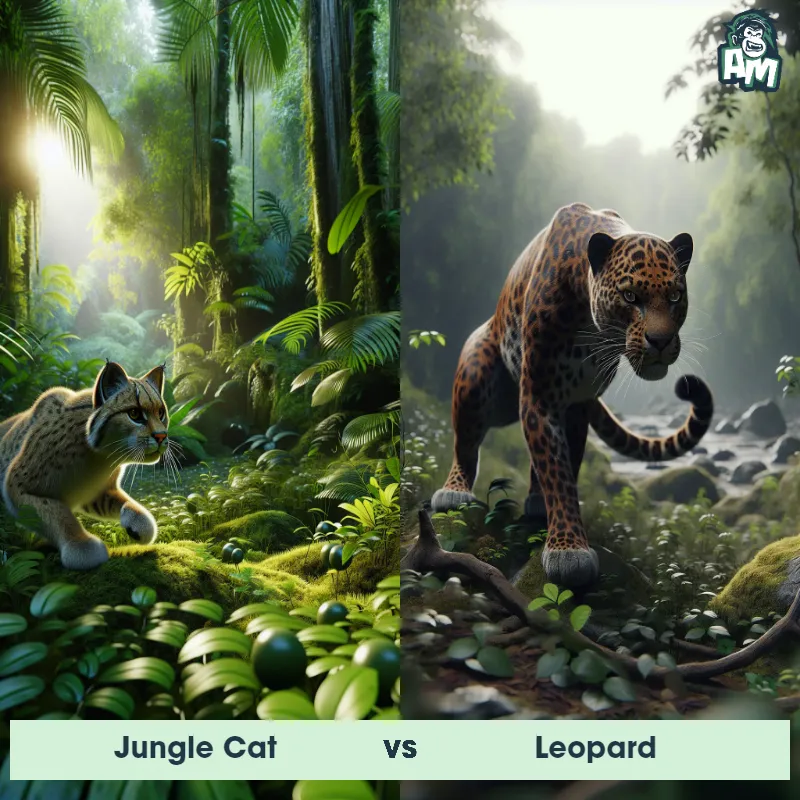
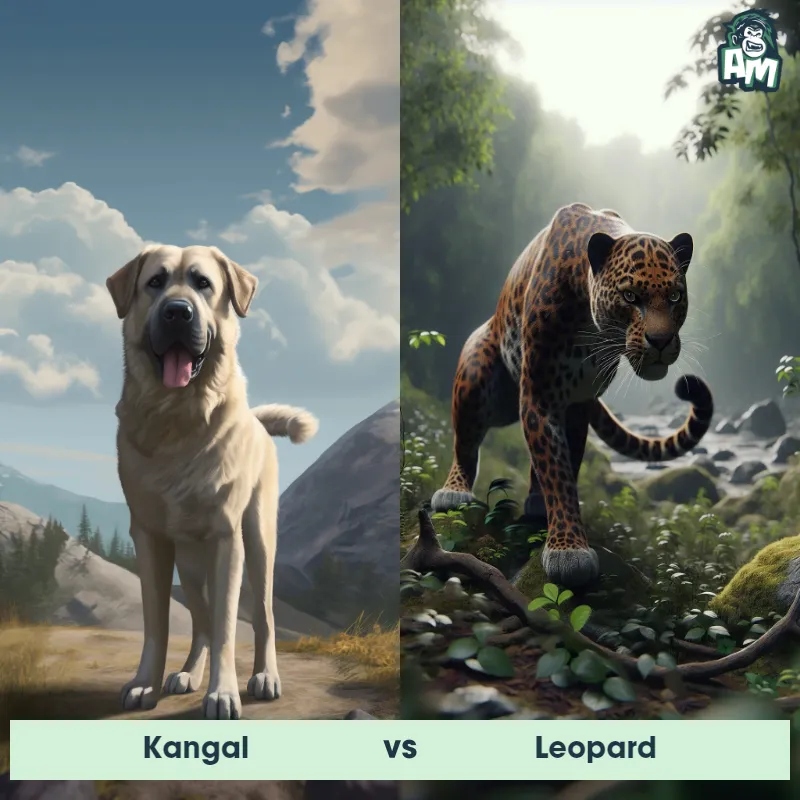
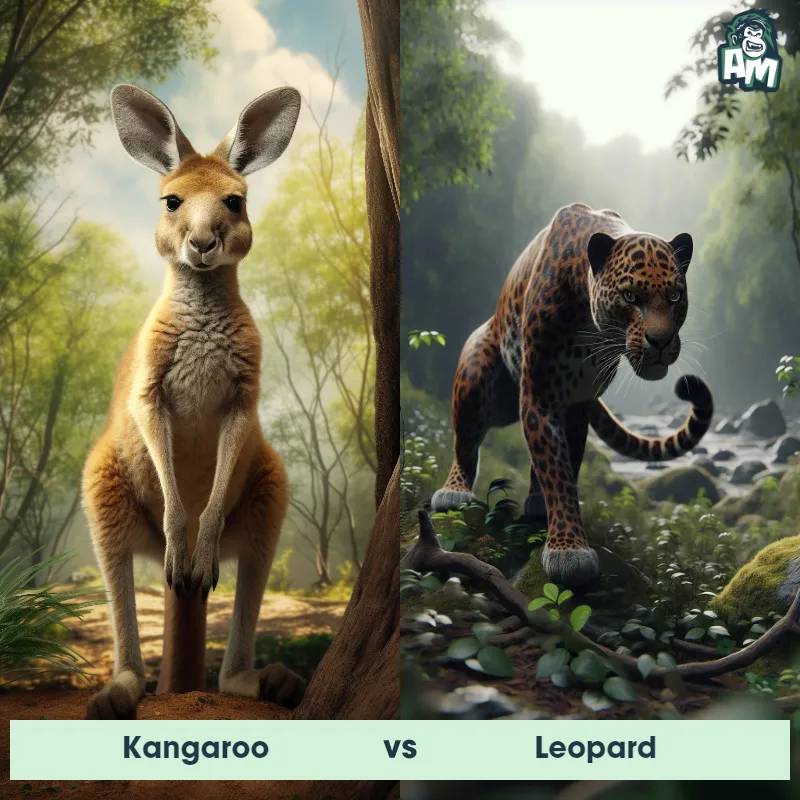
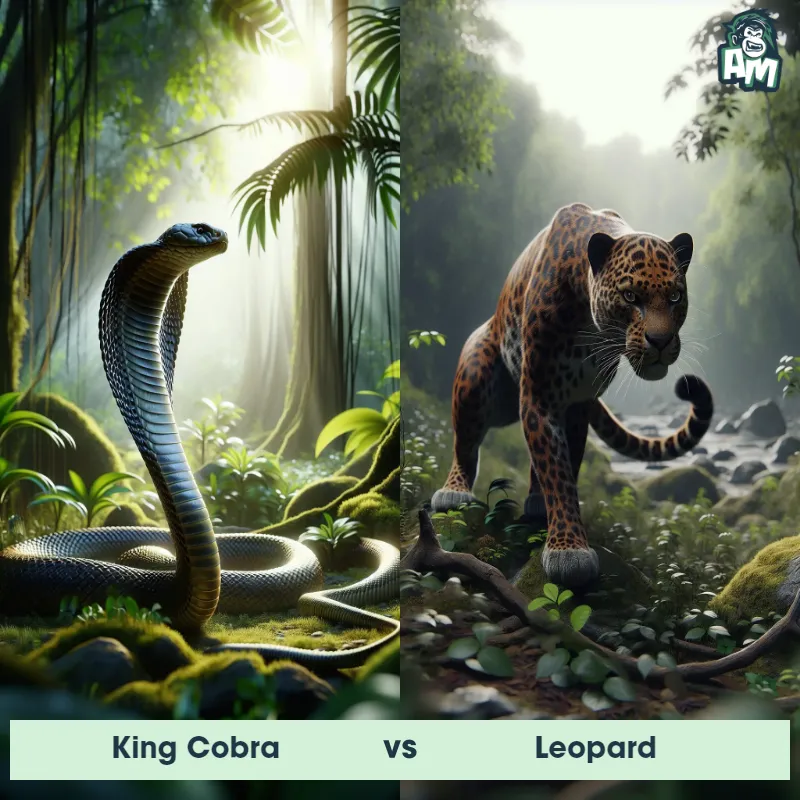
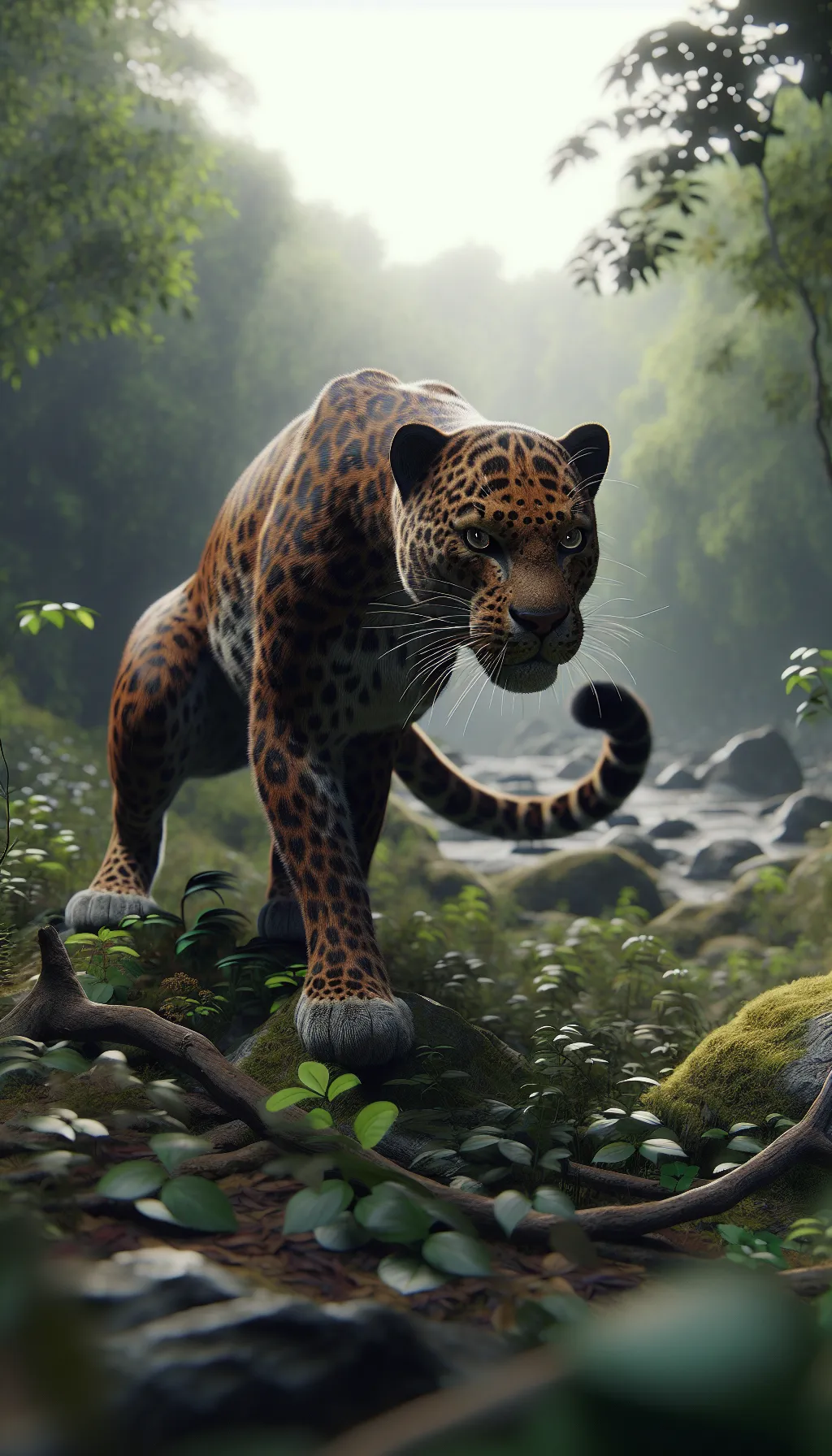
The Leopard, scientifically known as Panthera pardus, is one of the five species in the Panthera genus. It is a large and powerful big cat with a distinctive spotted coat, ranging in color from pale yellow to a rich golden hue. Known for its agility and strength, the leopard has a long, muscular body, strong jaws, and sharp retractable claws. They have excellent vision and are capable climbers, often resting in trees during the day. With a body length of around 4 to 6 feet and weighing between 80 to 200 pounds, leopards are highly adaptable and can be found in a wide range of habitats, including grasslands, forests, and even deserts.

