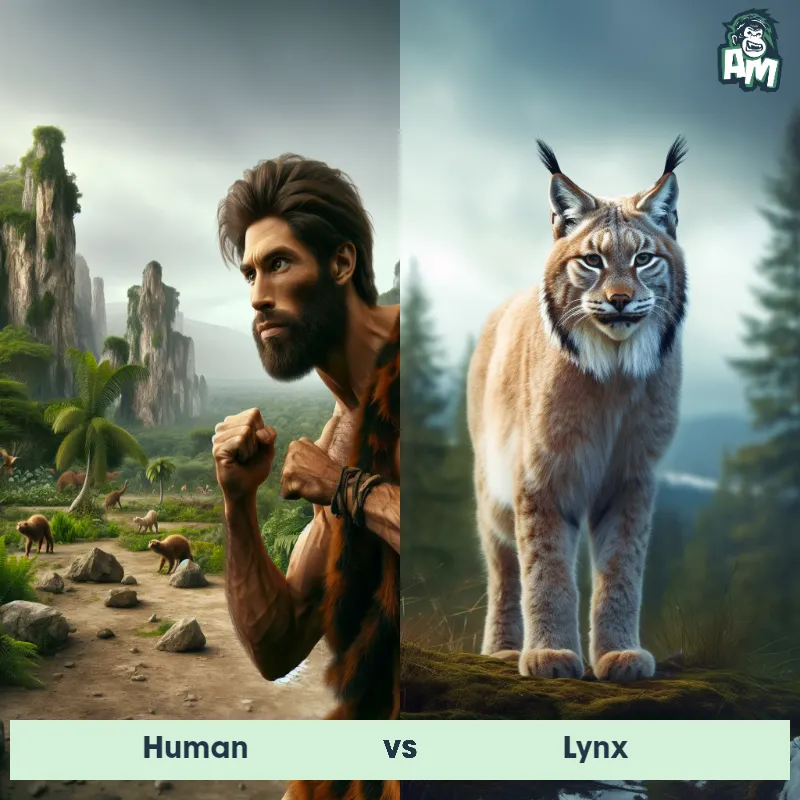
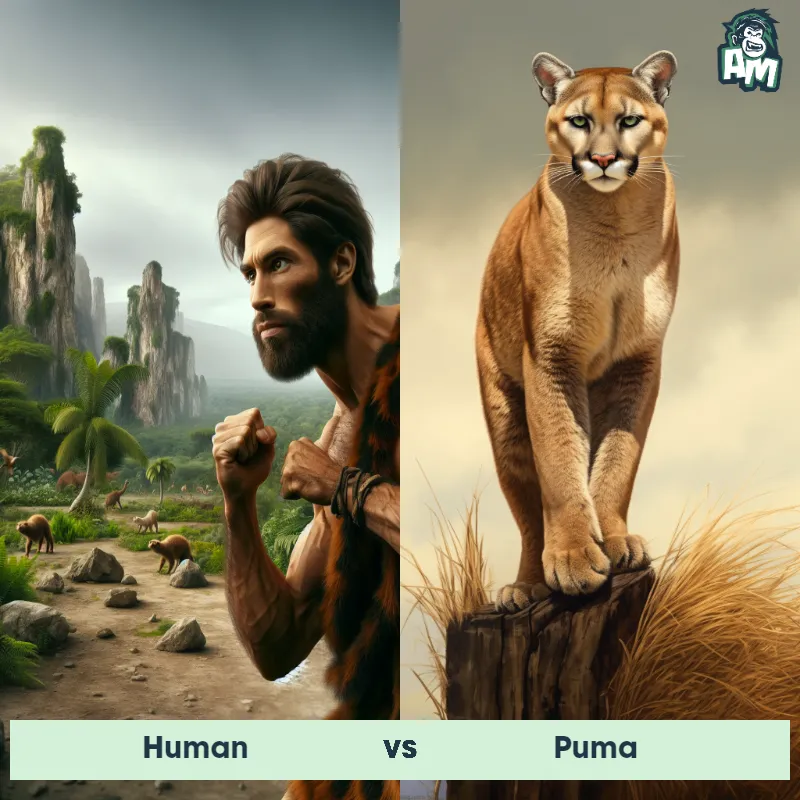
The Human
The human, also known as Homo sapiens, is a highly intelligent and sophisticated species belonging to the primate family. Humans are characterized by their upright posture, opposable thumbs, and complex brain structure. They have a wide range of physical appearances, with variations in hair color, skin tone, and facial features. Humans possess the ability to communicate effectively through language and have developed advanced tools and technology. They exhibit complex social behaviors and have a unique capacity for cognition and self-awareness.

| Human | |
|---|---|
| Size | Average height of 5 feet 7 inches (170 cm) |
| Weight | Average weight of 154 pounds (70 kg) |
| Speed | 27.8 mph (44.7 km/h) |
| Key Strength | Intelligence and ability to strategize |