| Leopard | |
|---|---|
| Size | 24-28 inches (60-71 cm) at the shoulder; 5-6 feet (1.5-1.8 meters) in length |
| Weight | 80-160 pounds (36-73 kilograms) |
| Speed | 36-37mph (58-60km/h) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaw and sharp claws |
| Biggest Weakness | Less endurance compared to some other big cats |
| Scientific Name | Panthera pardus |
| Family | Felidae |
| Habitat | Variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, and mountains |
| Geography | Africa, parts of Asia |
| Diet | Carnivorous, preys on various animals including ungulates, small mammals, birds, and reptiles |
| Lifespan | 12 years - 17 years |

The Leopard
The Leopard, scientifically known as Panthera pardus, is one of the five species in the Panthera genus. It is a large and powerful big cat with a distinctive spotted coat, ranging in color from pale yellow to a rich golden hue. Known for its agility and strength, the leopard has a long, muscular body, strong jaws, and sharp retractable claws. They have excellent vision and are capable climbers, often resting in trees during the day. With a body length of around 4 to 6 feet and weighing between 80 to 200 pounds, leopards are highly adaptable and can be found in a wide range of habitats, including grasslands, forests, and even deserts.
Fun Fact: Leopards are incredibly stealthy and possess the ability to blend seamlessly into their surroundings, thanks to their rosette-patterned coat, which acts as effective camouflage against potential prey and predators alike.
| Leopard | |
|---|---|
| Size | 24-28 inches (60-71 cm) at the shoulder; 5-6 feet (1.5-1.8 meters) in length |
| Weight | 80-160 pounds (36-73 kilograms) |
| Speed | 36-37mph (58-60km/h) |
| Key Strength | Powerful jaw and sharp claws |
| Biggest Weakness | Less endurance compared to some other big cats |
| Scientific Name | Panthera pardus |
| Family | Felidae |
| Habitat | Variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, and mountains |
| Geography | Africa, parts of Asia |
| Diet | Carnivorous, preys on various animals including ungulates, small mammals, birds, and reptiles |
| Lifespan | 12 years - 17 years |
Match Highlights
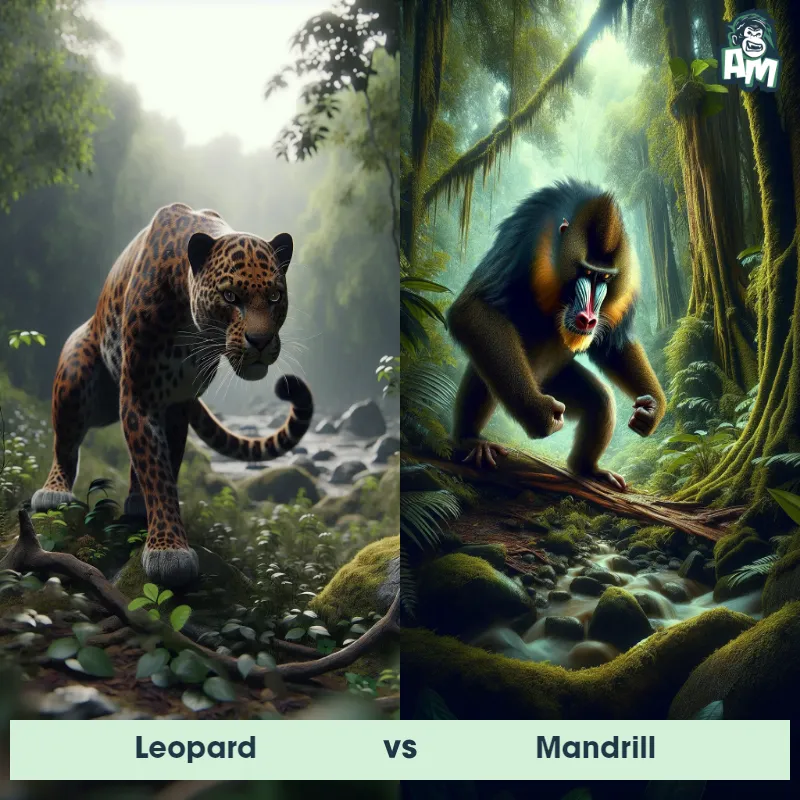
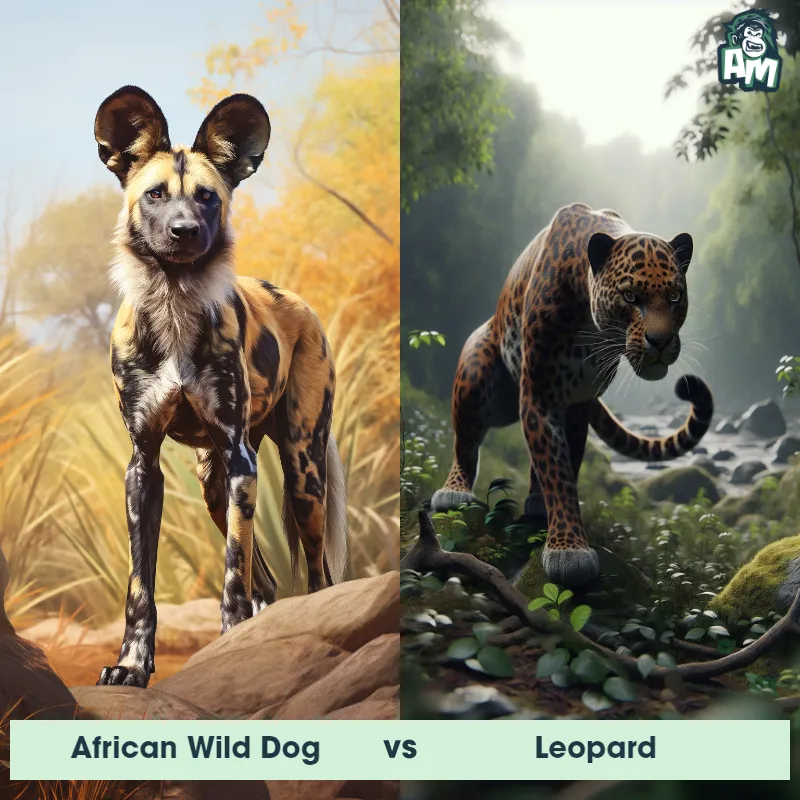
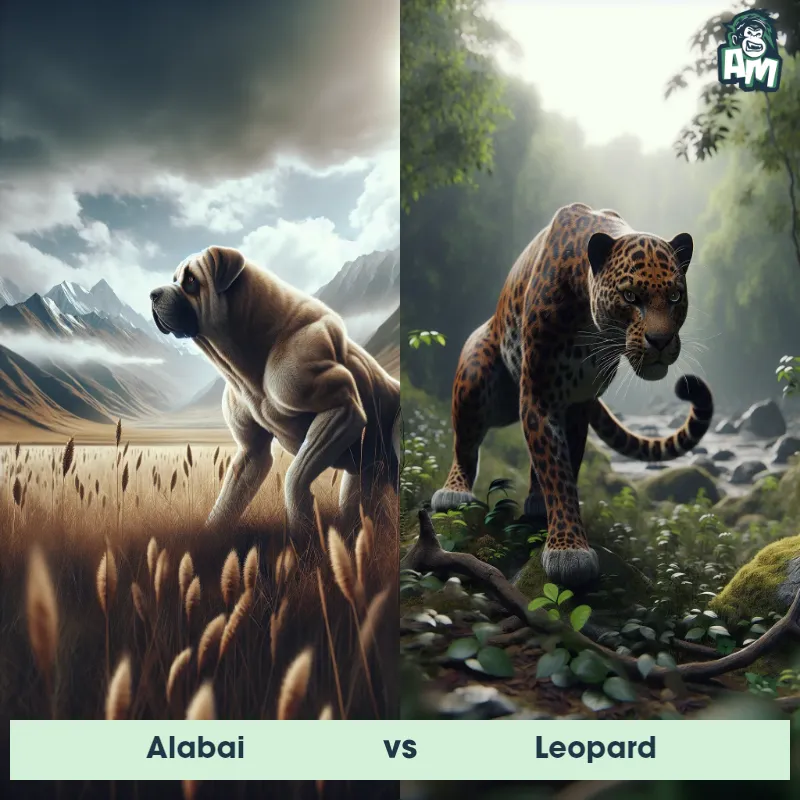
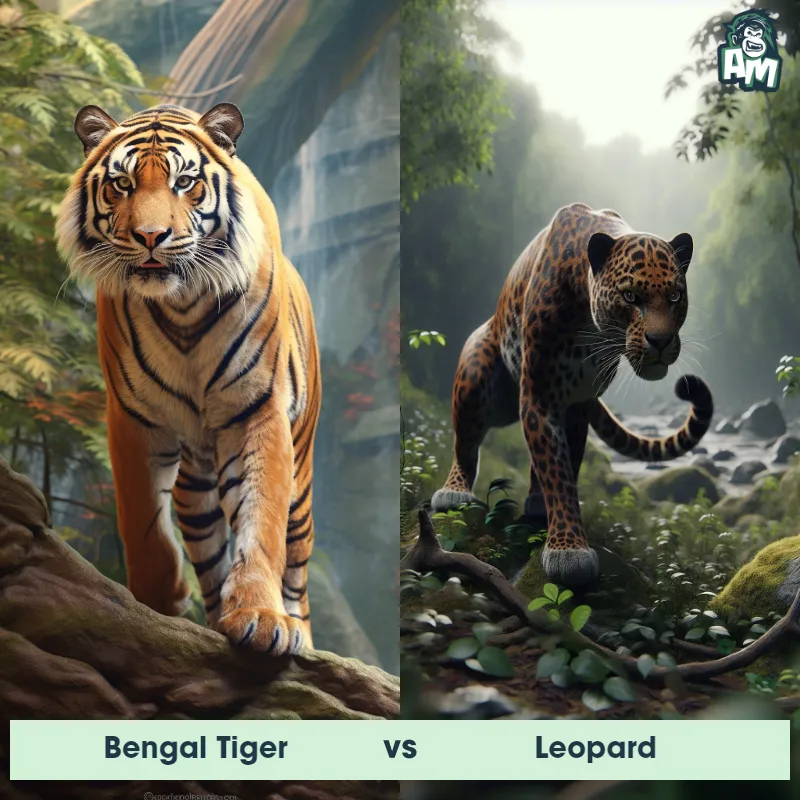
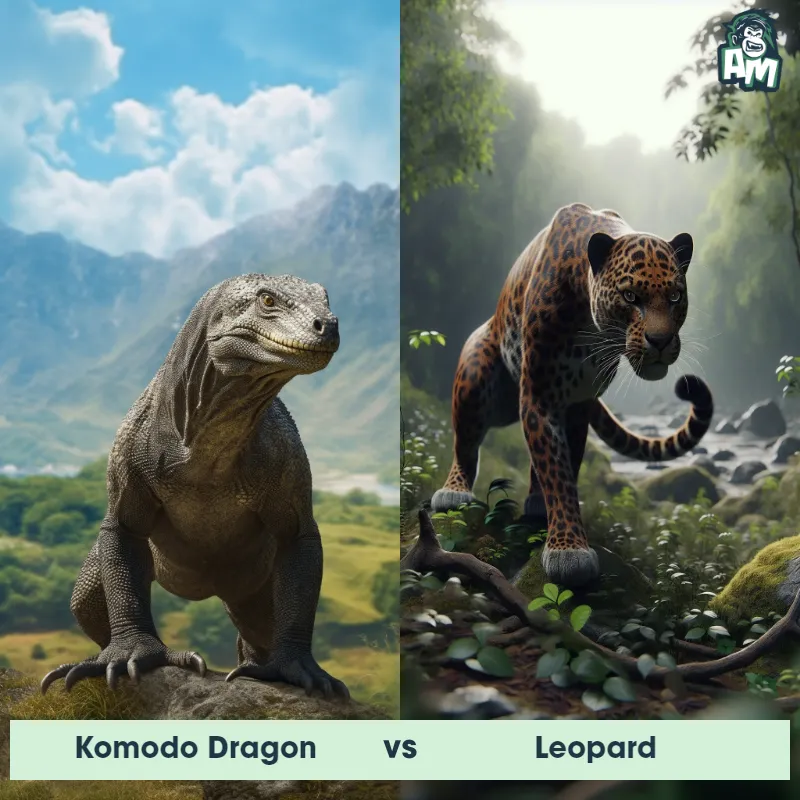
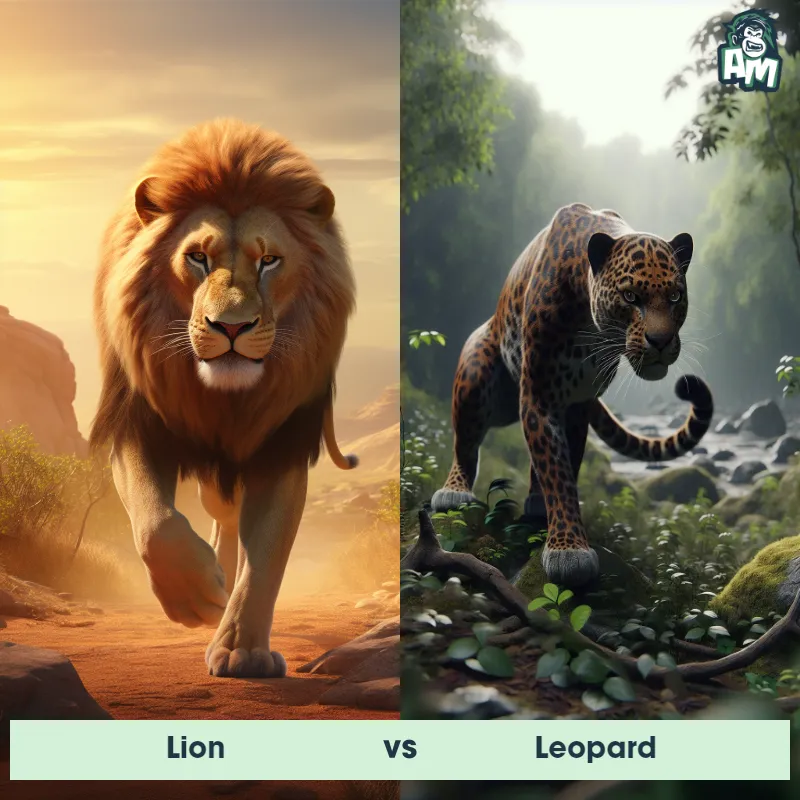
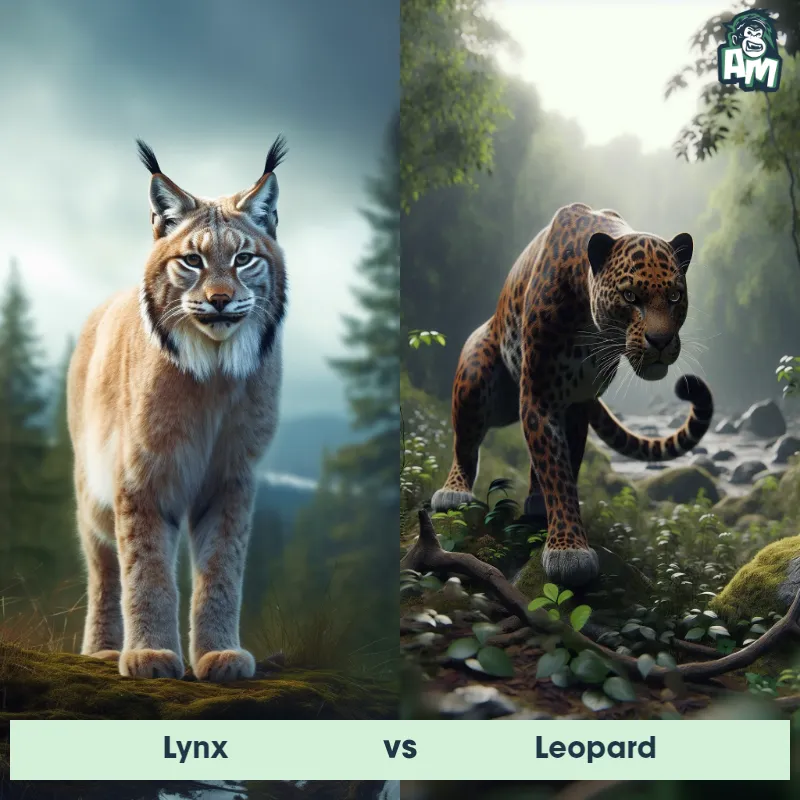
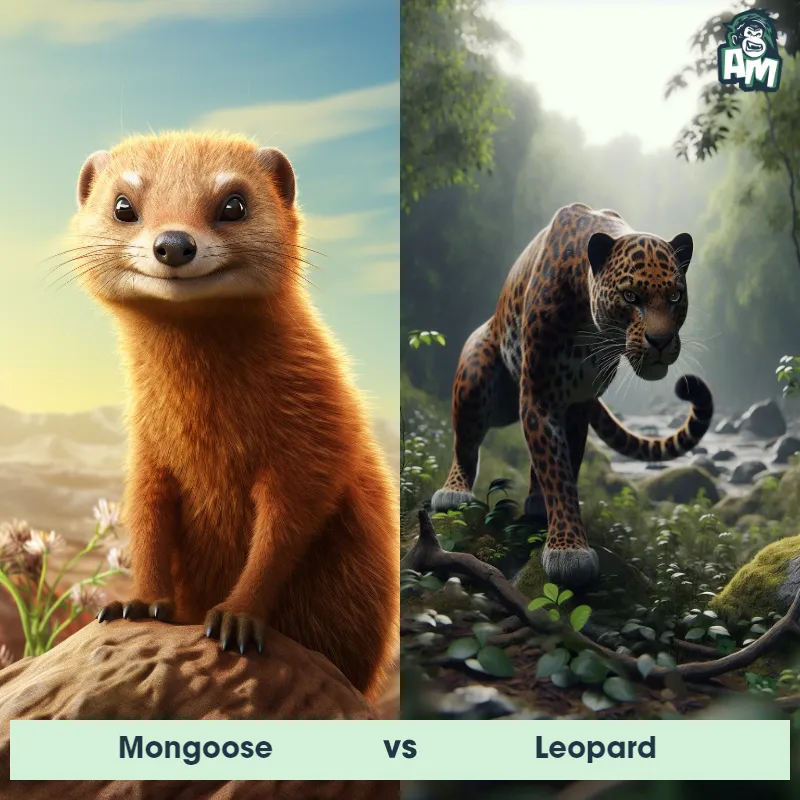
Leopard Matchups
We use AI to simulate matchups between the Leopard and other animals. Our simulation considers size, strength, and natural predatory behaviors to determine the most likely outcome.
Leopard: Diet, Predators, Aggression, and Defensive Behaviors
What do leopards eat?
Leopards are carnivores and primarily feed on a diet of meat. Their prey includes various mammals such as antelope, deer, monkeys, and even smaller animals like birds and insects. Leopards are known to be opportunistic hunters and will adapt their diet based on what is available in their habitat.
Do leopards have any predators?