| Biggest Weakness | Lack of physical strength compared to some animals |
| Scientific Name | Homo sapiens |
| Family | Hominidae |
| Habitat | Diverse habitats, including forests, grasslands, deserts, and urban areas |
| Geography | Found on all continents |
| Diet | Omnivorous, with a preference for cooked food |
| Lifespan | 70 years - 90 years |

The Human
The human, also known as Homo sapiens, is a highly intelligent and sophisticated species belonging to the primate family. Humans are characterized by their upright posture, opposable thumbs, and complex brain structure. They have a wide range of physical appearances, with variations in hair color, skin tone, and facial features. Humans possess the ability to communicate effectively through language and have developed advanced tools and technology. They exhibit complex social behaviors and have a unique capacity for cognition and self-awareness.
![[object Object] Gif](https://tenor.com/view/hungry-caveman-muppetwiki-muppet-wiki-jim-henson-gif-11005515308056547982.gif)
Fun Fact: Humans are the only species on Earth known to create and utilize complex systems of written language, allowing them to record, transfer, and advance knowledge across generations.
| Human | |
|---|---|
| Size | Average height of 5 feet 7 inches (170 cm) |
| Weight | Average weight of 154 pounds (70 kg) |
| Speed | 27.8 mph (44.7 km/h) |
| Key Strength | Intelligence and ability to strategize |
| Biggest Weakness | Lack of physical strength compared to some animals |
| Scientific Name | Homo sapiens |
| Family | Hominidae |
| Habitat | Diverse habitats, including forests, grasslands, deserts, and urban areas |
| Geography | Found on all continents |
| Diet | Omnivorous, with a preference for cooked food |
| Lifespan | 70 years - 90 years |
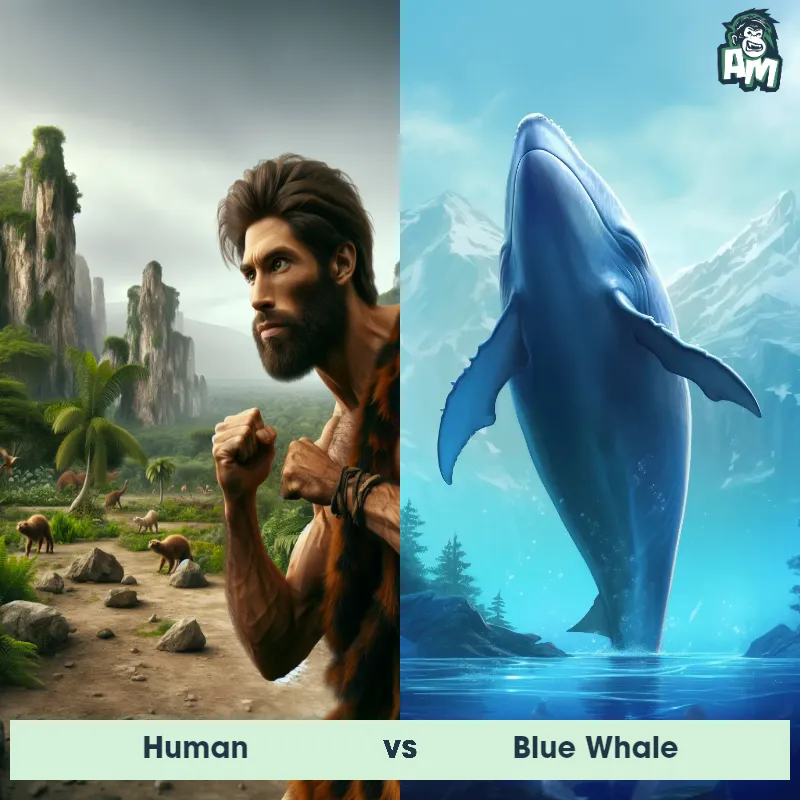
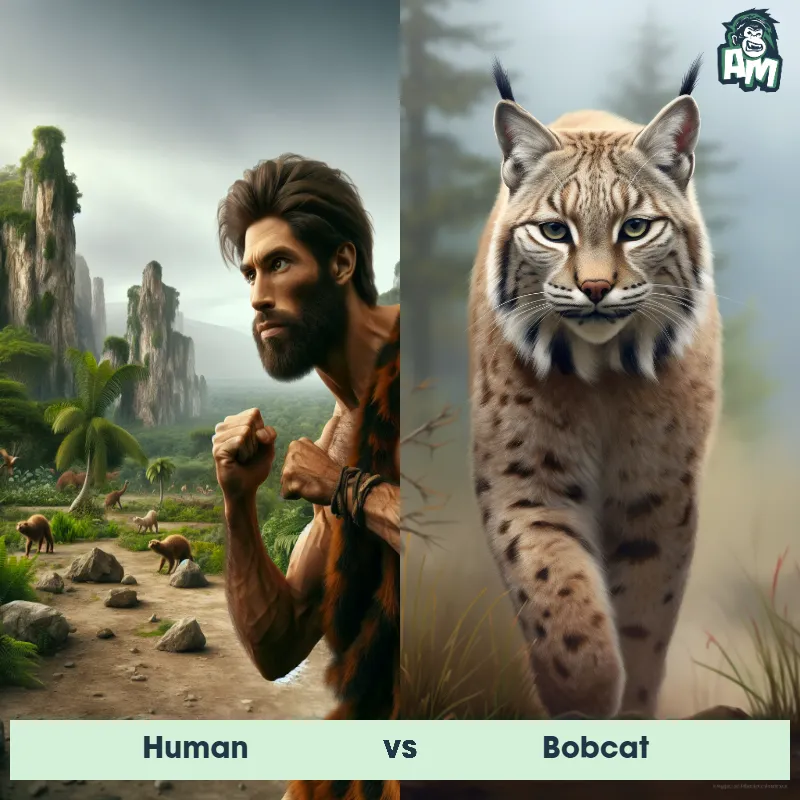
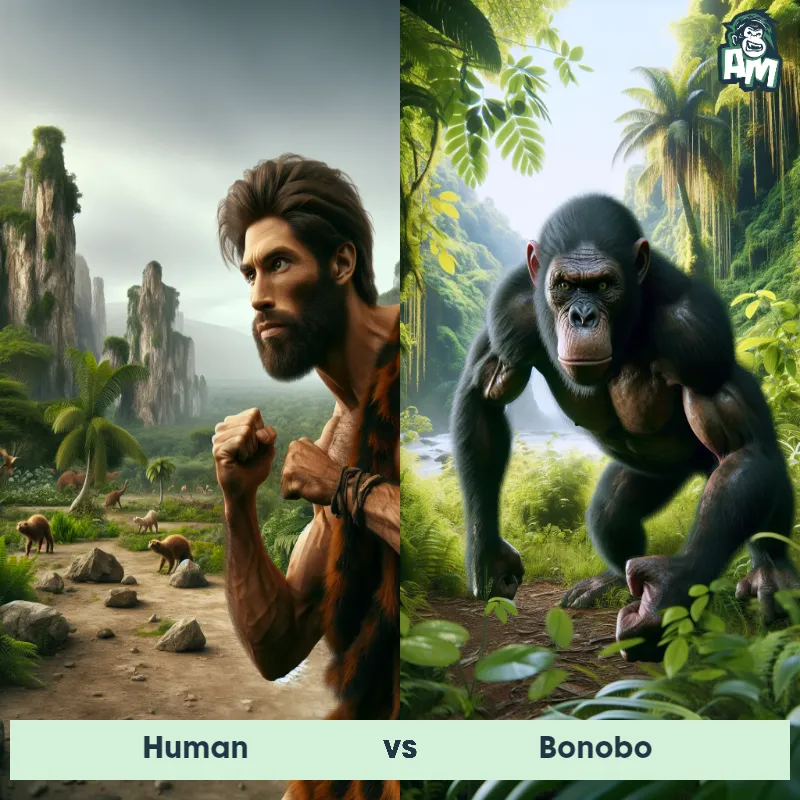
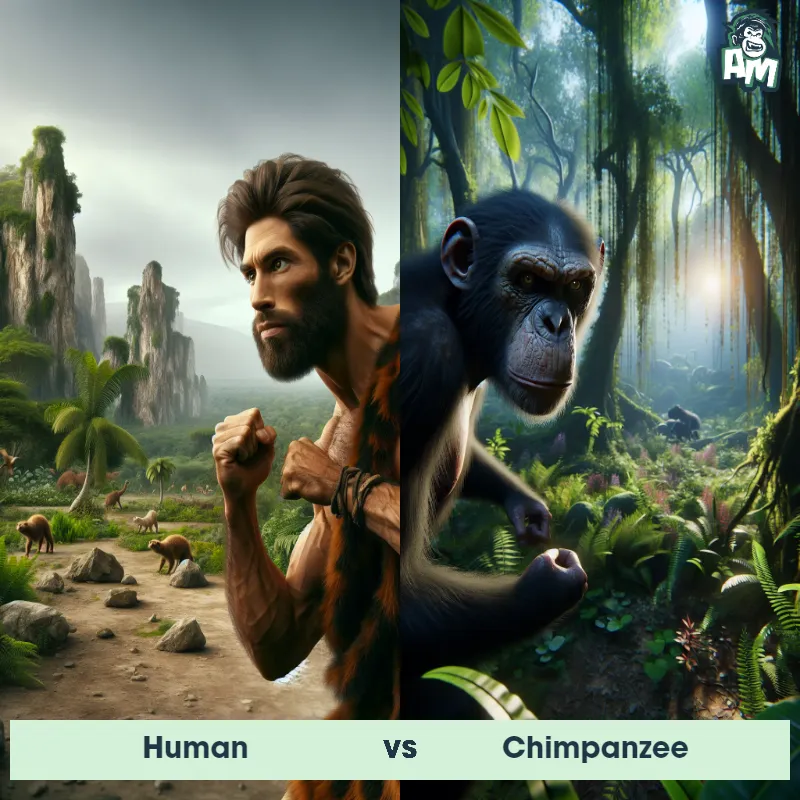
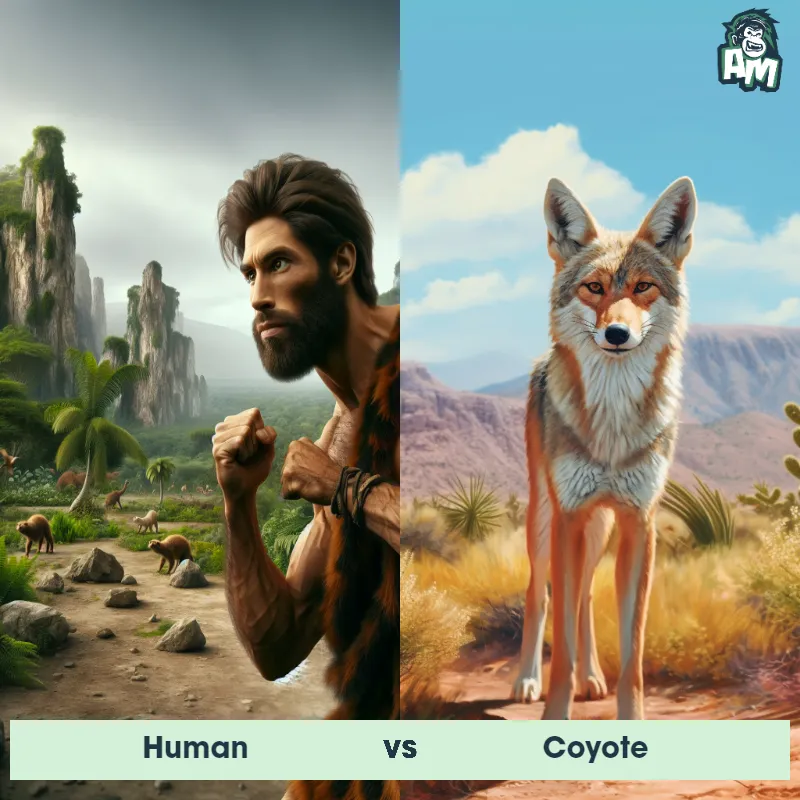
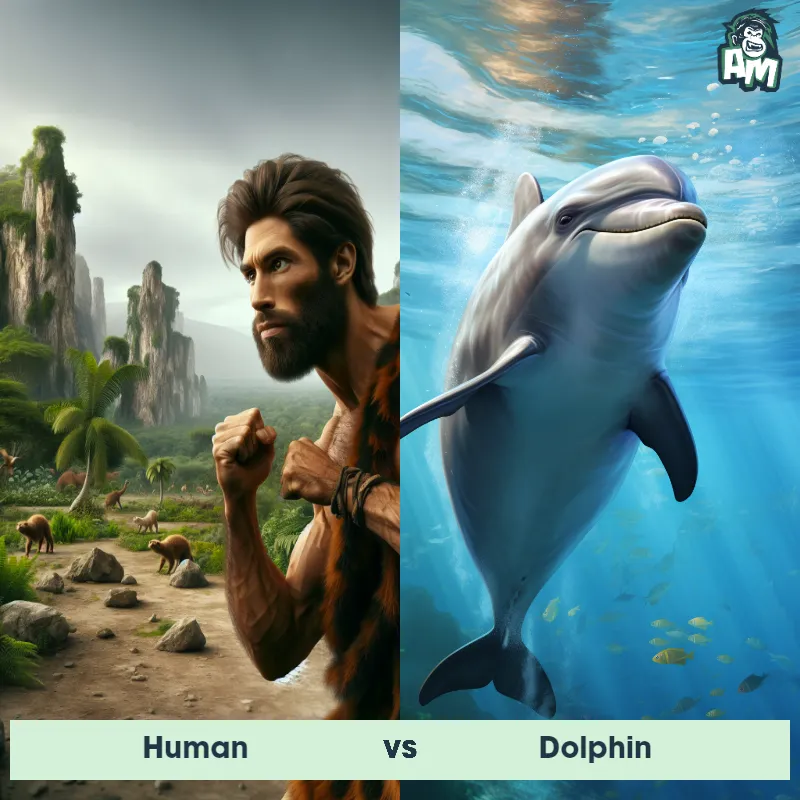
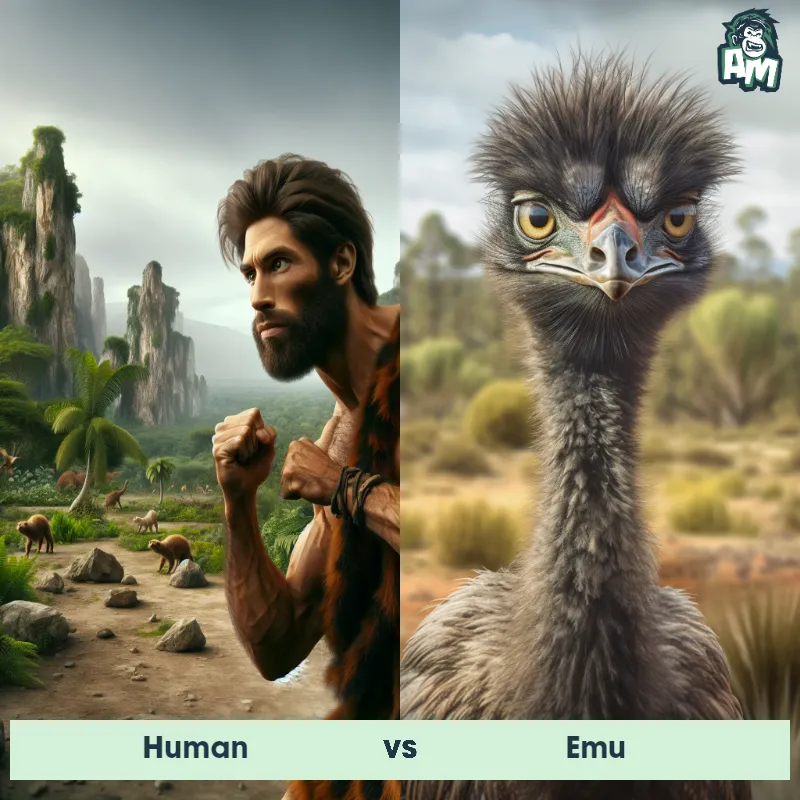
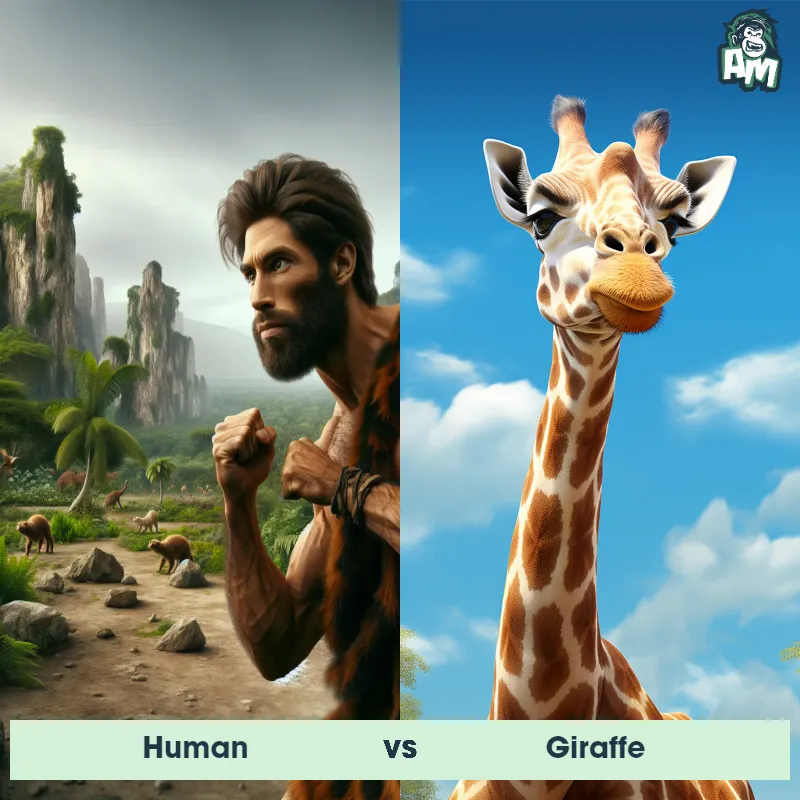
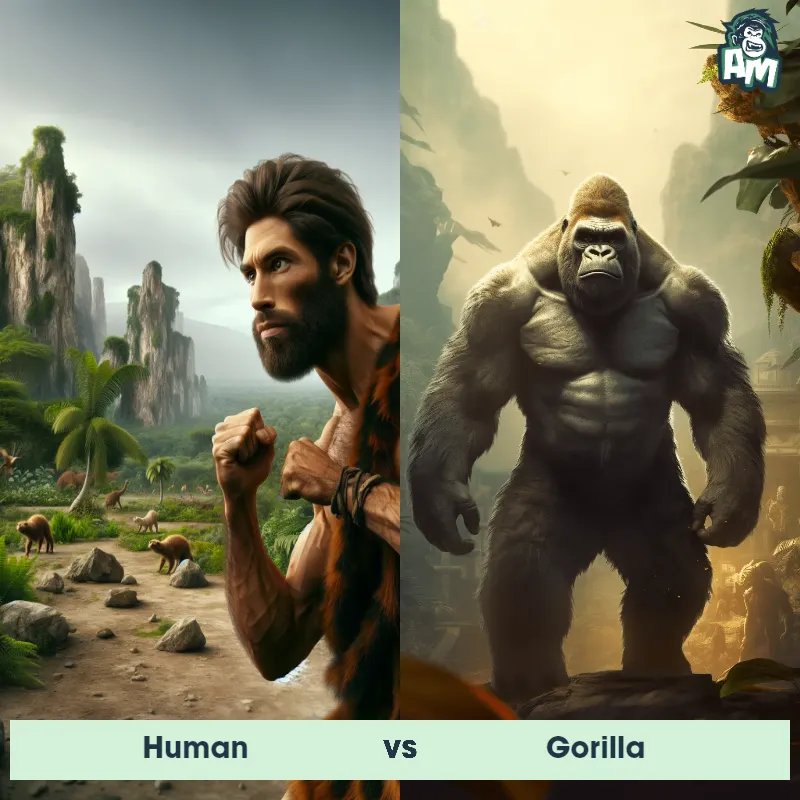
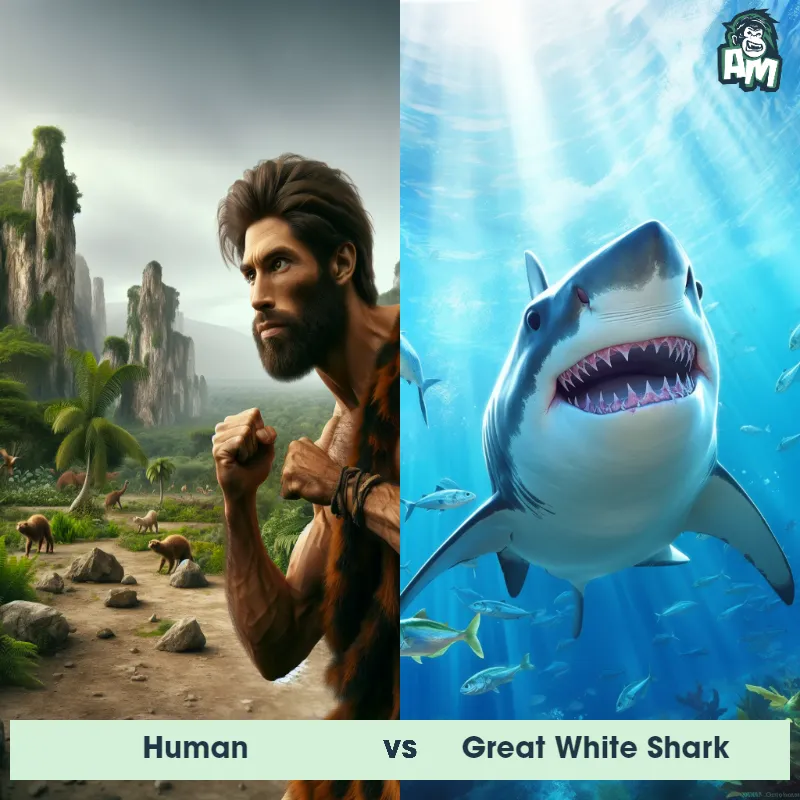
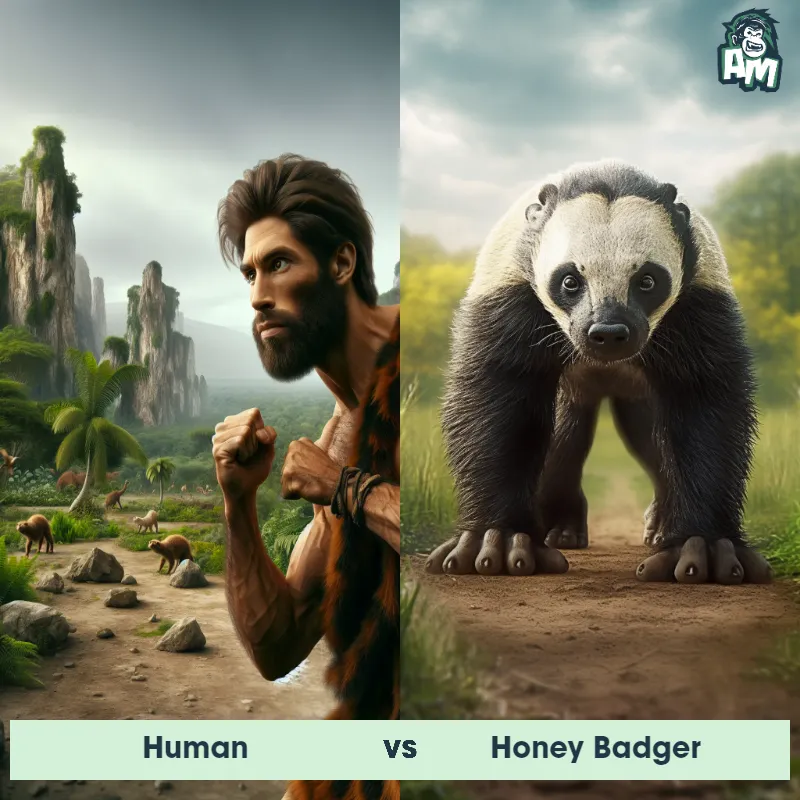
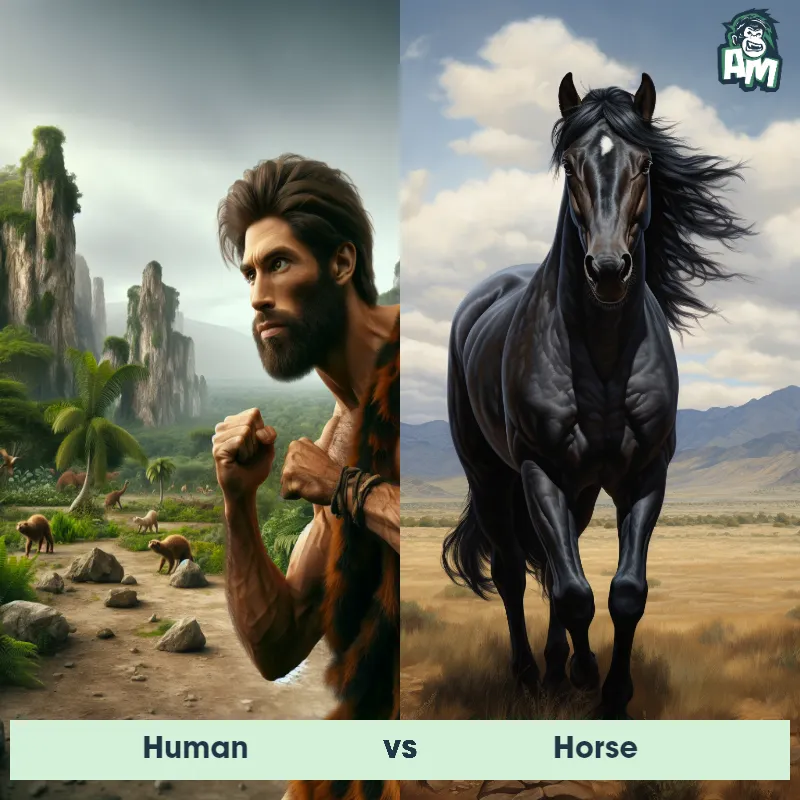
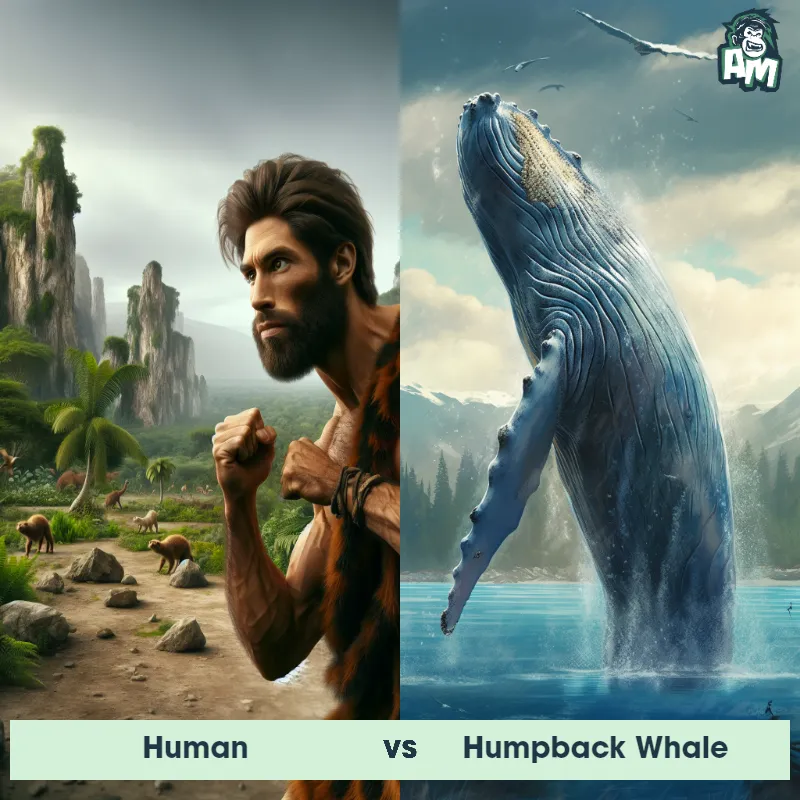
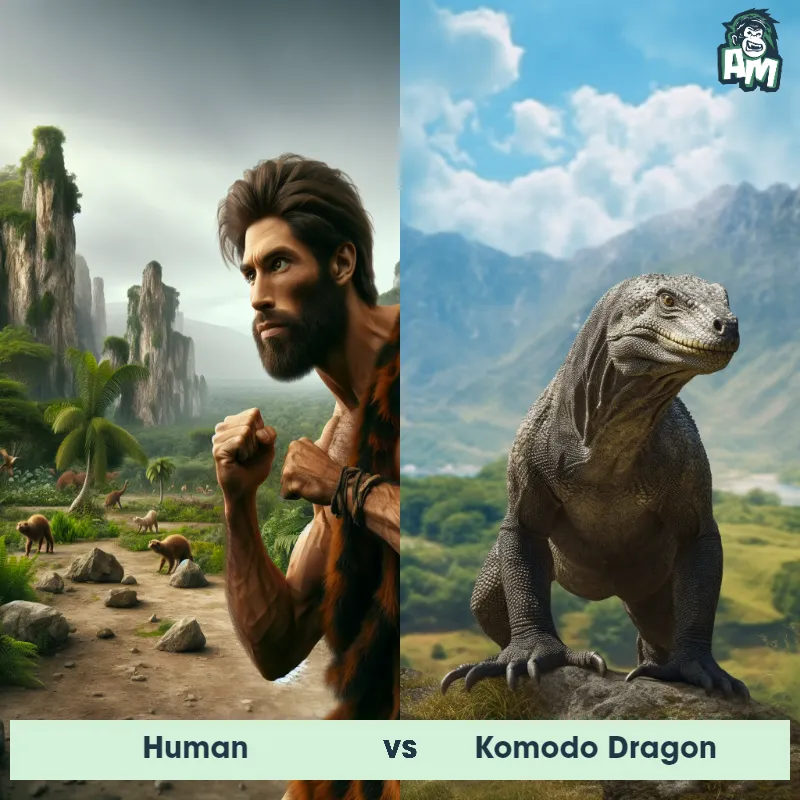
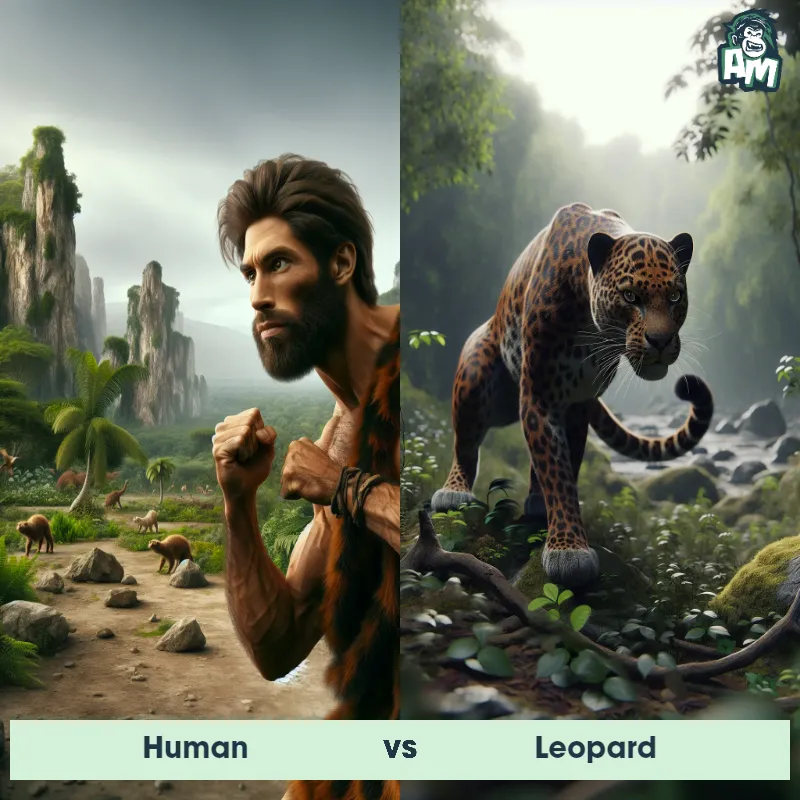
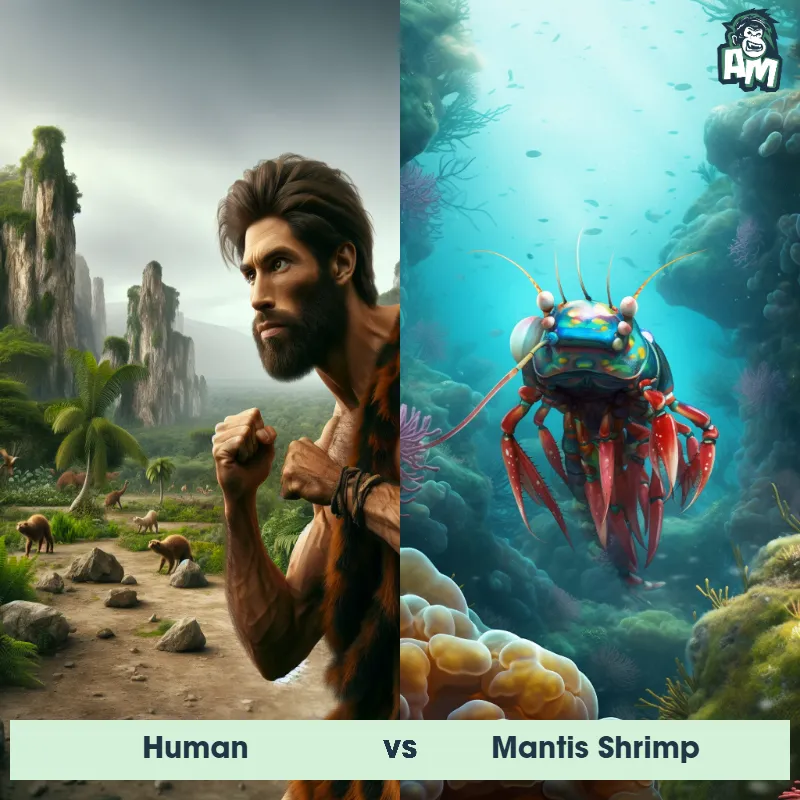
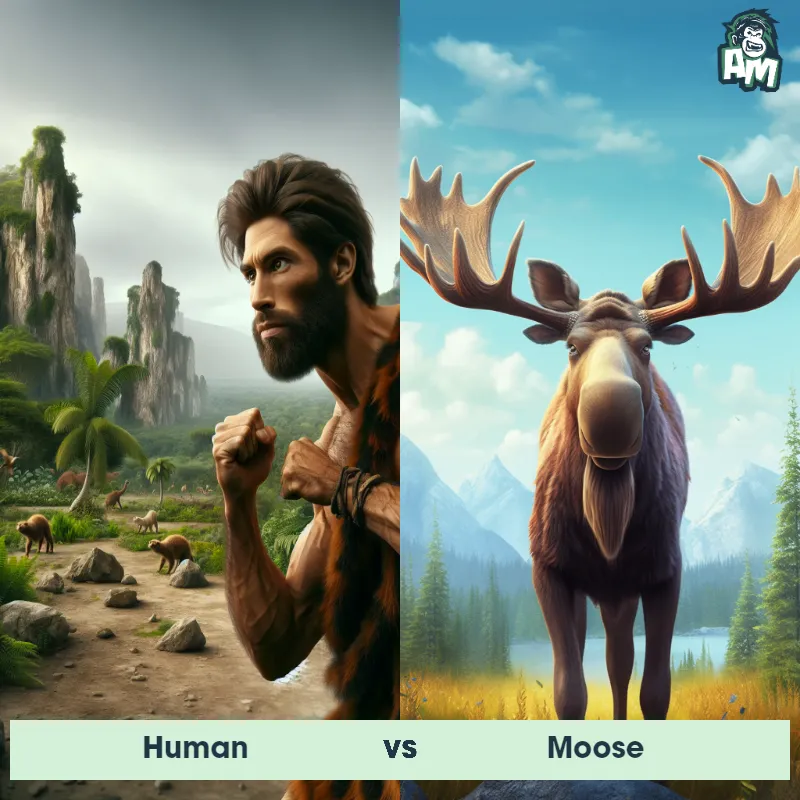
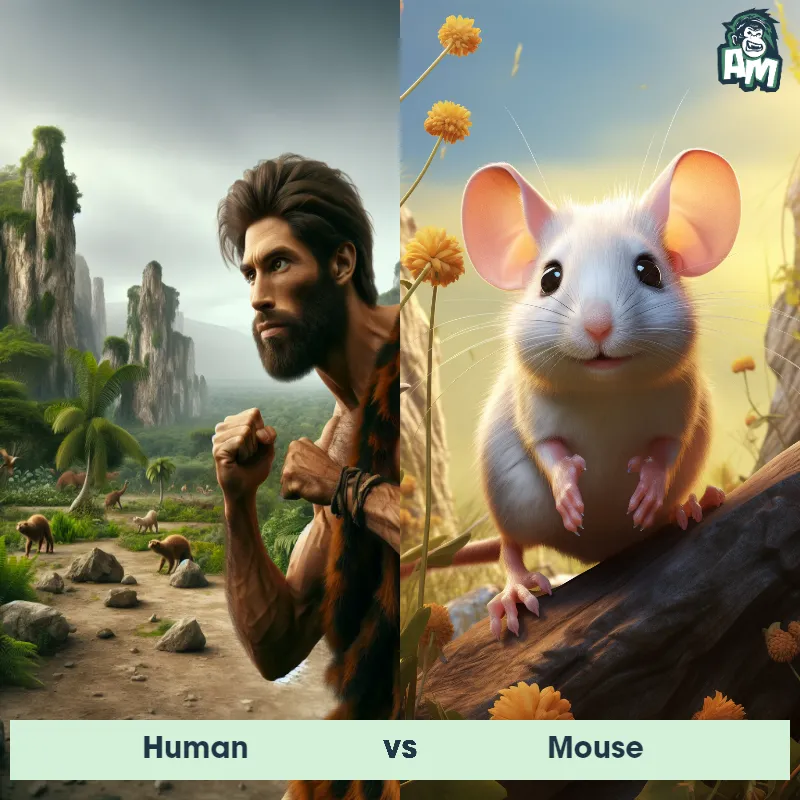
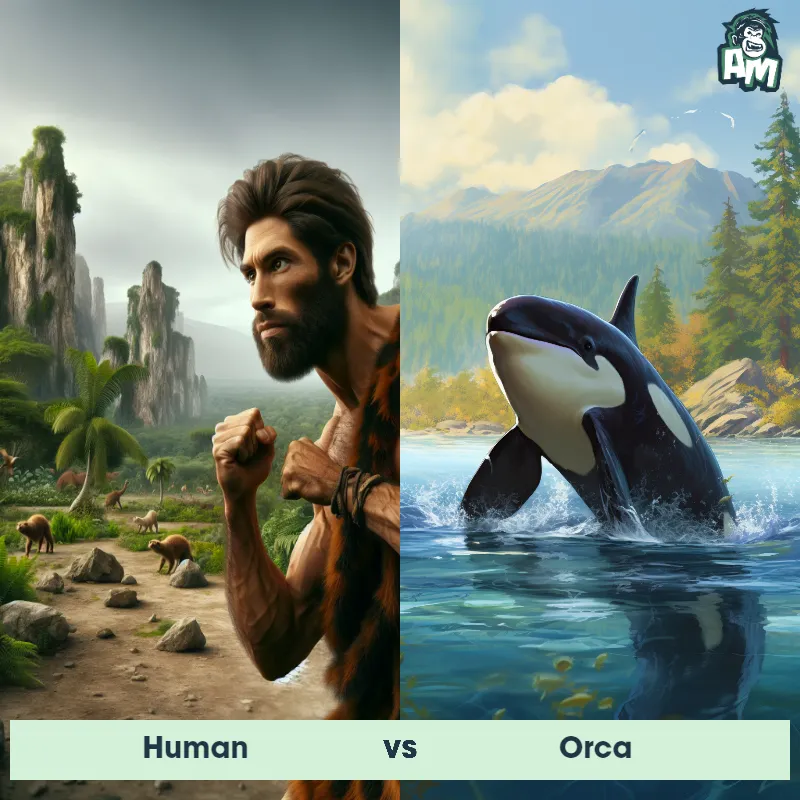
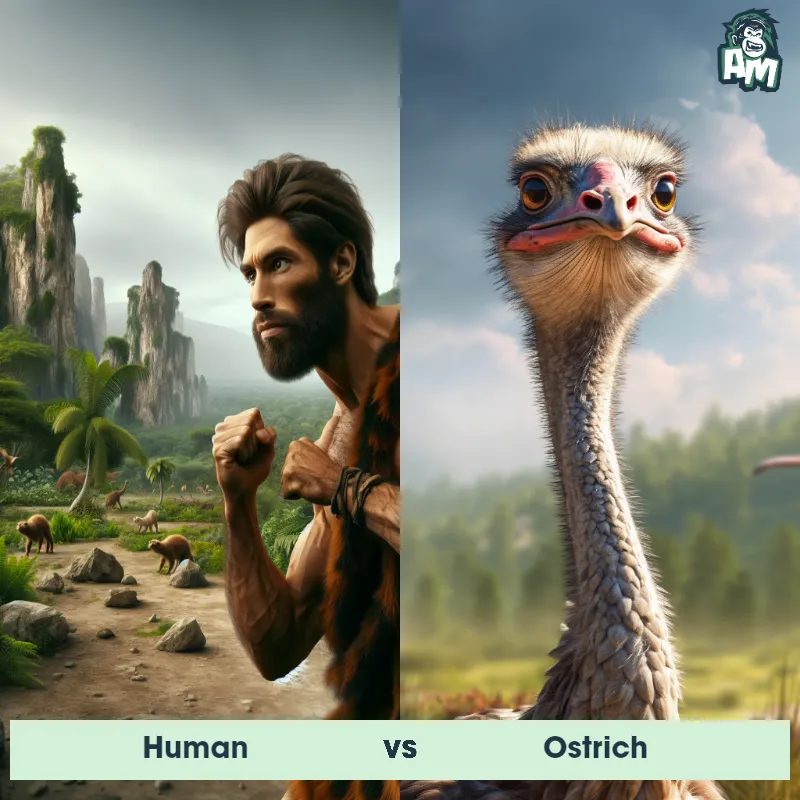
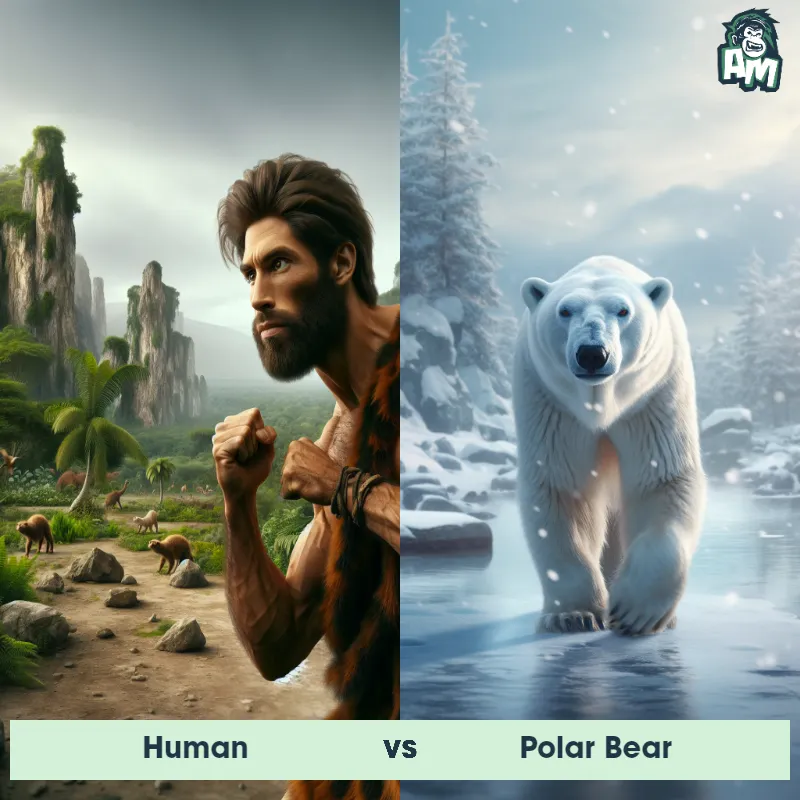