As apex predators, leopards do not have many natural predators. However, they may occasionally fall prey to larger predators such as lions, hyenas, or even crocodiles. In some cases, humans also pose a threat to leopards through hunting and habitat destruction.
Are leopards aggressive?
Leopards are solitary and elusive animals that tend to avoid conflict with other animals, including humans. However, they can display aggressive behavior when they feel threatened or when defending their territory or young cubs. Leopard attacks on humans are relatively rare, but can occur in circumstances where they perceive a threat.
Do leopards fight?
Leopards are known to be solitary animals and typically avoid confrontations with other animals. However, they may engage in fights with rival leopards over territory or mating rights. These battles can be fierce and sometimes result in injuries or death for one of the combatants.
How do leopards defend themselves?
Leopards have various ways of defending themselves from potential threats. They are agile climbers and can escape danger by retreating into trees. They also have powerful jaws and sharp claws that they can use to fight off attackers. Additionally, leopards have a keen sense of hearing and sight, which helps them detect potential dangers and avoid confrontations when possible.
What is a leopard's biggest weakness in a fight?
Despite their strength and agility, leopards have a few weaknesses that can be exploited in a fight. One of their main vulnerabilities is their relatively smaller size compared to other big cats like lions or tigers. This can put them at a disadvantage in direct confrontations with larger predators. Additionally, leopards rely on stealth and surprise during hunting, so they may struggle in prolonged fights that require sustained physical exertion.
Fun Fact: Leopards are known for their incredible strength and are capable of hauling heavy prey carcasses, such as antelopes, up into trees to keep them away from scavengers.
Fun Fact: Leopards are renowned for their adaptability and broad diet range, as they are opportunistic hunters and can consume a variety of prey including small mammals, birds, reptiles, and even fish when available, making them highly versatile predators.