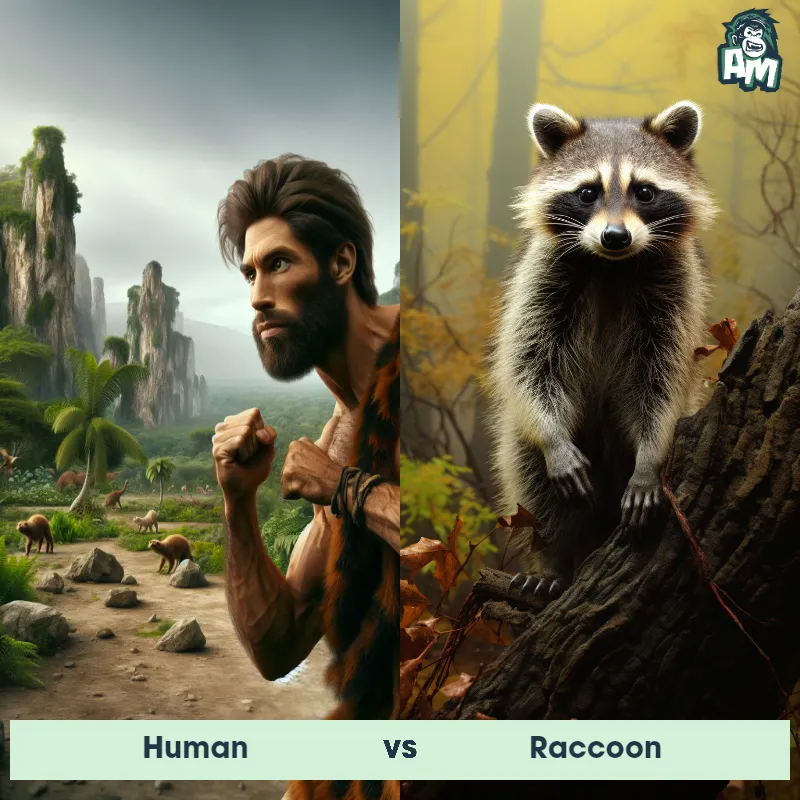
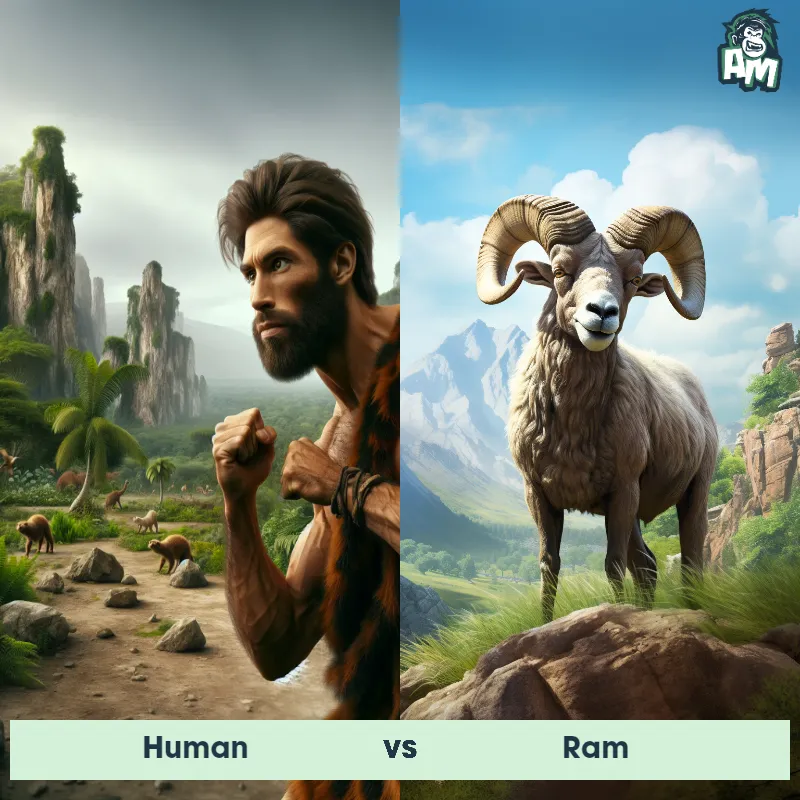
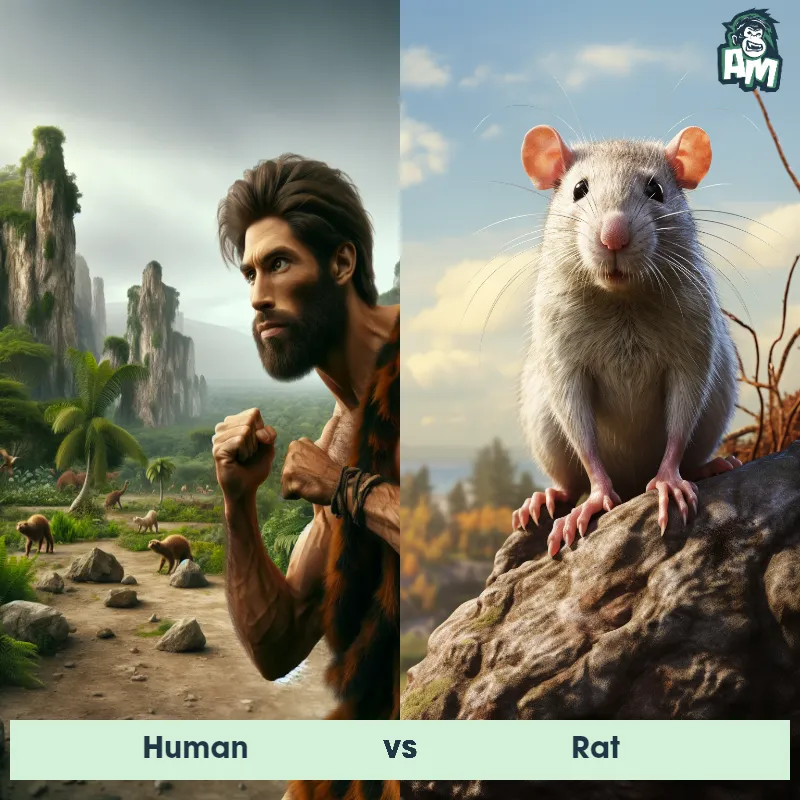
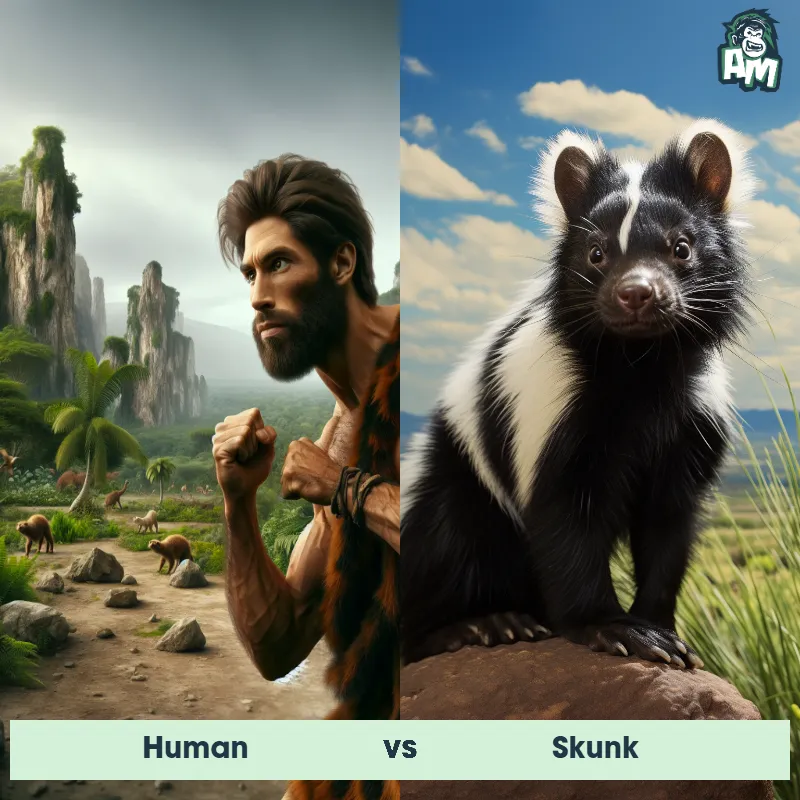
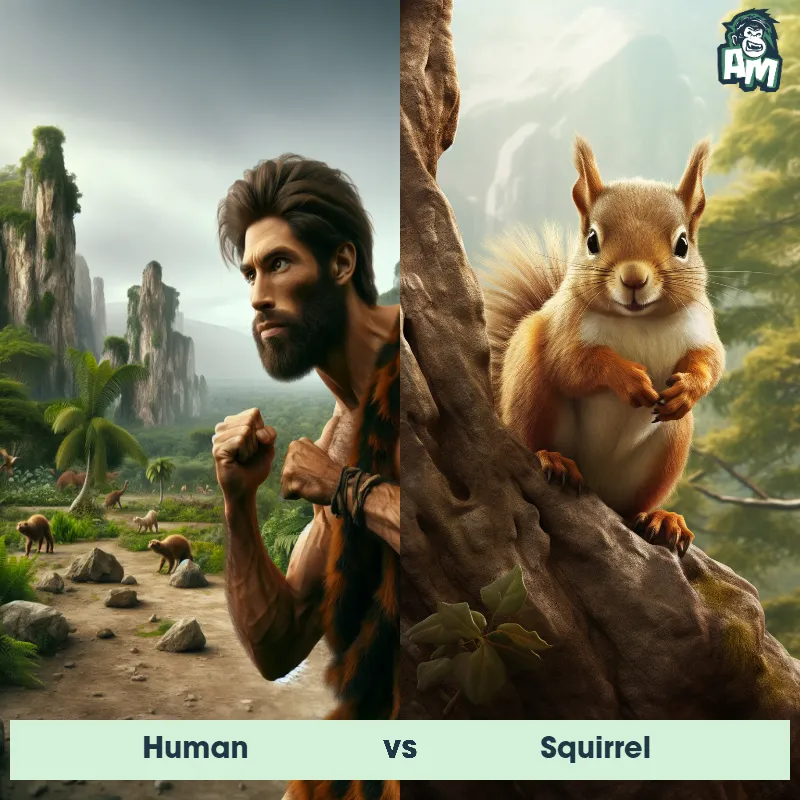
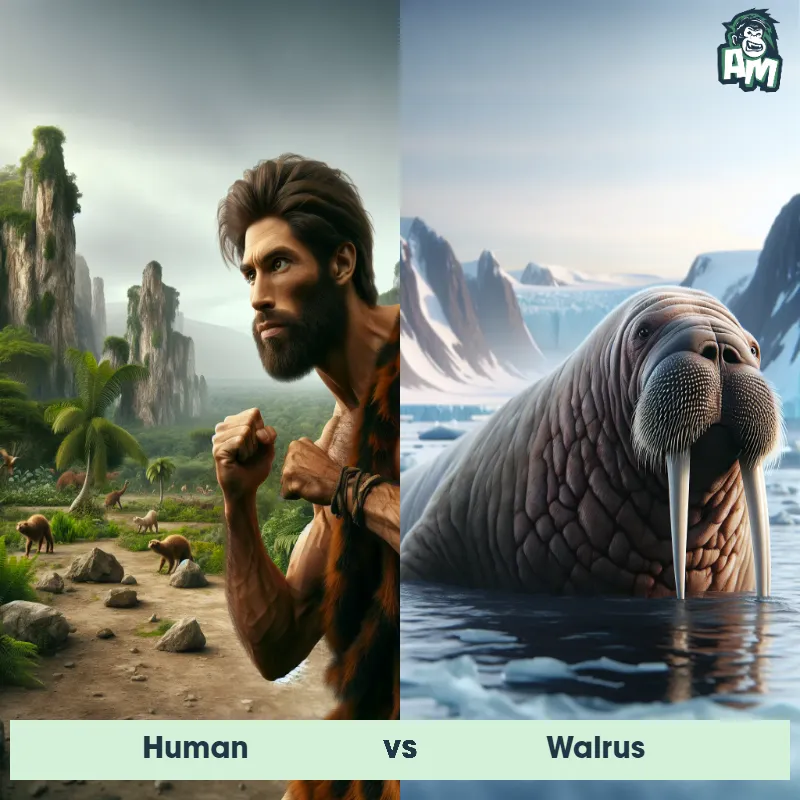
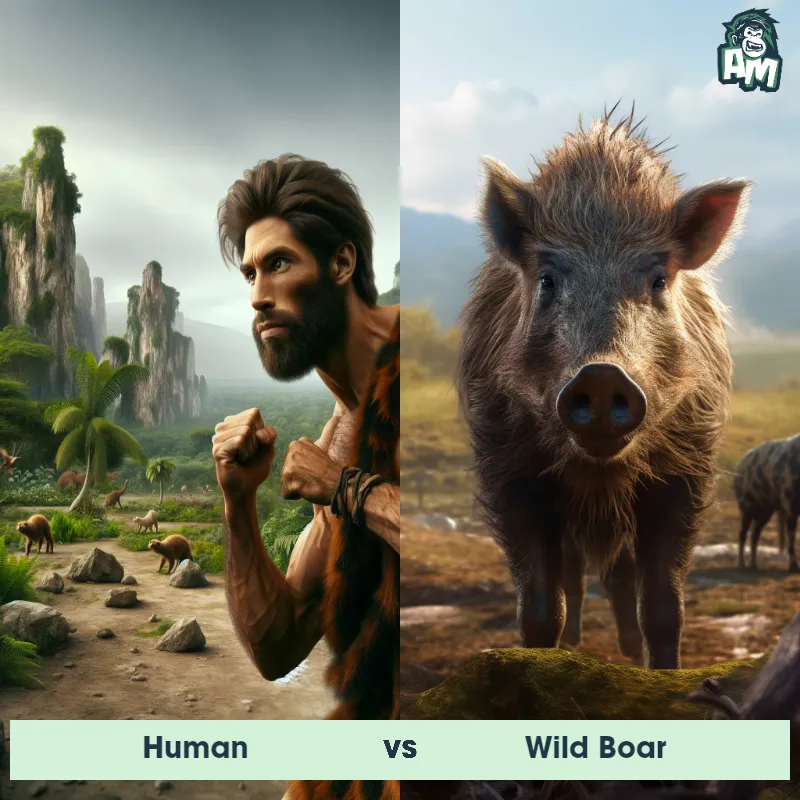
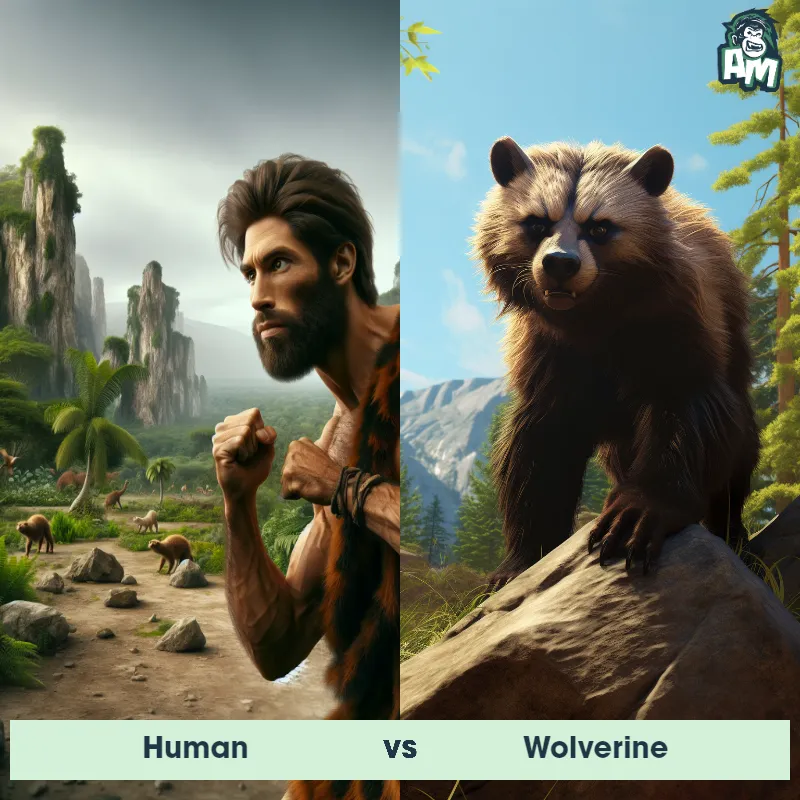
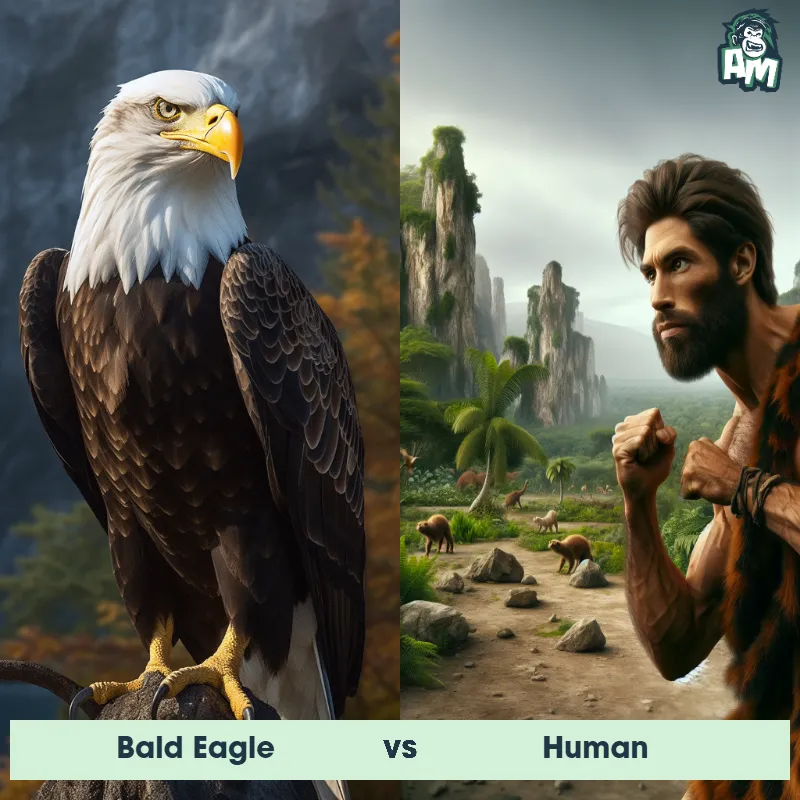
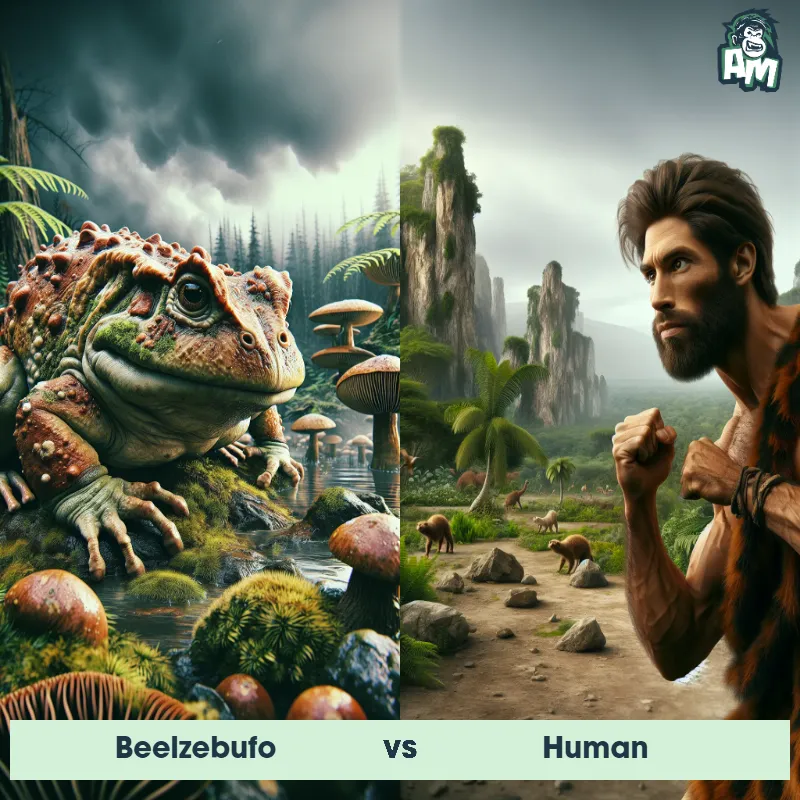
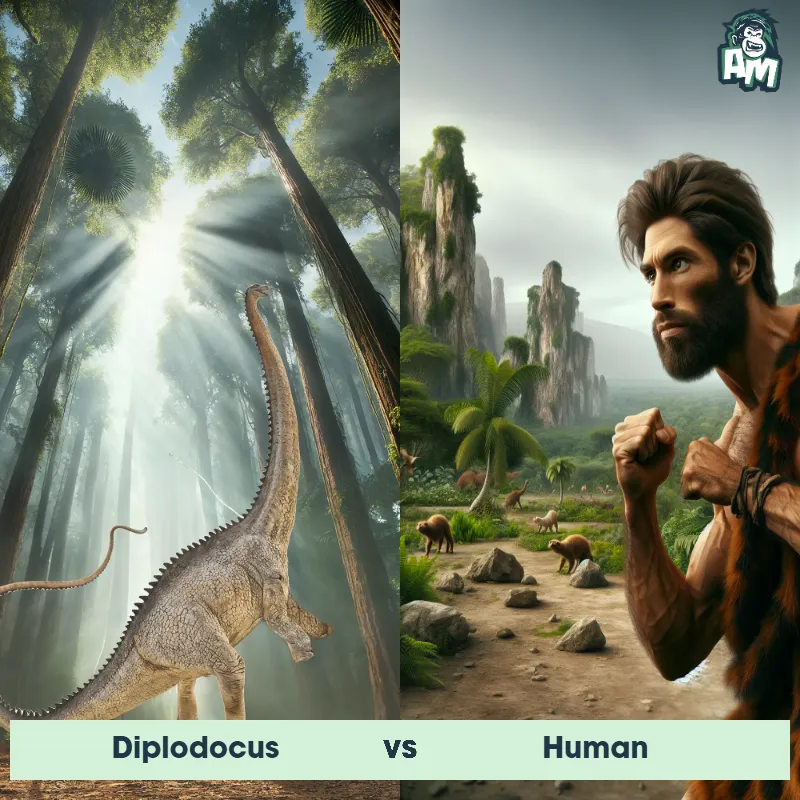
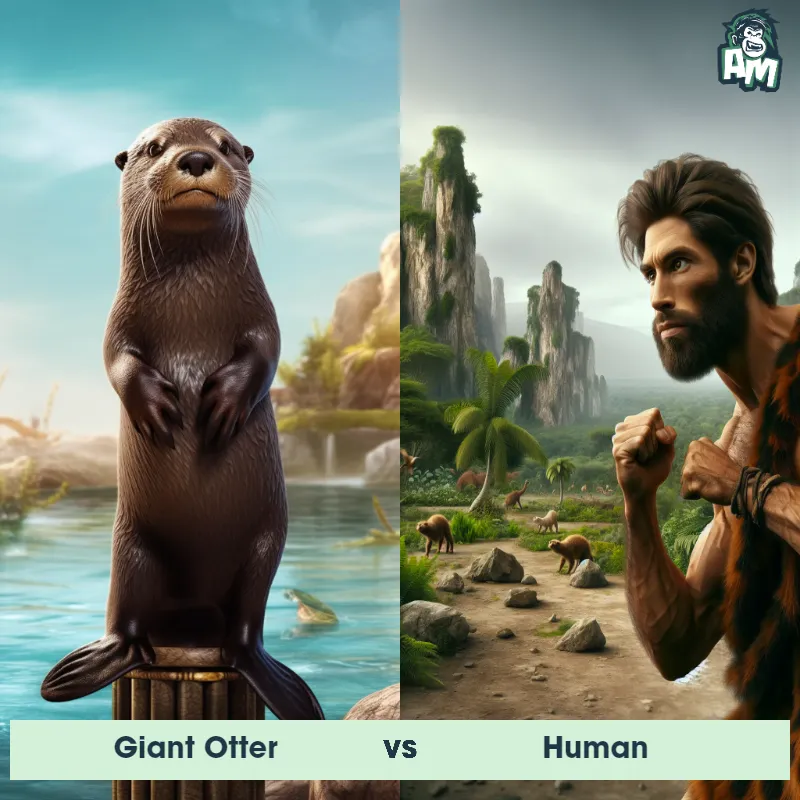
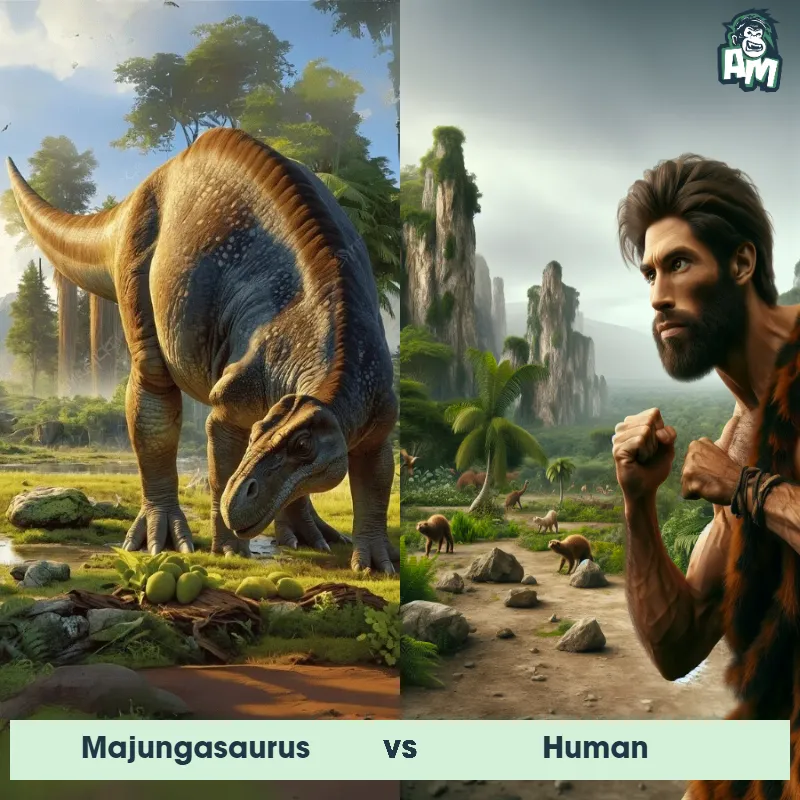
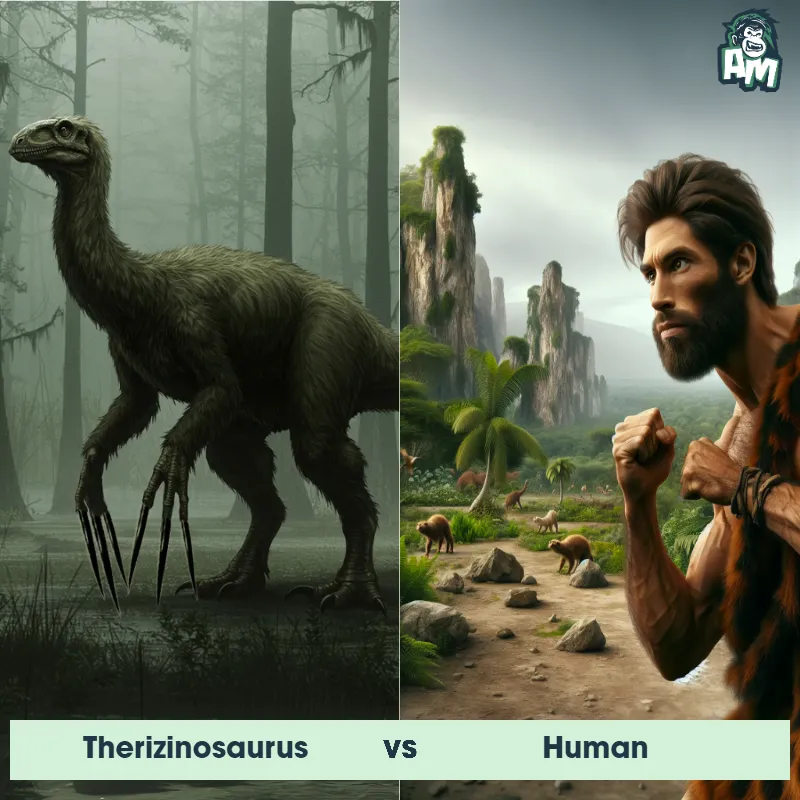
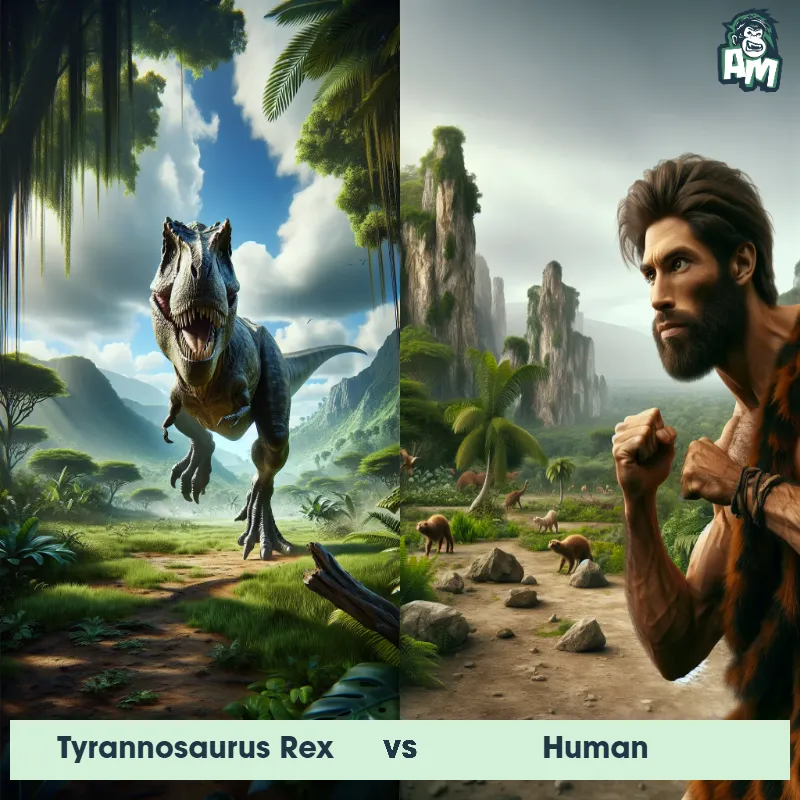
Human Matchups
We use AI to simulate matchups between the Human and other animals. Our simulation considers size, strength, and natural predatory behaviors to determine the most likely outcome.
Human: Diet, Predators, Aggression, and Defensive Behaviors
What do Humans eat?
Humans are omnivores, which means they have a diet that includes both plants and animals. Their diet can vary depending on cultural preferences, but generally includes fruits, vegetables, grains, meats, and dairy products. Humans have a diverse palate and can consume a wide range of foods.
Do Humans have any predators?
While Humans do not have natural predators in the traditional sense, they can face threats from various sources such as other Humans, diseases, and environmental hazards. Historically, Humans have had to defend themselves against predators such as large carnivorous animals, but due to their intelligence and ability to adapt, they have risen to the top of the food chain.
Are Humans aggressive?
Humans have the capacity for aggression, but it is not a defining characteristic. As a species, Humans exhibit a wide range of behaviors, from peaceful cooperation to violent conflict. Aggression in Humans can be influenced by factors such as genetics, environment, and social norms.
Do Humans fight?
Humans have a long history of engaging in conflict, both at an individual and societal level. Fighting can manifest in various forms, including physical altercations, verbal disputes, and even warfare. Humans have developed complex ways of resolving conflicts, but fighting remains a part of their nature.
How do Humans defend themselves?
Humans have evolved various defense mechanisms to protect themselves from threats. Physically, they can use tools, weapons, and martial arts techniques to fend off attackers. Emotionally, Humans can rely on their intelligence, communication skills, and social bonds to navigate dangerous situations. Additionally, Humans have built structures, institutions, and technologies to enhance their collective security.
What is Humans' biggest weakness in a fight?
Despite their intelligence and adaptability, Humans have physical limitations that can make them vulnerable in a fight. Compared to other animals, Humans are not as strong, fast, or durable. Their soft tissue, lack of natural weapons, and reliance on complex knowledge and strategies can be exploited by opponents. In a fight, Humans must rely on their wits, teamwork, and resourcefulness to overcome their biological weaknesses.
Fun Fact: Humans have a diverse range of emotions and are capable of experiencing a wide array of feelings, including happiness, sadness, fear, and love, which contributes to their complex social dynamics.
Fun Fact: Humans possess a strong capacity for empathy, allowing them to understand and share the feelings of others, which plays a significant role in their ability to form deep and meaningful interpersonal connections.